Gallium arsenide
Synonym(s):Gallium monoarsenide
- CAS NO.:1303-00-0
- Empirical Formula: AsGa
- Molecular Weight: 144.64
- MDL number: MFCD00011017
- EINECS: 215-114-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-13 14:48:16
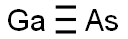
What is Gallium arsenide?
Chemical properties
Gallium arsenide contains 48.2% gallium and 51.8% arsenic and is considered an intermetallic compound. It occurs as cubic crystals with a dark gray metallic sheen. Gallium arsenide is electroluminescent in infrared light. Gallium arsenide readily reacts with oxygen in air, forming a mixture of oxides of gallium and arsenic on the crystal surface. Gallium arsenide presents the following properties: hardness, 4.5; thermal expansion coefficient, 5.9×106; thermal conductivity, 0.52Wunits; specific heat, 0.086 cal/g/ ℃; intrinsic electron concentration, 107; energy gap at room temperature, 1.38 eV; electron mobility, 8800 cm2/V/s; effective mass for electrons, 0.06m0; lattice constant,5.6–54 AO; dielectric constant, 11.1; intrinsic resistivity at 300K=3.7×108Ωcm; electron lattice mobility at 300K= 10,000 cm2/V/s; intrinsic charge density at 300K=1.4 106 cm-3; electron diffusion constant at 300K=310 cm2/s; and hole diffusion constant=11.5 cm2/s.

Garlic odor when moistened. Finely divided gallium arsenide can react vigorously with steam, energetic acids, and oxidizers to evolve arsine gas, and can release arsenic fumes when heated to decomposition. The molten form attacks quartz.
Physical properties
Gray cubic crystal; density 5.316 g/cm3; melts at 1,227°C; hardness 4.5 Mohs; lattice constant 5.653?; dielectric constant 11.1; resistivity (intrinsic) at 27°C, 3.7x108 ohm-cm.
The Uses of Gallium arsenide
In semiconductor applications (transistors, solar cells, lasers).Gallium arsenide is among the most widely used intermetallic semiconductor components (Harrison, 1986; McIntyr and Sherin, 1989). Gallium arsenide is also incorporated into light-emitting diodes and photovoltaic cells, while gallium alloys are used for dental amalgam as a low toxicity replacement for mercury.
The Uses of Gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide is electroluminscent in infrared light and is used for telephone equipment, lasers, solar cell, and other electronic devices. GaAs is used as the substrate of the infrared low-pass filter.
The Uses of Gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide, GaAs, is considered a possible substitute for silicon substrates, based on its potential for high speed applications where it can operate at high (1.9 GHz) frequencies using low power consumptions and high sensitivity. One reason that GaAs technology has not fulfilled its promise is that silicon technology has dramatically improved in the interim, particularly with improvements in speed, and has reduced the cost-effectiveness of pursuing GaAs development
Preparation
Gallium arsenide is prepared by passing a mixture of arsenic vapor and hydrogen over gallium(III) oxide heated at 600°C: Ga2O3 + 2As + 3H2 2GaAs + 3H2OThe molten material attacks quartz. Therefore, quartz boats coated with carbon by pyrolytic decomposition of methane should be used in refining the compound to obtain high purity material. Gallium arsenide is produced in polycrystalline form as high purity, single crystals for electronic applications. It is produced as ingots or alloys, combined with indium arsenide or gallium phosphide, for semiconductor applications.
Production Methods
Gallium (Ga) and arsenic (As), heated in a vacuum to eliminate oxygen, are filled in the silica boat
and the boat is vacuum-sealed in a silica tube. A single crystal is obtained by putting the silica tube
into the horizontal Stockbarger furnace with three zones: A (605℃), B (1250℃) and C (1100℃),
and by transporting the tube in the direction A→B→C with the speed of 2 cm/h. The Czochralski
method can also be used (refer to InAs).
The vapor phase method can be used to deposit the thin films. For instance, the GaAs single
crystal is grown on the low temperature area by heating the closed tube filled with GaAs together
with I2, Cl2, or HCl gas with a temperature gradient. Using this method, we can grow the
epitaxial layer.
General Description
Dark gray crystals with a metallic greenish-blue sheen or gray powder. Melting point 85.6°F (29.78°C).
Air & Water Reactions
Stable in dry air. Tarnishes in moist air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
GALLIUM ARSENIDE can react with steam, acids and acid fumes. Reacts with bases with evolution of hydrogen. Attacked by cold concentrated hydrochloric acid. Readily attacked by the halogens. The molten form attacks quartz.
Hazard
Toxic metal. Questionable carcinogen
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for GALLIUM ARSENIDE are not available; however, GALLIUM ARSENIDE is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. Mddly toxic by intraperitoneal route. Most arsenic compounds are poisons. Can react with steam, acids, and acid fumes to evolve the deadly poisonous arsine. Molten gallium arsenide attacks quartz. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of As. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS and GALLIUM COMPOUNDS.
Carcinogenicity
Carcinogenesis.
Gallium is antineoplastic in several
human and murine cancer cell lines and in some in vivo
cancers. It has been used experimentally in patients in the
treatment of lymphatic malignancies (including multiple
myelomas) and for urothelial malignancies. However,
the dissociation of gallium arsenide into gallium and arsenic
is a factor to take into account. A considerable number of
studies have evaluated the carcinogenic potential of arsenic
and various arsenic compounds.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of gallium arsenide (GaAs) belongs to the cubic system Td2, and its zincblende-type structure has a lattice constant of a=0.5654 nm and a distance to its nearest neighbor of 0.244 nm.
Properties of Gallium arsenide
| Melting point: | 1238°C |
| Density | 5.31 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | 3.57 |
| form | pieces |
| color | Dark gray |
| Specific Gravity | 5.31 |
| Resistivity | ≥1E7 Ω-cm |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in hydrochloric acid. Insoluble in water, ethanol, methanol and acetone. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m |
| Merck | 14,4347 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1303-00-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | (Vol. 86, 100C) 2012 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Gallium arsenide (1303-00-0) |
Safety information for Gallium arsenide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Gallium arsenide
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Gallium arsenide CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <111>, diam. × thickness 2” (50.8 mm) × 0.35 mm CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <111>, diam. × thickness 2” (50.8 mm) × 0.35 mm CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <100>, (undoped, 10 x 10 x 0.5 mm) CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <100>, (undoped, 10 x 10 x 0.5 mm) CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <001>, diam. × thickness 2” (50.8 mm) × 0.35 mm CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide (GaAs substrate), <001>, diam. × thickness 2” (50.8 mm) × 0.35 mm CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Gallium arsenide, 99.999% CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide, 99.999% CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Gallium arsenide CAS 1303-00-0View Details
Gallium arsenide CAS 1303-00-0View Details
1303-00-0 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
