Hydrocortisone
Synonym(s):Cortisol;Hydrocortisone - CAS 50-23-7 - Calbiochem;Hydrocortisone, Chromatographic Standard - CAS 50-23-7 - Calbiochem;Kendall’s compound F;Reichstein’s substance M
- CAS NO.:50-23-7
- Empirical Formula: C21H30O5
- Molecular Weight: 362.47
- MDL number: MFCD00011654
- EINECS: 200-020-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-12 07:03:40
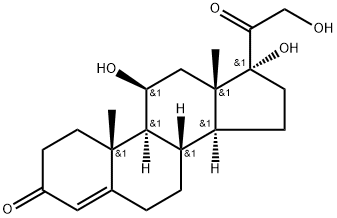
What is Hydrocortisone?
Absorption
Oral hydrocortisone at a dose of 0.2-0.3mg/kg/day reached a mean Cmax of 32.69nmol/L with a mean AUC of 90.63h*nmol/L A 0.4-0.6mg/kg/day dose reached a mean Cmax of 70.81nmol/L with a mean AUC of 199.11h*nmol/L. However, the pharmacokinetics of hydrocortisone can vary by 10 times from patient to patient.
Topical hydrocortisone cream is 4-19% bioavailable[8546995] with a Tmax of 24h.
Hydrocortisone retention enemas are have a bioavailability of 0.810 for slow absorbers and 0.502 in rapid absorbers. Slow absorbers take up hydrocortisone at a rate of 0.361±0.255/h while fast absorbers take up hydrocortisone at a rate of 1.05±0.255/h.
A 20mg IV dose of hydrocortisone has an AUC of 1163±277ng*h/mL.
Toxicity
Data regarding acute overdoses of glucocorticoids are rare. Chronic high doses of glucocorticoids can lead to the development of cataract, glaucoma, hypertension, water retention, hyperlipidemia, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, myopathy, osteoporosis, mood changes, psychosis, dermal atrophy, allergy, acne, hypertrichosis, immune suppression, decreased resistance to infection, moon face, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, metabolic acidosis, growth suppression, and secondary adrenal insufficiency. Overdose may be treated by adjusting the dose or stopping the corticosteroid as well as initiating symptomatic and supportive treatment.
Description
Hydrocortisone, also called cortisol, is a glucocorticoid produced by the adrenal glands. It has many physiological functions, including fighting inflammation. Synthetic hydrocortisone is sold over the counter as a topical anti-inflammatory and anti-itch agent.
T. Reichstein in 1937 and H. L. Mason et al. in 1938 isolated hydrocortisone from adrenal glands. (Reichstein was awarded the 1950 Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology for his work on adrenal cortex hormones.) Its?first synthesis?was reported by N. L. Wendler and co-workers in 1950.
Hydrocortisone is also called “the stress hormone”: It is released by the adrenal glands as a response to stress or fear. So expect your hydrocortisone level to increase on Halloween!
Chemical properties
crystalline white powder
Originator
Hydrocortone,MSD,US,1952
The Uses of Hydrocortisone
Cortisol, or Hydrocortisone, is a steroid hormone, more specifically a glucocorticoid, produced by the zona fasciculata of the adrenal gland. Cortisol is released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.
The Uses of Hydrocortisone
Principle glucocorticoid hormone produced by adrenal cortex. An anti-inflammatory hormone.
The Uses of Hydrocortisone
glucocorticoid, antiinflammatory
Indications
Otic solutions are indicated for infections of the external auditory canal caused by susceptible organisms and with inflammation. Hydrocortisone tablets are indicated for certain endocrine, rheumatic, collagen, allergic, ophthalmic, respiratory, hematologic, neoplastic, edematous, gastrointestinal, and other conditions. A hydrocortisone enema is indicated for ulcerative colitis, a topical ointment with antibiotics is indicated for corticosteroid responsive dermatoses with infections, and a topical cream with acyclovir is indicated to treat cold sores. Oral granules of hydrocortisone are used as a replacement therapy for Adrenocortical Insufficiency (AI) in children under 17 years of age.
Background
Hydrocortisone, or cortisol, is a glucocorticoid secreted by the adrenal cortex. Hydrocortisone is used to treat immune, inflammatory, and neoplastic conditions. It was discovered in the 1930s by Edward Kendall and named Compound F, or 17-hydroxycorticosterone.
Hydrocortisone was granted FDA approval on 5 August 1952.
