CADMIUM TELLURIDE
Synonym(s):Cadmium monotelluride
- CAS NO.:1306-25-8
- Empirical Formula: CdTe
- Molecular Weight: 240.01
- MDL number: MFCD00015998
- EINECS: 215-149-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
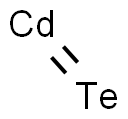
What is CADMIUM TELLURIDE?
Chemical properties
Brownish-black, cubic crystals.Oxidizes on prolonged expo- sure to moist air. Insoluble in water and mineral acids except nitric, in which it is soluble with decomposition.
Physical properties
Ladd investigated the temperature dependence of transmittance in the infrared region. As a result, transmittance in wavelength longer than 22 mm decreases as the temperature increases.
In the transmission spectra, weak absorption bands are observed in addition to the main absorption in λ: 60–70 mm.
The reflectance peaks in the infrared region are at 67 mm (300 K) and 65 mm (90 K)
The Uses of CADMIUM TELLURIDE
Cadmium telluride finds applications as the semiconductor material in photovoltaics and infrared optical window. It is used in the production of thin film solar cells. It is doped with chlorine and used as a radiation detector for x-rays, alfa and beta particles. .
The Uses of CADMIUM TELLURIDE
In semiconductor research, in phosphors.
The Uses of CADMIUM TELLURIDE
Cadmium telluride may be used in photovoltaic solar cells as the window layer. CdTe was used in the preparation of an Au/Cu2Te/CdTe/CdS/TCO/glass heterostructure for solar cell.
Production Methods
A single crystal of cadmium telluride is grown by many methods. In the case of vapor growth, the methods include flowing a carrier gas or condensing CdTe vapor on a low temperature area. In the case of growth from melt, pulling down a quartz ampoule encapsulated with CdTe at the speed of 10 mm/h in the Stockbarger furnace is the easiest method. The temperature difference of 50℃–60℃ between the upper furnace and lower furnace is appropriate. The traveling method performed in the horizontal Stockbarger furnace is another method. Zone refining is done vertically, while encapsulated in the quartz tube. Processing is possible in the same way as Ge and Si. The material made by pressing cadmium telluride powder is called Irtran-6.
Thin films are deposited by vacuum evaporation using a conical basket heater made of Ta or W, or by direct heating in a boat. The substrate temperature is heated at 250℃ for a glass and 20℃–380℃ for a mica.
What are the applications of Application
Cadmium telluride is used as the substrate of low-pass filters and as the infrared transmitting window with antireflection coating.
General Description
CdTe is a photonic material. Crystal structure of CdTe is zinc blende structure. 3CdTe is usually an obvious choice for photovoltaic applications because of its; low cost, direct band gap (1.44eV),3 high absorption coefficient, easily doped with p and n type dopants by several preparation techniques. 2
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of CdTe (Cadmium telluride) belongs to the cubic system, and the zinc-blend type structure has a lattice constant of a=0.646 nm and the nearest neighbor atomic distance of 0.279 nm. The cleavage plane is (110).
Properties of CADMIUM TELLURIDE
| Melting point: | 1092 °C |
| Density | 6.2 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 2.75 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, dilute acid solutions |
| form | crystalline |
| color | Black |
| Specific Gravity | 6.2 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal, Wurtzite (Zincite) Structure - Space Group P 63mc |
| Merck | 14,1629 |
| Boiling point: | 1130°C |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3; TWA 0.002 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 9 mg/m3; IDLH 25 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1306-25-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cadmium telluride (CdTe) (1306-25-8) |
Safety information for CADMIUM TELLURIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for CADMIUM TELLURIDE
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride, 99.999% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride, 99.999% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride, 99.99% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride, 99.99% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium Telluride ultrapure CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium Telluride ultrapure CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8 -
 Cadmium telluride pieces, 1-12 mm, 99.9999% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
Cadmium telluride pieces, 1-12 mm, 99.9999% CAS 1306-25-8View Details
1306-25-8
