Fenthion
Synonym(s):O,O′-Dimethyl O″-[3-methyl-4-(methylthio)phenyl] thiophosphate
- CAS NO.:55-38-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H15O3PS2
- Molecular Weight: 278.33
- MDL number: MFCD00055449
- EINECS: 200-231-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-14 15:18:25
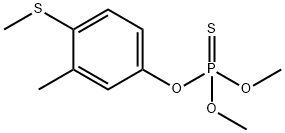
What is Fenthion?
Description
Fenthion is a colorless oily liquid (technical grade, brown oily liquid with a mercaptan-like odor).
Chemical properties
yellow brown oily liquid
Chemical properties
Pure fenthion is a colorless liquid. Technical fenthion is a yellow or brown oily liquid with a weak garlic odor. It is insoluble or very sparingly soluble in water, but soluble in all organic solvents, alcohols, ethers, esters, halogenated aromatics, and petroleum ethers. It is grouped by the US EPA under RUP and hence requires handling by qualifi ed, certifi ed, and trained workers. Fenthion is used for the control of sucking and biting pests, i.e., fruit fl ies, stem borers, mosquitoes, and cereal bugs. In mosquitoes, it is toxic to both the adult and immature forms (larvae). The formulations of fenthion include dust, emulsifi able concentrate, granular, liquid concentrate, spray concentrate, ULV, and wettable powder.
Chemical properties
Fenthion is a colorless liquid (when pure) with a weak, garlic-like odor. The technical grade is a yellow-to-brown oil.
The Uses of Fenthion
Fenthion is an organothiophosphate used as an insecticide. Fenthion is also a potent acaricide.
The Uses of Fenthion
antihypertensive
The Uses of Fenthion
Insecticide; acaricide.
The Uses of Fenthion
Insecticide for control of fruit ?ies, leaf hoppers and cereal bugs. Fenthion is also used as an acaracide.
What are the applications of Application
Fenthion is an organothiophosphate used as an insecticide
Definition
ChEBI: An organic thiophosphate that is O,O-dimethyl hydrogen phosphorothioate in which the hydrogen atom of the hydroxy group is replaced by a 3-methyl-4-(methylsulfanyl)phenyl group. It exhibits acaricidal and insecticidal activities.
General Description
Yellow to tan oily liquid with a slight odor of garlic.
Reactivity Profile
Fenthion may react with strong reducing agents such as hydrides to generate highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption; use may be restricted, cholinesterase inhibitor. Toxic by skin absorption; questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Fenthion is moderately toxic to mammals, and highly toxic to birds. Exposures to fenthion cause poisoning with symptoms among occupational workers as observed with organophosphate pesticide-induced toxicity. These include, but are not limited to, numbness, tingling sensations, incoordination, headache, dizziness, tremor, nausea, abdominal cramps, sweating, blurred vision, diffi culty breathing or respiratory depression, and slow heart beat. Very high doses may result in unconsciousness, incontinence, and convulsions or fatality. Reports have indicated that exposures to fenthion cause adverse effects on the central and peripheral nervous systems, and the heart of exposed workers.
Fire Hazard
Fenthion is probably combustible.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Larvicide, Veterinary medicine: Not registered for use in the U.S. Not approved for use in EU countries. Used in 20 countries including Australia. There are 23 global suppliers.
Trade name
B 29493®; BACID®; BAY 29493®; BAYCID®; BAYER 29493®; BAYER 9007®; BAYER S-1752®; BAYTEX®; ENTEX®; LEBAYCID®; MPP®; MPP (pesticide) OMS 2®; PHENTHION®; PILARTEX®; QUELETOX®; S 1752®; SPOTTON®; SULFIDOPHOS®; TALODEX®; TIGUVON®
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, or application of this agricultural chemical and pesticide; insecticide
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Ifexposure and/or symptoms have occurred, the person shouldbe under medical observation for several days, as somesymptoms may be delayed.
