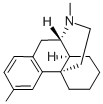
Dimemorfan phosphate
- CAS NO.:36304-84-4
- Empirical Formula: C18H25N.H3O4P
- Molecular Weight: 353.396
- MDL number: MFCD01714607
- EINECS: 252-958-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33

What is Dimemorfan phosphate?
Originator
Astomin,Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of 1-p-methylbenzyl-1,2,5,6,7,8-hexahydroisoquinoline:
a) To a suspension of 2.24 g of a metallic magnesium in 36 ml of an 1:1
mixture of tetrahydrofuran and ether was added dropwise a solution of 13.5 g of p-methylbenzyl chloride in 36 ml of an 1:1 mixture of tetrahydrofuran and
ether over a period of about 30 min and then the resultant mixture was
refluxed under heating for 30 min. The solution thus obtained was added
dropwise to a suspension of 17.5 g of 2-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinoline
bromide in 90 ml of an 1:1 mixture of tetrahydrofuran and ether cooled to 0-
5°C over a period of about 25 min. After stirring the mixture for 2 hours at
temperatures of from 0-5°C, 100 ml of cooled ether and 1.7 N ammonia were
added to the reaction product liquid and after shaking sufficiently the system,
the ether layer thus formed was recovered. The product in the aqueous layer
was further extracted with 50 ml of ether. The ether extract was combined
with the ether layer recovered above and then the product in the mixture was
extracted 4-times with 30 ml each of 1 N hydrochloric acid cooled. To the
hydrochloric acid extract was added 100 ml of cooled 1.7 N ammonia, and the
oily material formed was extracted thrice with 80 ml each of ether. After
drying the ether extract over anhydrous potassium carbonate, ether was
distilled away to provide 15.4 g of oily 1-p-methylbenzyl-1,2,5,6,7,8-
hexahydroisoquinoline.
b) In a mixture of 300 ml of methanol and 30 ml of water were dissolved 15.4
g of oily 1-p-methylbenzyl-2-methyl-1,2,5,6,7,8-hexahydroisoquinoline and
while stirring the mixture, 2 g of sodium borohydride was added little by little
to the mixture at room temperature over a period of about 15 min. After
stirring the light yellow solution obtained overnight at room temperature, the
solvent was distilled away under a reduced pressure. The residue was mixed
with 50 ml of water and 150 ml of ether and after sufficiently shaking the
mixture, the ether layer formed was separated. The aqueous layer thus
separated was adjusted to basicity by the addition of a small amount of 1.7 N
ammonia and then the product in the layer was extracted with 100 ml of
ether. The ether layer separated above was combined with the ether extract
and after washing the mixture with 1.7 N ammonia and water, the mixture
was dried over anhydrous potassium carbonate and then ether was distilled
away to provide 13.8 g of an orange oily material. By subjecting the product
to a distillation under a reduced pressure, oily D-1-p-methylbenzyl-2-methyl1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroisoquinoline was obtained. Boiling point 133-
136°C/0.35 mm Hg.
Preparation of D-3-methyl-N-methylmorphinane:
To 130 ml of 85% phosphoric acid was added 26.5 g of D-1-p-methylbenzyl2-methyl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroisoquinoline and the mixture was heated to
130-140°C for 72 hours. After the reaction was over, the reaction product
liquid was dispersed in ice-water and the solution was made strongly alkaline
by the addition of about 300 ml of concentrated aqueous ammonia, whereby
an oily material and a crystal were formed. The aqueous solution was mixed
with 500 ml of water and 500 ml of ether followed by sufficient shaking;
thereafter, the aqueous layer and the ether layer were separated. The
aqueous layer was extracted with 500 ml of ether and the extract was
combined with the ether layer separated above. Black resinous material
floating in the mixture was filtered away. After washing with water the ether
solution thus obtained and drying over anhydrous potassium carbonate, 14 g
of a black-orange oily material was obtained. When the oily material was
immediately distilled under a reduced pressure, 11 g of a faint yellow
transparent oily material showing a boiling point of 130-136°C/ 0.3 mm Hg
was obtained. The product was crystallized immediately after distillation. The crystals were recrystallized from 12 ml of acetone, recovered by filtration, and
washed with 7 ml of acetone to provide 7.3 g of the white prism crystal of D3-methyl-N-methylmorphinane. Furthermore, from the filtrate in the
recrystallization were recovered the same crystals. Melting point 90-93°C,
[α]D22 = +51.5° (c=1, methanol).
Therapeutic Function
Antitussive
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Used as an antitussive agent. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and POx.
Properties of Dimemorfan phosphate
| Melting point: | 267-269° |
| alpha | D23 +25.7° (c = 0.5 in methanol) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Water : 20 mg/mL (56.59 mM);DMSO : 1 mg/mL (2.83 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Dimemorfan phosphate
Computed Descriptors for Dimemorfan phosphate
Dimemorfan phosphate manufacturer
Nuray Chemicals Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Dimemorfan phosphate 98%View Details
Dimemorfan phosphate 98%View Details -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1