What are the applications of Application
Hydrocortisone is a primary glucocorticoid and anti-inflammatory agent
Definition
ChEBI: A C21-steroid that is pregn-4-ene substituted by oxo groups at positions 3 and 20 and hydroxy groups at positions 11, 17 and 21. Cortisol is a corticosteroid hormone or glucocorticoid produced by zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex, which is a part of the adrenal gland. It is usually referred to as the "stress hormone" as it is involved in response to stress and anxiety, controlled by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). It increases blood pressure and blood sugar, and reduces immun responses
Indications
Hydrocortisone (Cortizone, Cortaid, Anusol-HC, Hytone, LactiCare-HC, Sarnol HC, Penecort, Texacort, and many other branded products) may be purchased as a generic drug.
Manufacturing Process
The following example from US Patent 2,602,769 illustrates the preparation of
17-hydroxycorticosterone (compound F) from 11-desoxy-17-
hydroxycorticosterone (compound S). A medium was prepared from 0.5%
peptone, 2% dextrose, 0.5% soybean meal, 0.5% KH2PO4, 0.5% sodium
chloride and 0.3% yeast extract in tap water. To 200 ml of this sterilized
medium was added an inoculum of the vegetative mycella of Cunninghamella blakesleeana. The spores had first been transferred from a sport slant to a
broth medium and the broth medium was aerobically incubated at 24°C for 24
to 72 hours in a .reciprocating shaker until the development of vegetative
growth. The inoculated medium containing added vegetative mycella of
Cunninghamella blakesleeana was incubated for 48 hours at 24°C following
which was added 66 mg of compound S, 11-desoxy-17-hydroxycorticosterone
in solution in a minimum of ethanol, and incubation was maintained for 7
hours at 24°C. The beer containing steroid was diluted with 800 ml of
acetone, shaken 1 hour on a reciprocating shaker and filtered. The cake was
suspended in 500 ml of acetone, shaken another hour and again filtered. The
filtrates were combined and the acetone was volatilized under reduced
pressure at 50°C. Acetone was then added, if necessary, to bring the
concentration to 20% acetone and this resulting aqueous acetone solution was
extracted five times each with one-third volume of Skellysolve B petroleum
ether to remove fatty materials. These extracts were back washed two times
with one-tenth volume of 20% aqueous acetone and the washings were added
to the main acetone extract.
The combined acetone extracts were extracted six times with one-fourth
volume of ethylene dichloride and the ethylene dichloride extract was
evaporated under vacuum to leave the steroid residue. This steroid residue
was taken up in a minimum of methylene chloride and applied to the top of a
column packed with 30 grams of silica which had been previously triturated
with 21 ml of ethylene glycol. Then various developing mixtures, saturated
with ethylene glycol, were passed over the column. Cuts were made as each
steroid was eluted as determined by the lowering of the absorption of light at
240 nm on the automatic chromatographic fraction cutter.
Band Solvent Tube No. (60ml) Crude Solids (mg)
1 Cyclohexane 1-4 11
2 Cyclohexane-methylene chloride 3:1 5-13 6.4 compound S
3 Cyclohexane-methylene chloride 1:1 14-16 3.0
4 Cyclohexane-methylene chloride 2:3 17-23 6.0 compound E
5 Cyclohexane-methylene chloride 1:4 24-38 12.2 compound F
6 Methylene chloride 39-59 4.8
A 7.7 mg portion of band 5 was taken up in a minimum of acetone and
refrigerated until crystals separated. This cold acetone mixture was
centrifuged and the supernatant liquid removed by pipette. To the remaining
crystals, a few drops of ice-cold ether-acetone, three to one mixture, were
added, shaken, recentrifuged and the supernatant wash liquid removed by
pipette. The ether-acetone wash was repeated. The resulting crystals were
dried under vacuum yielding 3.3 mg of pure compound F, 17-
hydroxycorticosterone.
brand name
Acticort (Baker Norton); Ala-Cort (Del Ray); Cetacort (Healthpoint); Colocort (Paddock); Cort- Dome (Bayer); Cortef (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Cortenema (Solvay Pharmaceuticals); Cortril (Pfizer); Dermacort (Monarch); Dermacort (Solvay Pharmaceuticals); Eldecort (Valeant); Epicort (Bluline); Flexicort (Westwood- Squibb); Glycort (Heran); Hi-Cor (C & M); Hydro-Rx (X Gen); Hydrocortone (Merck); Hytone (Dermik); Hytone (Sanofi Aventis); Nutracort (Healthpoint); Penecort (Allergan); Proctocort (Monarch); Stie-Cort (Stiefel); Synacort (Medicis); Texacort (Sirius).
