N,N-Dimethylformamide
Synonym(s):DMF;DMF, N,N-Dimethylmethanamide, Formic acid dimethylamide;Formic Acid Dimethylamide, DMF;Formic Acid Dimethylamide, FM approval;N,N-Dimethylformamide
- CAS NO.:68-12-2
- Empirical Formula: C3H7NO
- Molecular Weight: 73.09
- MDL number: MFCD00003284
- EINECS: 200-679-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
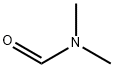
What is N,N-Dimethylformamide?
Description
N,N-dimethylformamide also called DMF, is a flammable, colorless liquid. It is a valuable solvent in organic chemical reactions because of its polarity and low evaporation rate. Dimethylformamide has powerful solvent properties for a wide range of organic compounds. It finds particular usage in themanufacture of polyacrylic fibers, butadiene, purified acetylene, pharmaceuticals, dyes, petroleum products, and otherorganic chemicals.
Chemical properties
N,N-Dimethylformamide is a colorless or slightly yellow liquid with a boiling point of 153°C and a vapor pressure of 380 Pa at 20°C. It is freely soluble in water and soluble in alcohols, acetone and benzene. N,N-Dimethylformamide is used as solvent, catalyst and gas absorbent. React violently with concentrated sulfuric acid, fuming nitric acid and can even explode. Pure Dimethylformamide is odorless, but industrial grade or modified Dimethylformamide has a fishy smell because it contains impurities of Dimethylamine. Dimethylformamide is unstable (especially at high temperatures) in the presence of a strong base such as sodium hydroxide or a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid, and is hydrolyzed to formic acid and dimethylamine.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless to light yellow, hygroscopic, mobile liquid with a faint, characteristic, ammonialike odor. An experimentally determined odor threshold concentration of 100 ppmv was reported by Leonardos et al. (1969).
The Uses of N,N-Dimethylformamide
N,N-Dimethylformamide has been widely used in industries as a solvent, an additive, or an intermediate because of its extensive miscibility with water and most common organic solvents.
Dimethylformamide solutions are used toprocess polymer fibers, films, and surface coatings; to permit easy spinning of acrylic fibers; to produce wire enamels, and as a crystallization medium in the pharmaceutical industry.
DMF can also be used for formylation with alkyllithium or Grignard reagents. It is used as a reagent in Bouveault aldehyde synthesis and also in Vilsmeier-Haack reaction. It acts as a catalyst in the synthesis of acyl chlorides.
Definition
ChEBI: N,N-dimethylformamide is a member of the class of formamides that is formamide in which the amino hydrogens are replaced by methyl groups. It has a role as a polar aprotic solvent, a hepatotoxic agent and a geroprotector. It is a volatile organic compound and a member of formamides. It is functionally related to a formamide.
Production Methods
Industrial production of N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) is via three separate processes (Eberling 1980). Dimethylamine in methanol is reacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of sodium methoxide or metal carbonyls at 110-150°C and high pressure. Alternately, methyl formate is produced from carbon monoxide and methanol under high pressure at 60-100°C in the presence of sodium methoxide. The resulting methyl formate is distilled and then reacted with dimethylamine at 80-100°C and low pressure. The third process involves reaction of carbon dioxide, hydrogen and dimethylamine in the presence of halogen-containing transition metal compounds to yield DMF.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
N,N-Dimethylformamide may react violently with a broad range of chemicals, e.g.: alkaline metals (sodium, potassium), azides, hydrides (sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride), bromine, chlorine, carbon tetrachloride, hexachlorocyclohexane, phosphorus pentaoxide, triethylaluminum, magnesium nitrate, organic nitrates. Forms explosive mixtures with lithium azide [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 453]. Oxidation by chromium trioxide or potassium permanganate may lead to explosion [Pal B. C. et al., Chem. Eng. News, 1981, 59, p. 47].
Health Hazard
The acute toxicity of DMF is low by inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. Contact with liquid DMF may cause eye and skin irritation. DMF is an excellent solvent for many toxic materials that are not ordinarily absorbed and can increase the hazard of these substances by skin contact. Exposure to high concentrations of DMF may lead to liver damage and other systemic effects. Dimethylformamide is listed by IARC in Group 2B ("possible human carcinogen"). It is not classified as a "select carcinogen" according to the criteria of the OSHA Laboratory Standard. No significant reproductive effects have been observed in animal tests. Repeated exposure to DMF may result in damage to the liver, kidneys, and cardiovascular system
Flammability and Explosibility
DMF is a combustible liquid (NFPA rating = 2). Vapors are heavier than air and may travel to source of ignition and flash back. DMF vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 2.2 to 15.2% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight DMF fires.