Environmental Fate
Biological. From the first-order biotic and abiotic rate constants of fenthion in estuarine water and sediment/water systems, the estimated biodegradation half-lives were 22.4 and 3.9–14.5 days, respectively (Walker et al., 1988).
Surface Water. In estuarine water, the half-life of fenthion was 4.6 days (Lacorte et al., 1995).
Plant. In plants, fenthion oxidizes to the mesulfenfos and sulfone which further degrades to the sulfone phosphate before undergoing hydrolysis (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Photolytic. Fenthion was oxidized to the corresponding sulfoxide and trace amounts (<5% yield) of sulfone when sorbed on soil and exposed to sunlight. The photosensitized oxidation was probably due to the presence of singlet oxygen. The degradation rate was higher in soils containing the lowest organic carbon (Gohre and Miller, 1986).
Chemical/Physical. Stable at temperatures below 210°C (Worthing and Hance, 1991). Emits very toxic fumes of phosphorus and sulfur oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987; Lewis, 1990).
Metabolic pathway
The major route of fenthion metabolism is by oxidation to the sulfoxide which has a higher insecticidal activity than the parent compound. The subsequent oxidation of the sulfoxide to fenthion sulfone, the biological activity of which is considerably lower, is slow in plants but of major significance in animals. An additional route of bioactivation is through oxidative desulfuration to form fenoxon and, in all, five oxidative metabolites (fenthion sulfoxide, fenthon sulfone, fenoxon, fenoxon sulfoxide and fenoxon sulfone) have been detected in most biological systems. Hydrolysis, in contrast to most insecticidal phosphorothioates, appears to proceed via direct hydrolysis of fenthion rather than its oxon. The phenolic leaving group (3-methyl-4-thiomethylphenol) is identical to that of fenamiphos and although no studies have described the fate of the phenolic moiety for fenthion, it is likely that it will be metabolised by similar routes to those described for fenamiphos.
storage
: Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from oxidizers, alkalies and alkalinepesticides. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Fenthion is stable in light, stable to acid and moderately stable to alkaline
conditions. The DT50s at pH 4, 7 and 9 were 223, 151 and 151 days
respectively (PM).
The effect of the cuticular waxes of fruit upon the photodegradation of
fenthion was studied by Cabras et al. (1997). Waxes were extracted with
acetone and the fenthion added to the solution. The wax plus fenthion
was applied as a film which was irradiated by natural sunlight. The
analysis of fenthion and its metabolites was by GLC-FID (Cabras and
Plumitallo, 1991). The potential metabolites synthesised were fenthion
sulfoxide (2), fenthion sulfone (3), fenoxon (4), fenoxon sulfoxide (5) and
fenoxon sulfone (6). Waxes from different fruits affected the decay rate,
with wax from oranges and nectarines increasing the rate of decomposition
but cuticular wax from olives retarding the rate. In all cases the
products of photodegradation were fentluon sulfoxide (2), which
steadily increased with time, and fenthion sulfone (3), which remained at
a low but detectable level throughout the experiment. Minelli et al. (1996)
exposed fenthion in glass jars to natural sunlight and analysed the photodegradation
products by GLC-FID. The major product was fenthion
sulfoxide (2) which very slowly degraded to the sulfone (3). This in turn
was even more slowly photo-oxidised to fenoxon sulfone (6). The routes
for the photodegradation of fenthion are shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for rats: ca. 250 mg /kg
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, alkaline insecticides. Organothiophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Waste Disposal
Hydrolysis and landfill for small quantities; incineration with flue gas scrubbing for large amounts. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office
Properties of Fenthion
| Melting point: | 7.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 87°C (0.01 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.25 |
| vapor pressure | 7.4 x 10-4 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.5698 |
| Flash point: | >100 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Sparingly) |
| form | liquid |
| Water Solubility | 0.0055 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 13,4030 |
| BRN | 1974129 |
| Exposure limits | OSHA PEL: TWA 0.2 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 55-38-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Fenthion(55-38-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenthion (55-38-9) |
Safety information for Fenthion
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Fenthion
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4