Therapeutic Function
Glucocorticoid
General Description
Hydrocortisone, 11β,17,21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is the primary natural GCin humans. Despite the large number of synthetic GCs, hydrocortisone,its esters, and its salts remain a mainstay ofmodern adrenocortical steroid therapy and the standard forcomparison of all other GCs and MCs . It isused for all the indications mentioned previously.
Health Hazard
Cortisol Increases (1) protein catabolism (excepting liver) gluconeogenesis; (2) carbohydrate anabolism (liver); (3) blood sugar; (4) glucose absorption; (5) brain excitation; (6) spread of infections; (7)urinary glucose and nitrogen; (8) stress tolerance; (9) lactation; (10) water diuresis.
Regulates general adaptation syndrome, water balance, blood pressure, and hormone release.
Decreases (1) fat anabolism; (2) growth rate; (3) inflammation; (4) eosinophils; (5) lymphocytes; (6) antigen sensitivity; (7) respiratory quotient; (8) ketosis; (9) wound healing; (10) skin pigmentation; (11)RBC hemolysis.
Biological Activity
hydrocortisone is a main glucocorticoid secreted by the adrenal cortex.
Contact allergens
Hydrocortisone is the principal glucocorticoid hor- mone produced by the adrenal cortex and is used topi- cally or systemically. It belongs to the allergenic A group. Marker of allergy is tixocortol pivalate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Product does not compete with ATP.
Mechanism of action
Hydrocortisone exhibits anti-shock, anti-allergy, and anti-inflammatory action. It raises sugar content in the blood, increases potassium secretion, and lowers sodium excretion from the body. It exhibits anti-metabolic action and reduces histamine synthesis in the body.
Pharmacokinetics
Hydrocortisone binds to the glucocorticoid receptor leading to downstream effects such as inhibition of phospholipase A2, NF-kappa B, other inflammatory transcription factors, and the promotion of anti-inflammatory genes. Hydrocortisone has a wide therapeutic index and a moderate duration of action. Patients should stop taking the medication if irritation or sensitization occurs.
Clinical Use
Hydrocortisone is endogenous, and it has both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity. It is the fundamental structure by which the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activities of all other corticosteroids are judged. Functional groups that are essential for both mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid activity include the pregnane skeleton with an all-trans backbone, the ring A-en-one system (?4 -3-one ring A) and the 17β-ketol side chain (C-20-keto-C-21-hydroxy). The glucocorticoid activity is enhanced by the C-11 and C-17 hydroxyl groups. Hydrocortisone can be used to treat severe asthmatic attacks that do not respond to conventional treatment. It is available as various ester forms.
Safety Profile
Poison by
Synthesis
Hydrocortisone, 11|?,17|á,21-trihydroxypregn-4-en-3,20-dione (27.1.8), is synthesized in various ways and from various compounds containing a steroid skeleton. According to one of them, hydrocortisone is synthesized from dextropregnenolone. The double bond between C16 and C17 of dextropregnenolone is oxidized using hydrogen peroxide in a base, forming an epoxide 27.1.1. Interacting this with hydrobromic acid opens the epoxide ring, forming 16-bromo-17-hydroxydextropregnenolone (27.1.2). The resulting bromo derivative undergoes debromination by hydrogen using a palladium on carbon catalyst, and then the secondary hydroxyl group undergoes esterification using formic acid in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid, giving 3-formyloxy-17-hydroxydextropregnenolone (27.1.3). The resulting 3-formyloxy- 17-hydroxydextropregnenolone undergoes bromination by bromine, which results in bromination of the C4¨CC5 double bond and the methyl group of acetyl moiety, which forms a tribromo derivative 27.1.4. Reacting the product with sodium iodide results in dehalogenation of the resulting vicinal dibromide, during which the double bond is simultaneously shifted into the position between carbon atoms C5 and C6 that gives the bromoketone 27.1.5. This is reacted with potassium acetate and then with acetic anhydride in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid, forming a diacetate 27.1.6. Taking into account that unlike acetates, formates are easily oxidized and give exactly the same products as do the corresponding alcohols, the resulting diacetate is oxidized in an Oppenauer oxidation reaction, using aluminum isopropoxide and cyclohexanone as a hydrogen acceptor. During this, isomerization of the double bond into the primary position between C4 and C5 simultaneously takes place, forming a stable, conjugated vinylketone, after which the acetyl protection of both hydroxyl groups is hydrolyzed using potassium hydroxide, giving 17-hydroxy-11-deoxycorticosterone (27.1.7). This undergoes microbiological oxidation at position C1, forming the desired hydrocortisone (27.1.8). Side reactions of microbiological oxidation using the very same microorganisms can cause hydroxylation of steroids in different positions, using easily accessible progesterone as an initial substance.