Industrial uses
World production capacity of DMF is about 225 x 103 tons per year. The main application of DMF is as solvent in industrial processes, especially for polar polymers such as Polyvinylchloride, polyacrylonitrile and polyurethanes. DMF solutions of high molecular weight polymers are processed to fibers, films, surface coatings and synthetic leathers. Since salts can be dissolved and dissociated in DMF, the solutions are used in electrolytic capacitors and certain electrolytic processes (Eberling 1980).
Contact allergens
This is an organic solvent for vinyl resins and acetylene, butadiene, and acid gases. It caused contact dermatitis in a technician at an epoxy resin factory and can provoke alcohol-induced flushing in exposed subjects.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit
Carcinogenicity
DMF is not carcinogenic to animals except under very high inhalation exposure conditions. No increase in tumors was seen in rats that inhaled 25, 100, or 400 ppm for 6 h/day, 5 days/week for 2 years. Similarly, no tumors were produced in mice under the same conditions for 18 months. In that chronic experiment, rats and mice were exposed by inhalation (6 h/day, 5 days/week) to 0, 25, 100, or 400 ppm DMF for 18 months (mice) or 2 years (rats). Body weights of rats exposed to 100 (males only) and 400 ppm were reduced and, conversely, body weights were increased in 400 ppm mice. Serum sorbitol dehydrogenase activity was increased in rats exposed to 100 or 400 ppm. DMF-related morphological changes in rats were observed only in the liver and consisted of increased relative liver weights, centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy, lipofuscin/hemosiderin accumulation in Kupffer cells, and centrilobular single cell necrosis (400 ppm only). The same liver effects were seen in all groups of mice, although the response at 25 ppm was judged as minimal.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Incubation of [14C]N,N-dimethylformamide (0.1–100 μg/L) in natural seawater
resulted in the compound mineralizing to carbon dioxide. The rate of carbon dioxide formation
was inversely proportional to the initial concentration (Ursin, 1985).
Chemical. Reacts with acids or bases forming formic acid and dimethylamine (BASF, 1999)
Toxicity
The acute LD50 (oral, rats and mice) is 2.2–7.55 g/kg.Hazards of DMF have been examined.
Metabolic pathway
Three urinary metabolites are identified in humans and rodents, and the metabolites quantified are N- (hydroxymethyl)-N-methylformamide (HMMF), resulting in N-methylformamide (NMF) and N-acetyl-S-(N- methylcarbamoyl)cysteine (AMCC). Ten volunteers who absorb between 28 and 60 mmol/kg DMF during an 8 h exposure to DMF in air at 6 mg=m3 excrete in the urine within 72 h between 16.1 and 48.7% of the dose as HMMF, between 8.3 and 23.9% as formamide, and between 9.7 and 22.8% as AMCC. AMCC together with HMMF is also detected in the urine of workers after occupational exposure to DMF. There is a quantitative difference between the metabolic pathway of DMF to AMCC in humans and rodents.
Storage
DMF should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.
Incompatibilities
Though stable at normal temperatures and storage conditions, DMF may react violently with halogens, acyl halides, strong oxidizers, and polyhalogenated compounds in the presence of iron. Decomposition products include toxic gases and vapors such as dimethylamine and carbon monoxide. DMF will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Excess DMF and waste material containing this substance should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines.
Properties of N,N-Dimethylformamide
| Melting point: | -61 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 153 °C (lit.) |
| alpha | 0.94 º |
| Density | 0.944 g/mL (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 2.7 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 136 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | water: miscible |
| form | liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | -0.44±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | APHA: ≤15 |
| Odor | Faint, ammonia-like odor detectable at 100 ppm |
| Relative polarity | 0.386 |
| PH | 7 (200g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 2.2-16%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 1.8ppm |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 275 nm Amax: 0.30 λ: 295 nm Amax: 0.10 λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 340-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,3243 |
| BRN | 605365 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3), IDLH 500 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 10
ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 36.710000000000001 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 68-12-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 47, 71, 115) 2018 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Formamide, N,N-dimethyl-(68-12-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N,N-Dimethylformamide (68-12-2) |
Safety information for N,N-Dimethylformamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for N,N-Dimethylformamide
| InChIKey | ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
N,N-Dimethylformamide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
C.H. Chemicals
Manav Biochem Impex Private Limited
Fine Chemicals & Solvents
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Dimethylformamide 99%View Details
Dimethylformamide 99%View Details -
 N,N-Dimethylformamide 99%View Details
N,N-Dimethylformamide 99%View Details -
 NN-DIMETHYLFORMAMIDE 99%View Details
NN-DIMETHYLFORMAMIDE 99%View Details -
 N,N-Dimethylformamide, HPLC Grade 99%View Details
N,N-Dimethylformamide, HPLC Grade 99%View Details -
 N,N-Dimethylformamide, 99% 99%View Details
N,N-Dimethylformamide, 99% 99%View Details -
 DMF CASView Details
DMF CASView Details -
 Dimethyl Formamide CASView Details
Dimethyl Formamide CASView Details -
 DMF CASView Details
DMF CASView Details
