L-Leucine
Synonym(s):(S)-2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid;(S)-(+)-Leucine;Leu;L-Leucine;L-Leucine - CAS 61-90-5 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:61-90-5
- Empirical Formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 131.17
- MDL number: MFCD00002617
- EINECS: 200-522-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
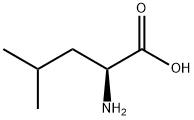
What is L-Leucine?
Description
Small, white, lustrous plates, or a white, crystalline powder, with a slightly bitter taste. One g dissolves in about 40 mL of water and in about 100 mL of acetic acid. It is sparingly soluble in alcohol, but is soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and in solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates. ι-Leucine may be synthesized by bromination, followed by amination of isocaproic acid; via the acetamidomalonic ester; by isolation from gluten, casein, keratin; from hydantoin.
Chemical properties
Leucine occurs as a white or almost off-white crystalline powder or shiny flakes.
Chemical properties
L-Leucine is odorless and has a slightly bitter taste. L-Leucine is a branched-chain, essential amino acid that stimulates muscle protein synthesis.
Occurrence
Reported found as a constituent in proteins; also present in the free state in the human body
The Uses of L-Leucine
L-Leucine plays a vital role in hemoglobin formation, protein synthesis and metabolic functions. It assists the growth and repair of muscle and bone tissue. It is used in the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - Lou Gehrig's disease. It prevents the breakdown of muscle proteins after trauma or severe stress and may be beneficial for individuals with phenylketonuria. It is also used as a food additive and flavor enhancer. Further, it is used to preserve muscle glycogen.
The Uses of L-Leucine
L-Leucine is an essential amino acid. It is also considered to be a branched chain amino acid, along with L-Isoleucine and L-Valine. It is used as a cell culture media component in the commercial biomanufacture of therapeutic recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies.
The Uses of L-Leucine
L-Leucine is an essential amino acid. L-Leucine acts as a nutrient signal to stimulate protein synthesis. It has also activates the mammalian target of rapamycin kinase that regulates cell growth.
What are the applications of Application
L-Leucine is an essential, branched-chain amino acid
Definition
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of leucine.
Production Methods
Leucine is produced microbially by incubating an amino-acidproducing microorganism including but not exclusive to Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Bacillus, or Staphylococcus in the presence of oxygen and a hydrocarbon. The nutrient medium should contain an inhibitory amount of a growth inhibitor that is a chemically similar derivative of leucine (e.g. methylallylglycine, a-hydrozinoisocaproic acid, or b-cyclopentanealanine) to inhibit the growth of the organism except for at least one mutant that is resistant to the inhibitory effect. The resistant mutant is then isolated and grown in the presence of oxygen and the hydrocarbon in the absence of the inhibitor. The mutant cells are then harvested and a nutrient medium is formed that includes a hydrocarbon as the sole source of carbon. Finally, the harvested cells are incubated in the medium in the presence of oxygen.
Preparation
By bromination followed by amination of isocaproic acid; via the acetamidomalonic ester; by isolation from gluten, casein, keratin; from hydantoin.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Leucine is used in pharmaceutical formulations as a flavoring agent. It has been used experimentally as an antiadherent to improve the deagglomeration of disodium cromoglycate micro-particles and other compounds in inhalation preparations; and as a tablet lubricant. Leucine copolymers have been shown to successfully produce stable drug nanocrystals in water.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Leucine is a non-glucogenic, essential amino acid. It is a branched-chain amino acid that is a structural component of proteins. Leucine positively influences insulin release to eliminate toxic sugars out of the blood. The degradation of leucine leads to the formation of ketone bodies.
Safety
Leucine is an essential amino acid and is consumed as part of a
normal diet. It is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant
material. It is moderately toxic by the subcutaneous route.
LD50 (rat, IP): 5.379 g/kg
Storage
Leucine is sensitive to light and moisture, and should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dark, dry place.
Purification Methods
Likely impurities are isoleucine, valine, and methionine. Crystallise L-leucine from water by adding 4 volumes of EtOH. It sublimes at 180-188o/0.3mm with 99.1% recovery, and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 p 2075-2094 1961, Kameda et al. J Pharm Soc Jpn 78 763 1958, Beilstein 4 IV 2738.]
Incompatibilities
Leucine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV infusion; oral tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Properties of L-Leucine
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| alpha | 15.4 º (c=4, 6N HCl) |
| Boiling point: | 122-134 °C(Press: 2-3 Torr) |
| Density | 1,293 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | <1 hPa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 3297 | L-LEUCINE |
| refractive index | 1.4630 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 145-148°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1 M HCl: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.328(at 25℃) |
| color | White to Off-white |
| PH | 5.5-6.5 (20g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +15.5°, c = 2 in 6 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 22.4 g/L (20 C) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 |
| JECFA Number | 1423 |
| Merck | 14,5451 |
| Sublimation | 145-148 ºC |
| BRN | 1721722 |
| Stability: | Stability Moisture and light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidising agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 61-90-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Leucine(61-90-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Leucine (61-90-5) |
Safety information for L-Leucine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Leucine
L-Leucine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 L-leucine 99%View Details
L-leucine 99%View Details -
 L-Leucine extrapure CHR CAS 61-90-5View Details
L-Leucine extrapure CHR CAS 61-90-5View Details
61-90-5 -
 L-Leucine CAS 61-90-5View Details
L-Leucine CAS 61-90-5View Details
61-90-5 -
 L-Leucine CASView Details
L-Leucine CASView Details -
 H-Leu-OH USP grade 99% CAS 61-90-5View Details
H-Leu-OH USP grade 99% CAS 61-90-5View Details
61-90-5 -
 H-Leu-OH 99% CAS 61-90-5View Details
H-Leu-OH 99% CAS 61-90-5View Details
61-90-5 -
 L Leucine Powder, HDPE BagView Details
L Leucine Powder, HDPE BagView Details
61-90-5 -
 L Leucine PowderView Details
L Leucine PowderView Details
61-90-5