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Because of its rapid effect and relatively high mineralocorticoid effect,
hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef?) is the most
commonly used form of this medication when an acute glucocorticoid/
mineralocorticoid effect is desired (e.g., acute adrenal insufficiency).
Corticosteroids have not been shown beneficial in treating
hypovolemic shock, but low dose glucocorticoids probably reduce
mortality associated with septic shock.
Glucocorticoids have been used in an attempt to treat practically
every malady that afflicts man or animal, but there are three broad
uses and dosage ranges for use of these agents. 1) Replacement of
glucocorticoid activity in patients with adrenal insufficiency, 2)
as an antiinflammatory agent, and 3) as an immunosuppressive.
Among some of the uses for glucocorticoids include treatment of:
endocrine conditions (e.g., adrenal insufficiency), rheumatic diseases
(e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), collagen diseases (e.g., systemic
lupus), allergic states, respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma), dermatologic
diseases (e.g., pemphigus, allergic dermatoses), hematologic
disorders (e.g., thrombocytopenias, autoimmune hemolytic anemias),
neoplasias, nervous system disorders (increased CSF pressure),
GI diseases (e.g., ulcerative colitis exacerbations), and renal
diseases (e.g., nephrotic syndrome). Some glucocorticoids are used
topically in the eye and skin for various conditions or are injected
intra-articularly or intra-lesionally. The above listing is certainly
not complete.
Metabolism
Hydrocortisone is metabolised to 6-beta hydrocortisol via CYP3A, 5-beta tetrahydrocortisol via 3-oxo-5-beta-steroid 4-dehydrogenase, 5-alpha tetrahydrocortisol via 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase 2, cortisone via Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1 and Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2, and glucuronide products. Cortisone is further metabolized to tetrahydrocortisone and dihydrocortisol.
storage
Store at RT
Purification Methods
Recrystallise hydrocortisone from EtOH or isoPrOH. It is bitter tasting and has UV with max at 242 nm (log 4.20). Its solubility at 25o is: H2O (0.28%), EtOH (1.5%), MeOH (0.62%), Me2CO (0.93%), CHCl3 (0.16%), propylene glycol (1.3%) and Et2O (0.35%). It gives an intense green colour with conc H2SO4. [Wendler et al. J Am Chem Soc 72 5793 1950, Beilstein 8 IV 3422.]
Properties of Hydrocortisone
| Melting point: | 211-214 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 414.06°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 166 º (c=1, C2H5OH 25 ºC) |
| Density | 1.0812 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6120 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 220°C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 319.7mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Decomposition | 220 ºC |
| Merck | 14,4787 |
| BRN | 1354819 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-23-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hydrocortisone(50-23-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hydrocortisone (50-23-7) |
Safety information for Hydrocortisone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone manufacturer
Allmpus Laboratories Pvt Ltd
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




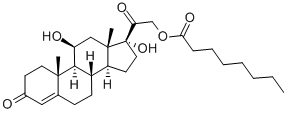
You may like
-
 50-23-7 98%View Details
50-23-7 98%View Details
50-23-7 -
 Hydrocortisone 99%View Details
Hydrocortisone 99%View Details -
 Hydrocortisone 97% CAS 50-23-7View Details
Hydrocortisone 97% CAS 50-23-7View Details
50-23-7 -
 Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
50-23-7 -
 Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
50-23-7 -
 Hydrocortisone Aceate EP Impurity A 97.94View Details
Hydrocortisone Aceate EP Impurity A 97.94View Details
50-23-7 -
 HYDROCORTISONE Extra Pure CAS 50-23-7View Details
HYDROCORTISONE Extra Pure CAS 50-23-7View Details
50-23-7 -
 Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
Hydrocortisone CAS 50-23-7View Details
50-23-7
