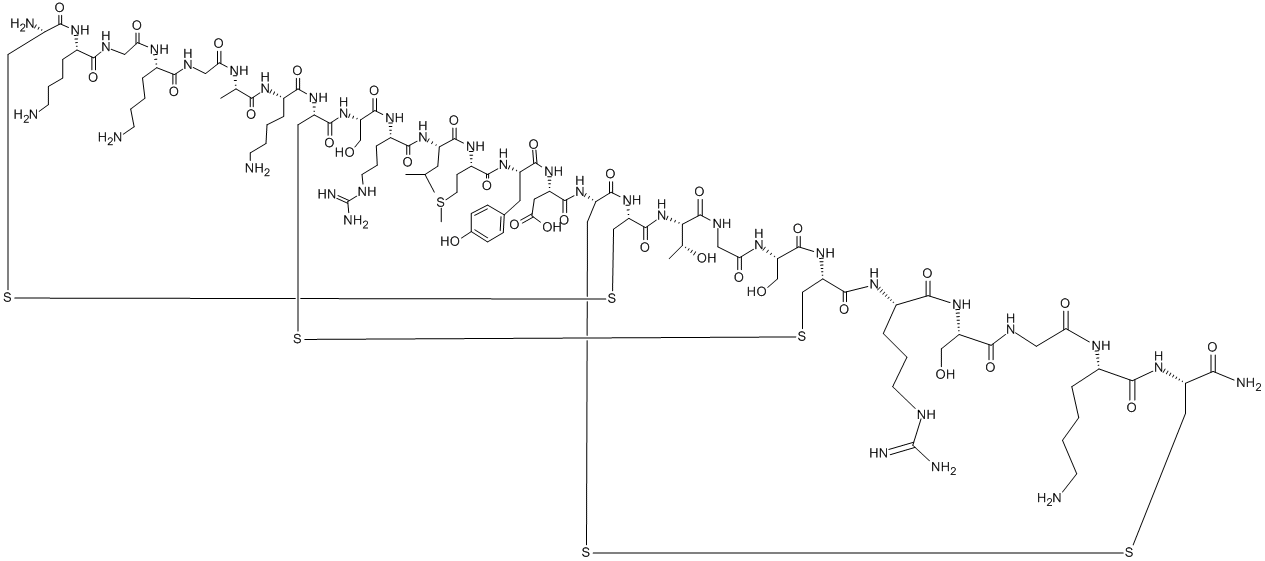
Bivalirudin
Synonym(s):;Hirulog trifluoroacetate salt
- CAS NO.:128270-60-0
- Empirical Formula: C98H138N24O33
- Molecular Weight: 2180.29
- MDL number: MFCD08282793
- EINECS: 274-570-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
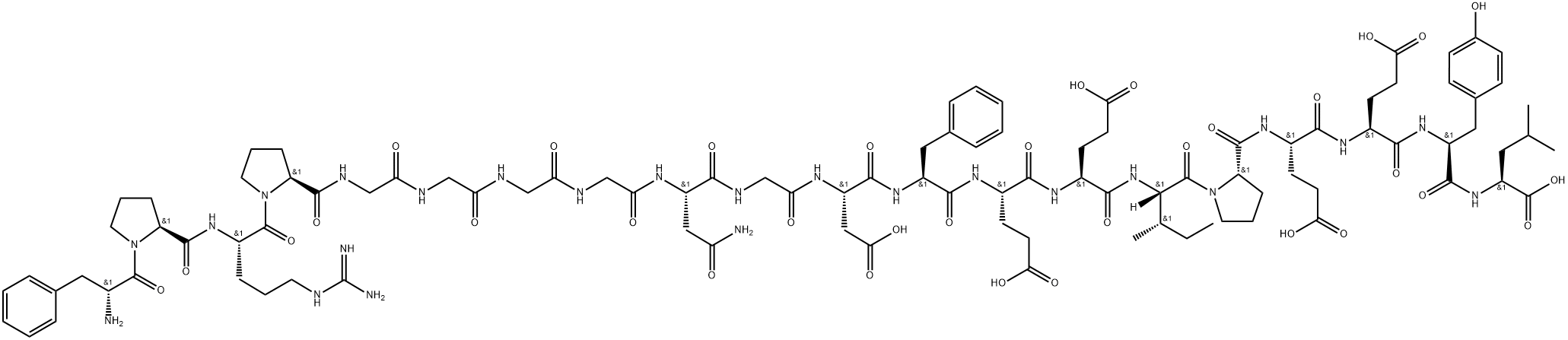
What is Bivalirudin?
Absorption
Following intravenous administration, bivalirudin exhibits linear pharmacokinetics. The mean steady state concentration is 12.3 +/- 1.7mcg/mL after administration of an intravenous bolus of 1mg/kg followd by a 2.5mg/kg/hr intravenous infusion given over 4 hours.
