Hydrocortisone acetate
Synonym(s):11β,17α,21-Trihydroxy-4-pregnene-3,20-dione 21-acetate;17-α-Hydroxycorticosterone acetate;17-Hydroxycorticosterone 21-acetate;21-Acetoxy-4-pregnene-11β,17α-diol-3,20-dione;4-Pregnene-11β,17α,21-triol-3,20-dione 21-acetate
- CAS NO.:50-03-3
- Empirical Formula: C23H32O6
- Molecular Weight: 404.5
- MDL number: MFCD00037714
- EINECS: 200-004-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
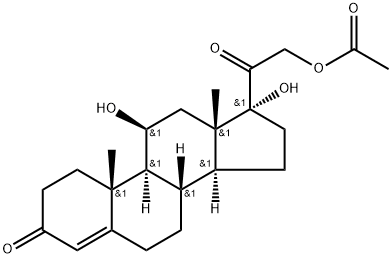
What is Hydrocortisone acetate?
Absorption
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption.
Toxicity
Side effects include inhibition of bone formation, suppression of calcium absorption and delayed wound healing
Chemical properties
white powder
The Uses of Hydrocortisone acetate
Hydrocortisone acetate is used to treat hemorrhoids and itching/swelling in the rectum and anus. It is used to treat certain intestinal problems (such as ulcerative colitis of the rectum and other rectal/anal inflammatory conditions).
The Uses of Hydrocortisone acetate
Glucocorticoid
Indications
For the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Also used to treat endocrine (hormonal) disorders (adrenal insufficiency, Addisons disease). It is also used to treat many immune and allergic disorders, such as arthritis, lupus, severe psoriasis, severe asthma, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease.
What are the applications of Application
Hydrocortisone 21-acetate is a corticosteroid with anti-inflammatory properties
Definition
ChEBI: Cortisol 21-acetate is a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a cortisol ester.
brand name
Cortef Acetate (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Cortifoam (Schwarz Pharma); Cortril (Pfizer); Dricort (Ingram); Hydrocortone (Merck).
Pharmacokinetics
Hydrocortisone is the most important human glucocorticoid. It is essential for life and regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic functions. Topical hydrocortisone is used for its anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive properties to treat inflammation due to corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by an ability to bind with the cortisol receptor and trigger a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic and homeostatic effects. Glucocorticoids are distinguished from mineralocorticoids and sex steroids by having different receptors, target cells, and effects. Technically, the term corticosteroid refers to both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, but is often used as a synonym for glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines IL-1, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha, the most important of which is the IL-2. Reduced cytokine production limits T cell proliferation. Glucocorticoids also suppress humoral immunity, causing B cells to express lower amounts of IL-2 and IL-2 receptors. This diminishes both B cell clonal expansion and antibody synthesis. The diminished amounts of IL-2 also leads to fewer T lymphocyte cells being activated.
Clinical Use
Corticosteroid:
Local inflammation of joints and soft tissue
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin;
concentration of isoniazid possibly reduced.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and
phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine, phenobarbital, fosphenytoin,
phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin - avoid; metabolism possibly inhibited
by itraconazole and ketoconazole.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: rare reports of convulsions in patients
on ciclosporin and high-dose corticosteroids
.
Cobicistat: concentration of hydrocortisone possibly
increased - increased risk of adrenal suppression.
Diuretics: enhanced hypokalaemic effects of
acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazide diuretics.
Vaccines: high dose corticosteroids can impair
immune response to vaccines - avoid concomitant
use with live vaccines.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic via CYP3A4
Metabolism
Hydrocortisone is metabolised in the liver and most body tissues to hydrogenated and degraded forms such as tetrahydrocortisone and tetrahydrocortisol. These are excreted in the urine, mainly conjugated as glucuronides, with a very small proportion of unchanged hydrocortisone.
Purification Methods
The acetate recrystallises from Me2CO/Et2O or aqueous Me2CO as hygroscopic monoclinic crystals. UV has max at 242 nm (A1cm 1% 390) in MeOH. Its solubility at 25o is: H2O (0.001%), EtOH (0.45%), MeOH (0.04%), Me2CO (1.1%), CHCl3 (0.5%), Et2O (0.15%), and it is very soluble in Me2NCHO. [Wendler et al. J Am Chem Soc 74 3630 1952; Antonucci et al. J Org Chem 18 7081 1953, Beilstein 8 IV 3424.]
Properties of Hydrocortisone acetate
| Melting point: | 223 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 446.1°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +166° (c = 0.4 in dioxane); D25 +150.7° (c = 0.5 in acetone) |
| Density | d420 1.289 |
| refractive index | 1.4593 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 223°C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.42±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Decomposition | 223 ºC |
| Merck | 14,4787 |
| BRN | 2066841 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be light or moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-03-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hydrocortisone acetate(50-03-3) |
Safety information for Hydrocortisone acetate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Hydrocortisone acetate
Hydrocortisone acetate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Hydrocortisone Acetate 99%View Details
Hydrocortisone Acetate 99%View Details -
 Hydrocortisone acetate 99%View Details
Hydrocortisone acetate 99%View Details -
 Hydrocortisone acetate 97% CAS 50-03-3View Details
Hydrocortisone acetate 97% CAS 50-03-3View Details
50-03-3 -
 Hydrocortisone acetate 95.00% CAS 50-03-3View Details
Hydrocortisone acetate 95.00% CAS 50-03-3View Details
50-03-3 -
 Hydrocortisone acetate 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-03-3View Details
Hydrocortisone acetate 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-03-3View Details
50-03-3 -
 Hydrocortisone Acetate CAS No. : 50-03-3View Details
Hydrocortisone Acetate CAS No. : 50-03-3View Details
50-03-3 -
 Hydrocortisone Acetate Cas 50 03 3, Grade Standard: BPView Details
Hydrocortisone Acetate Cas 50 03 3, Grade Standard: BPView Details
50-03-3 -
 Hydrocortisone Acetate PowderView Details
Hydrocortisone Acetate PowderView Details
50-03-3
