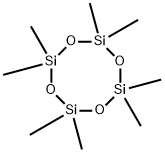
Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Synonym(s):Polydimethylsiloxane;Dimethylpolysiloxane;Octamethyltrisiloxane;α-(Trimethylsilyl)-ω-methylpoly[oxy(dimethylsilylene)] mixture with silicon dioxide;Antifoam A
- CAS NO.:9016-00-6
- Empirical Formula: (C2H6OSi)n
- Molecular Weight: 94.18664
- MDL number: MFCD00148360
- EINECS: 618-493-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-27 17:16:38
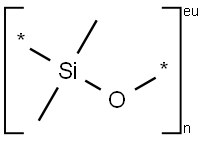
What is Poly(dimethylsiloxane)?
Description
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is the simplest member of the silicone polymer family. It is formed by hydrolyzing Me2SiCl2, which is produced from high-purity SiO2?and CH2Cl2?by the Muller–Rochow reaction. The term “silicone” was coined by chemist F. S. Kipping in 1901.
Low–molecular weight PDMS is a liquid used in lubricants, antifoaming agents, and hydraulic fluids. Its use in breast implants is not as popular as it once was because of safety concerns.
At higher molecular weights, PDMS is a soft, compliant rubber or resin. It is used in caulks, sealants, an even Silly Putty. More recently, PDMS resins have been used in soft lithography, a key process in biomedical microelectromechanical systems (bio-MEMS).
Chemical properties
colourless liquid with a viscosity, The polydimethylsiloxane materials are excellent examples of silicones because of their chemical properties and widespread industrial use. They can be manufactured as gels, resins, fluids, or elastomers, depending on the cross-linking characteristics. Toxicity testing using polydimethylsiloxane compounds on animals has found little, if any, harmful effects associated with chronic exposure. These tests include oral dosing and teratogenicity testing (Cutler et al., 1974; Kennedy et al., 1976). Human health effects associated with silicone implants have been reported. Polydimethylsiloxane is the most prevalent silicone used medically and has been incorporated into many prostheses, including breast implants.
The Uses of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) is an antifoaming agent used in fats and oils. It prevents foaming and spattering when oils are heated and prevents foam formation during the manufacture of wine, refined sugar, gelatin, and chewing gum. It is also termed methyl polysilicone and methyl silicone.
The Uses of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Antiflatulent.
The Uses of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Silicones are polymeric materials having silicon and oxygen on their composition. They are largely inert compounds usually heat-resistant, nonstick, and rubberlike. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS, molecular formula (C2H6OSi)n, density 965 kg/m3, boiling point: < 200℃, shear modulus between 100 kPa and 3 MPa, loss tangent less than 0.001) is a viscoelastic polymer (elastomer). PDMS is widely used in microfluidic technology thanks to some of its unique properties: it is low cost, nontoxic, chemically resistant, and stable against humidity and temperature variations. PDMS also presents low interfacial energy, which allows it to avoid chemical interactions with other polymers and solutions in the microfluidic channels. After polymerization and cross-linking, solid PDMS presents hydrophobic surface. A treatment using plasma oxidation is frequently used to alter the surface chemistry by adding silanol (SiOH) groups to the surface terminations and make the surface hydrophilic (wettable). PDMS is usually used as sealant, structural microchannel material or elastomer stamping matrix in soft lithography techniques like microcontact printing and micromolding.
brand name
Gas-X (Novartis); Mylanta Gas Relief (Johnson & Johnson-Merck Consumer); Mylicon Infant’s Drops (Johnson & Johnson-Merck Consumer); Sentry Simethicone (Witco); Sentry Simethicone Emulsion (Witco).
General Description
Colorless odorless liquid, Floats on water.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) is a weak reducing agent.
Health Hazard
Contact of liquid with eyes may cause temporary discomfort. Does not irritate skin. Harmless when ingested.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Simethicone is a mixture of poly(dimethyl siloxane) and silica gel, known for their antifoaming properties. It is an orally administered suspension containing polysiloxanes and silicon dioxide. It is an antifoaming agent and is used to reduce bloating by decreasing the surface tension in bubbles. Excessive formation of gas bubbles in the stomach and intestines can be painful and can also be of hindrance for any ultrasound examination. Simethicone can be found in antacids and in suspensions given to babies against colic.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Dimethylpolysiloxane is a silicon-based organic polymer, inert and non-toxic. It is applicable in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industry. Dimethylpolysiloxane is excreted unchanged unaltered in the faeces and is non-mutagenic.
Properties of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
| Melting point: | -35°C |
| Boiling point: | 155-220°C |
| Density | 0.971 |
| vapor pressure | 5 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4035 |
| Flash point: | 63°C |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Viscous Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.918 |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable or combustible. Flammability depends upon extent of polymerization. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Poly[oxy(dimethylsilylene)] (9016-00-6) |
Safety information for Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H227:Flammable liquids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Simethicone 99%View Details
Simethicone 99%View Details -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 17,000 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 17,000 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 17,000 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 17,000 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 237 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 770 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 770 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6 -
 Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 770 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
Polydimethylsiloxane, trimethylsiloxy terminated, M.W. 770 CAS 9016-00-6View Details
9016-00-6