Toxicity
Based on a study by Gleason et al., the no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) for bivalirudin, administered to rats via intravenous infusion over a 24-hour period, was 2000 mg/kg/24 h.
Description
Bivalirudin was launched in New Zealand as an anticoagulant for i.v. treatment of patients with unstable angina undergoing percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Bivalirubin is a synthetic 20 amino acid peptide rationally modeled on hirudin (residues 53- 64), the most potent and specific naturally-occuring known inhibitor of thrombin, the enzyme that plays a key role in hemostasis and blood clot formation. This peptide is a direct thrombin inhibitor that maintains the unique bivalent binding properties of hirudin to the catalytic site and to the fibrin-recognition exosite of the enzyme, so acting directly on thrombin with high affinity and specificity. In vitro studies demonstrated that alpha- and zeta-thrombins, both with the higher fibrinogen-procoagulant activities, were inhibited. In rats receiving high doses of bivalirudin, the platelet deposition in carotide was reduced by 63% compared to controls. The results of clinical studies, conducted only in patients receiving concomitant aspirin, suggested that the use of bivalirudin was more efficacious and more predictable than unfractionated heparin, with fewer bleeding complications. Despite some unresolved developmental issues, the attractive properties of this novel agent could make it a useful alternative to heparin in a variety of coagulation disorders.
Description
Bivalirudin is an inhibitor of α- and ζ-thrombin (Kis = 2.56 and 1.84 nM, respectively), enzymes that exhibit high fibrinogen-clotting activities. It is selective for α- and ζ-thrombin, lacking activity at trypsin and γ-thrombin, which lacks clotting activity, at a >1,000-fold excess of bivalirudin. Bivalirudin inhibits α-thrombin-stimulated activation of the clotting factors Factor X, Factor V, and prothrombin in contact-activated plasma at a concentration of 0.1 μM. Administration of bivalirudin (0.5-1.5 mg/kg, i.v.) reduces platelet deposition in a rat carotid endarterectomy model in a dose-dependent manner. Formulations containing bivalirudin have been used to prevent ischemic events during angioplasty for thrombus-containing lesions.
Originator
Biogen (US)
The Uses of Bivalirudin
Anticoagulant; antithrombotic.
Indications
For treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and for the prevention of thrombosis. Bivalirudin is indicated for use in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), in patients at moderate to high risk acute coronary syndromes due to unstable angina or non-ST segment elevation in whom a PCI is planned.
Background
Bivalirudin is a synthetic 20 residue peptide (thrombin inhibitor) which reversibly inhibits thrombin. Once bound to the active site, thrombin cannot activate fibrinogen into fibrin, the crucial step in the formation of thrombus. It is administered intravenously. Because it can cause blood stagnation, it is important to monitor changes in hematocrit, activated partial thromboplastin time, international normalized ratio and blood pressure.
Definition
ChEBI: A synthetic peptide of 20 amino acids, comprising D-Phe, Pro, Arg, Pro, Gly, Gly, Gly, Gly, Asn, Gly, Asp, Phe, Glu, Glu, Ile, Pro, Glu, Glu, Tyr, and Leu in sequence. A congener of hirudin (a naturally occurring drug found in the saliva o the medicinal leech), it a specific and reversible inhibitor of thrombin, and is used as an anticoagulant.
Manufacturing Process
A 20 amino acid polypeptide [1], bivalirudin (hirulog) is a synthetic version of
hirudin. Its amino-terminal D-Phe-Pro-Arg-Pro domain, which interacts with
the active site of thrombin, is linked via four Gly residues to a dodecapeptide
analogue of the carboxy-terminal of hirudin. Like hirudin, bivalirudin also
forms a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. Once bound, however, the
Arg-Pro bond at the amino-terminal of bivalirudin is cleaved by thrombin,
thereby restoring active site functions of the enzyme complexes of α-thrombin
[2].
Hirulog-8 has the formula: H-(D-Phe)-Pro-Arg-Pro-(Gly)4-Asn-Gly-Asp-Phe-
Glu-Glu-Ile-Pro-Glu-Glu-Tyr-Leu-OH. Hirulog-8 was synthesized by
conventional solid-phase peptide synthesis employing an Applied Biosystems
430 A Peptide Synthesizer. This peptide was synthesized using BOC-L-Leucine-
O-divinylbenzene resin. Additional t-BOC-amino acids (Peninsula Laboratories, Belmont, Calif.) used included BOC-O-2,6-dichlorobenzyl tyrosine, BOC-Lglutamic
acid (γ-benzyl ester), BOC-L-proline, BOC-L-isoleucine, BOC-Lphenylalanine,
BOC-L-aspartic acid (β-benzyl ester), BOC-glycine, BOC-Lasparagine,
BOC-L-phenylalanine, and BOC-L-arginine. In order to achieve
higher yields in synthesis, the (Gly)4 linker segment was attached in two
cycles of manual addition of BOC-glycylglycine (Beckman Biosciences, Inc.,
Philadelphia, Pa.). After completion of synthesis, the peptide was fully
deprotected and uncoupled from the divinylbenzene resin by treatment with
anhydrous HF:p-cresol:ethylmethyl sulfate (10:1:1, v/v/v). Following removal
from the resin, the peptide was lyophilized to dryness.
