L-Valine
Synonym(s):Val;(S)-(+)-Valine;L -2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid;L -Valine;(S)-α-Aminoisovaleric acid
- CAS NO.:72-18-4
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 117.15
- MDL number: MFCD00064220
- EINECS: 200-773-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
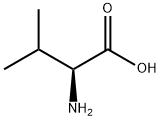
What is L-Valine?
Absorption
Absorbed from the small intestine by a sodium-dependent active-transport process.
Toxicity
Symptoms of hypoglycemia, increased mortality in ALS patients taking large doses of BCAAs.
Description
Valine (abbreviated as Val or V) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2. L-Valine is one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. Human dietary sources are any proteinaceous foods such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes.
Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. It is named after the plant valerian. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid in hemoglobin. Because valine is hydrophobic, the hemoglobin is prone to abnormal aggregation.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of L-Valine
L-Valine is an essential amino acid and one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. L-Valine cannot be manufactured by the body and must be acquired through diet or supplementation. L-valine is found in grai ns, dairy products, mushrooms, meats, peanuts and soy proteins. L-Valine has been used in studies to attenuate arrhythmias and induce hypotensive effects.
The Uses of L-Valine
valine is an amino acid used as a skin-conditioning and odor-masking agent. It is more commonly used in hair care preparations than in skin care.
The Uses of L-Valine
L-Valine is an essential amino acid and one of 20 proteinogenic amino acids. L-Valine cannot be manufactured by the body and must be acquired through diet or supplementation. L-valine is found in grains, dairy products, mushrooms, meats, peanuts and soy proteins. L-Valine has been used in studies to attenuate arrhythmias and induce hypotensive effects.
Indications
Promotes mental vigor, muscle coordination, and calm emotions. May also be of use in a minority of patients with hepatic encephalopathy and in some with phenylketonuria.
Background
Valine is a branched-chain essential amino acid that has stimulant activity. It promotes muscle growth and tissue repair. It is a precursor in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway.
What are the applications of Application
L-Valine is an essential branched amino acid with potential arrhythmia attenuation
Definition
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of valine.
Biosynthesis
Valine is an essential amino acid, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. It is synthesized in plants via several steps starting from pyruvic acid. The initial part of the pathway also leads to leucine. The intermediate α-ketoisovalerate undergoes reductive amination with glutamate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include :
Acetolactate synthase
Acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase
Dihydroxyacid dehydratase
Valine aminotransferase.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 22, p. 2411, 1981 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82922-1
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 23, p. 167, 1975 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.23.167
General Description
Valine is an essential amino acid, involved in the biosynthesis of glutamine and alanine. Valine being a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), maintains a balance among the BCAAs. L-Valine serves as an energy fuel.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Valine is an essential amino acid, involved in the biosynthesis of glutamine and alanine. Valine being a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) maintains a balance among the BCAAs. L-Valine serves as an energy fuel. Long term deficiency of L-Valine leads to growth failure, organ damage and loss of muscle mass.
Pharmacokinetics
L-valine is a branched-chain essential amino acid (BCAA) that has stimulant activity. It promotes muscle growth and tissue repair. It is a precursor in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway. Valine is one of three branched-chain amino acids (the others are leucine and isoleucine) that enhance energy, increase endurance, and aid in muscle tissue recovery and repair. This group also lowers elevated blood sugar levels and increases growth hormone production. Supplemental valine should always be combined with isoleucine and leucine at a respective milligram ratio of 2:1:2. It is an essential amino acid found in proteins; important for optimal growth in infants and for growth in children and nitrogen balance in adults. The lack of L-valine may influence the growth of body, cause neuropathic obstacle, anaemia. It has wide applications in the field of pharmaceutical and food industry.
Side Effects
L-valine is a natural substance that is necessary for our health. As such, it generally does not have any side effects. However, taking large quantities of L-valine can cause fatigue, nausea, and a lack of muscle coordination.
Extremely high doses of L-valine can be dangerous. Excessive levels of L-valine can cause your body to produce excess ammonia which is toxic.
Extremely high levels of L-valine can cause your skin to tingle and can lead to hallucinations.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Synthesis
Racemic valine can be synthesized by bromination of isovaleric acid followed by amination of the α-bromo derivative
HO2CCH2CH(CH3)2 + Br2 → HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + HBr
HO2CCHBrCH(CH3)2 + 2 NH3 → HO2CCH(NH2)CH(CH3)2 + NH4Br
.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-valine from water by addition of EtOH. It sublimes at 178-188o/0.03mm with 99.3% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. [Perrin J Chm Soc 3125 1958, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2368-23771961, Beilstein 4 IV 2659.]
Nomenclature
According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially starting from 1 denoting the carboxyl carbon, whereas 4 and 4' denote the two terminal methyl carbons.
Properties of L-Valine
| Melting point: | 295-300 °C (subl.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 213.6±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 28 º (c=8, 6N HCl) |
| Density | 1.23 |
| refractive index | 28 ° (C=8, HCl) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 25 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.29(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.5-6.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +27.0±0.5°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 85 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1 |
| Merck | 14,9909 |
| BRN | 1721136 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 72-18-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Valine(72-18-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Valine (72-18-4) |
Safety information for L-Valine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Valine
| InChIKey | KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
L-Valine manufacturer
Jeevan Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
HRV Global Life Sciences
Meteoric Biopharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 72-18-4 L-Valine 98%View Details
72-18-4 L-Valine 98%View Details
72-18-4 -
 72-18-4 98%View Details
72-18-4 98%View Details
72-18-4 -
 L-Valine for tissue culture CAS 72-18-4View Details
L-Valine for tissue culture CAS 72-18-4View Details
72-18-4 -
 L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
72-18-4 -
 L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
72-18-4 -
 L-Valine 99%View Details
L-Valine 99%View Details -
 L-Valine 99% CAS 72-18-4View Details
L-Valine 99% CAS 72-18-4View Details
72-18-4 -
 L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
L-Valine CAS 72-18-4View Details
72-18-4