Zinc sulfide
Synonym(s):Zinc sulfide;Zinc sulphide;Zinc(II) sulfide;ZN536010;ZN536100
- CAS NO.:1314-98-3
- Empirical Formula: SZn
- Molecular Weight: 97.46
- MDL number: MFCD00011301
- EINECS: 215-251-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:18
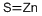
What is Zinc sulfide?
Description
Zinc sulfide (ZnS), a naturally occurring salt, is the main source of zinc. It has two common crystalline forms (polymorphs): Sphalerite (“zinc blende”), with a cubic crystal structure, is the form that predominates in nature. Wurtzite, with hexagonal crystals, is scarcer, but it can be made by heating sphalerite to ≈1020 oC.1
In nature, both ZnS polymorphs usually contain significant amounts of iron that makes them appear black. The purified salts are white-to-pale yellow or gray. The most common use of ZnS is as a pigment for paints, plastics, and rubber. Lithopone, a mixture of ZnS and barium sulfate (BaSO4), is a widely used pigment for low-gloss paints.
ZnS is phosphorescent, which makes it useful for several electronic and decorative applications. Among its earlier uses were X-ray and television screens and clock and watch dials. In this age of nanotechnology, ZnS frequently forms the shells of semiconductor quantum dots, with cadmium selenide (CdSe) as the cores.
Phosphorescent, nontoxic ZnS makes it ideal for use in “glow-in-the-dark” cosmetics. The US Food and Drug Administration approved it for this use in 2000. According to FDA, “It’s the only luminescent color approved for cosmetic use, and it’s not for every day and not for near your eyes. You can recognize it by its whitish-yellowish-greenish glow.”
This Halloween you can thank ZnS for allowing you scare people when you wear your ghoulish, glowing face paint.
1. In the images, the zinc atoms are purple; the sulfur atoms are yellow.
Chemical properties
Yellowish-white powder. ZnS exists in two crystalline forms, α (wurtzite) and β (sphalerite). Stable if kept dry. α: d 3.98. β: d 4.102, changes to α form at 1020C. Sublimes at 1180C. Soluble in acids; insoluble in water.
The Uses of Zinc sulfide
Pigment for paints, oilcloths, linoleum, leather, dental rubber, etc., especially in the form of lithopone; mixed with ZnO as "mineral white." Anhydrous zinc sulfide is used in x-ray screens and with a trace of a radium or mesothorium salt in luminous dials of watches; also television screens.
The Uses of Zinc sulfide
Zinc sulfide (ZnS) is used as a pigment and to make white glass, rubber, and plastics. It is an ingredient in pesticides, luminous paints, and X-ray and television screens.
The Uses of Zinc sulfide
Zinc Sulfide is used as a friction material to carry sulfur, which hardens rotor surfaces and thereby reduces wear. Also in printing inks, UV-hardened systems, powder coatings, adhesives, insulating & sealing compounds, thermoplastic pigmentation, thermosets, flame resistant plastics, glass-fiber reinforced plastics, pigment concentrates, elastomers,. textile fibers, paper, mastics, lubricants, electroluminescent lamps, infrared windows, domes and optical elements.
Definition
zinc sulphide: A yellow-whitewater-soluble solid, ZnS. It occursnaturally as sphalerite (see also zincblende) and wurtzite. The compoundsublimes at 1180°C. It is used as apigment and phosphor.
Production Methods
Production is similar to that of lithopone. A Na2S solution is mixed with a zinc salt solution under precisely controlled conditions. The resulting zinc sulfide precipitate is calcined and processed to give the finished product. Na2S + ZnSO4 →ZnS + Na2SO4.
General Description
A yellowish-white powder in a liquid. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Primary hazard is to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Easily penetrates the soil to contaminate groundwater and nearby waterways.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
These sulfides are rather inert, dissolve into acid, insoluble in water and alkalis.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of material may be harmful. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Inhalation of Asbestos dust may have a damaging effect on the lungs. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Some liquids produce vapors that may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Some may burn but none ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Some may be transported hot.
Industrial uses
Zinc sulfide(Sachtolith) is mainly used in plastics. Functional properties such as lightening and hiding power are criteria for the use of Sachtolith. It has proved to be very useful for coloring many thermoplasts. During the dispersion process it does not cause abrasion of metallic production machinery or adversely effect the polymer, even at high operating temperatures or during multistage processing. Even ultrahigh molecular mass thermoplasts can be colored without problems. In glass-fiber-reinforced plastics, the soft texture of Sachtolith prevents mechanical fiber damage during extrusion. Sachtolith is also used as a dry lubricant during the fabrication of these materials.
The low abrasiveness of Sachtolith prolongs the operating life of stamping tools used in the manufacture of industrial rubber articles. The lightfastness and ageing resistance of many elastomers are improved by using Sachtolith. It is also used as a dry lubricant for roller and plain bearings, and as a white pigment for greases and oils.
Toxicology
The use of zinc sulfide and barium sulfate in contact with foods is permitted by the FDA (United States) and in most European countries. Some restrictions apply in France, Italy, the United Kingdom, and Czechoslovakia.
Soluble zinc is toxic in large amounts, but the human body requires small quantities (10–15 mg d−1) for metabolism. Zinc sulfide is harmless in the human due to its low solubility. The acid concentration in the stomach and the rate of dissolution following ingestion are not sufficient to produce physiologically significant quantities of soluble zinc. LD50 values in the rat exceed 15 g kg−1. No cases of poisoning or chronic damage to health have been observed in the manufacture of zinc sulfide pigments.
Properties of Zinc sulfide
| Melting point: | 1700°C |
| Boiling point: | 1185°C (estimate) |
| Density | 4.1 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | 6.5–6.9 mg/la |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in dilute acid |
| form | powder |
| appearance | white, grayish-white, or yellow crystals or powder |
| color | white to faint yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 4.1 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in acids. insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,10160 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: α-ZnS 23.80;β-ZnS 21.60 |
| Dielectric constant | 1.7(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. May react with water to give toxic hydrogen sulfide. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. Air and moisture sensitive. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/S.Zn |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-98-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Zinc sulfide (1314-98-3) |
Safety information for Zinc sulfide
Computed Descriptors for Zinc sulfide
| InChIKey | WGPCGCOKHWGKJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | S=[Zn] |
Zinc sulfide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Zinc sulfide CAS 1314-98-3View Details
Zinc sulfide CAS 1314-98-3View Details
1314-98-3 -
 Zinc sulfide CAS 1314-98-3View Details
Zinc sulfide CAS 1314-98-3View Details
1314-98-3 -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfide CASView Details
Zinc sulfide CASView Details