Crude Hirulog-8 was purified by reverse-phase HPLC employing an Applied
Biosystems 151A liquid chromatographic system and a Vydac C18 column
(2.2x25 cm). The column was equilibrated in 0.1% TFA/water and developed
with a linear gradient of increasing acetonitrile concentration from 0 to 80%
over 45 minutes in the 0.1% TFA at a flow-rate of 4.0 ml/min. The effluent
stream was monitored for absorbance at 229 nm and fractions were collected
manually. We purified 25-30 mg of crude Hirulog-8 by HPLC and recovered
15-20 mg of pure peptide.
The structure of purified Hirulog-8 was confirmed by amino acid and sequence
analyses.
brand name
Angiomax (Medicinova).
Therapeutic Function
Anticoagulant
Biochem/physiol Actions
Bivalirudin is a specific and reversible bivalent direct thrombin inhibitor. Bivalirudin specifically binds to both the catalytic site and to the anion-binding exosite of circulating and clot-bound thrombin.
Mechanism of action
Bivalirudin is a rapid-onset, short-acting DTI that binds to both the active site and the exosite-1 of thrombin. Unlike lepirudin, bivalirudin is a reversible inhibitor of both free thrombin and thrombin bound to fibrin. This reversibility is possible because the bound bivalirudin undergoes cleavage at the second N-terminal proline to release the portion of the drug bound to the active site. The carboxyl-terminal portion of bivalirudin dissociates from thrombin to regenerate thrombin. Bivalirudin does not bind to plasma protein.
Pharmacokinetics
Bivalirudin mediates an inhibitory action on thrombin by directly and specifically binding to both the catalytic site and anion-binding exosite of circulating and clot-bound thrombin. The action of bivalirudin is reversible because thrombin will slowly cleave the thrombin-bivalirudin bond which recovers the active site of thrombin.
Pharmacokinetics
Bivalirudin is administered via intravenous bolus injection, followed by continuous infusion (Table 31.4). The drug exhibits a rapid onset and a short duration of action. Bivalirudin is eliminated by renal excretion. It has been suggested that dosage adjustments be made in patients with severe renal impairment and in patients undergoing dialysis. Approximately 30% is eliminated unchanged along with proteolytic cleavage products. Because of the reversible nature of bivalirudin the drug exhibits less risk of bleeding than other antithrombotics, and there have been no reported cases of antibody formation to bivalirudin.
Clinical Use
Bivalirudin, a 20-amino-acid peptide, has been approved for use in patients with unstable angina undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of haemorrhage with IV
diclofenac and ketorolac.
Antiplatelets and anticoagulants: increased risk of
bleeding.
Thrombolytics: may increase risk of bleeding
complications; enhance effect of bivalirudin.
Metabolism
80% proteolytic cleavage
Metabolism
As a peptide, bivalirudin is expected to undergo catabolism to its constituent amino acids, with subsequent recycling of the amino acid in the body pool. Bivalirudin is metabolised by proteases, including thrombin. The primary metabolite resulting from the cleavage of Arg3 -Pro4 bond of the N-terminal sequence by thrombin is not active because of the loss of affinity to the catalytic active site of thrombin.
References
[1]. shammas n w. bivalirudin: pharmacology and clinical applications[j]. cardiovascular drug reviews, 2005, 23(4): 345-360.
Properties of Bivalirudin
| Density | 1.52±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | ≥54.5 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming; ≥10.18 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥43.5 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming |
| form | powder |
| color | white to off-white |
Safety information for Bivalirudin
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Bivalirudin
| InChIKey | OIRCOABEOLEUMC-GEJPAHFPSA-N |
Bivalirudin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Bivalirudin 98%View Details
Bivalirudin 98%View Details -
 128270-60-0 98%View Details
128270-60-0 98%View Details
128270-60-0 -
 Bivalirudin 98%View Details
Bivalirudin 98%View Details
128270-60-0 -
 Bivalirudin 128270-60-0 98%View Details
Bivalirudin 128270-60-0 98%View Details
128270-60-0 -
 Bivalirudin trifluoroacetate salt CAS 128270-60-0View Details
Bivalirudin trifluoroacetate salt CAS 128270-60-0View Details
128270-60-0 -
 Bivalirudin Powder APIView Details
Bivalirudin Powder APIView Details
128270-60-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
