Dimethyl sulfate
Synonym(s):Sulfuric acid dimethyl ester
- CAS NO.:77-78-1
- Empirical Formula: C2H6O4S
- Molecular Weight: 126.13
- MDL number: MFCD00008416
- EINECS: 201-058-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
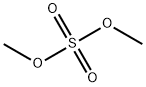
What is Dimethyl sulfate?
Description
Dimethyl sulfate is a colorless, oily liquid with a faint, onionlike
odor. It is soluble in water, ether, dioxane, acetone,
benzene, and other aromatic hydrocarbons, miscible with
ethanol, and sparingly soluble in carbon disulfide. It is stable
under normal temperatures and pressures, but hydrolyzes
rapidly in water at or above 18 ℃.
Dimethyl sulfate has been produced commercially since at
least the 1920s. One production method is continuous reaction
of dimethyl ether with sulfur trioxide. In 2009, dimethyl sulfate
was produced by 33 manufacturers worldwide, including 1 in
the United States, 14 in China, 5 in India, 5 in Europe, 6 in East
Asia, and 2 in Mexico, and was available from 44 suppliers,
including 16 US suppliers. There are no data on US imports or
exports of dimethyl sulfate. Reports filed from 1986 through
2002 under the US Environmental Protection Agency’s Toxic
Substances Control Act Inventory Update Rule indicate that US
production plus imports of dimethyl sulfate totaled 10–50
million pounds. The simplest way of synthesizing dimethyl
sulfate is by esterification of sulfuric acid with methanol as
follows:2CH3OH+ H2SO4→(CH3)2SO4 + 2H2O
Chemical properties
Dimethyl sulfate is essentially odorless. The specific gravity of this colorless, corrosive, oily liquid is 1.3322 g/cm3. Dimethyl sulfate is soluble in ether, dioxane, acetone, benzene, and other aromatic hydrocarbons. It is sparingly soluble in carbon disulfide and aliphatic hydrocarbons, and only slightly soluble in water (28 g/l at 18 °C) (O'Neil, 2006).
The Uses of Dimethyl sulfate
Dimethyl sulfate is a strong alkylating agent and might also react with the carboxylic acid substrate, further reducing the DMS concentration in the mixture. It is used as a methylating agent in themanufacture of many organic compounds,such as, phenols and thiols. Also, it is used inthe manufacture of dyes and perfumes, andas an intermediate for quaternary ammoniumsalts. It was used in the past as a militarypoison.
The Uses of Dimethyl sulfate

A solution of the SM (1.0 g, 6.2 mmol), K2CO3 (0.939 g, 6.8 mmol), and DMF (10 mL) was heated to 65 C and treated dropwise with Me2SO4 (0.78 g, 6.2 mmol) over 15 min, keeping the temperature between 65-70 C. The reaction was stirred at 80 C for 1 h, after which time it was poured into ice/water. The resulting solids were collected by filtration and dried in vacuo to provide the product. [0.91 g, 86%]
Definition
ChEBI: Dimethyl sulfate is the dimethyl ester of sulfuric acid. It has a role as an alkylating agent and an immunosuppressive agent.
Preparation
Dimethyl sulfate is prepared by distillation of an oleum/methanol mixture; technical production using dimethyl ether and SO3 has also been reported (NLM, 2013).
What are the applications of Application
Dimethyl Sulfate is a diester of methanol and sulfuric acid. Dimethyl Sulfate is commonly used as a reagent for the methylation of phenols, amines, and thiols. Dimethyl Sulfate is an effective and widely used probe for sequence-specific protein-DNA interactions.
General Description
Dimethyl sulfate is a colorless oily liquid, odorless to a faint onion-like odor. Dimethyl sulfate is very toxic by inhalation. Dimethyl sulfate is a combustible liquid and has a flash point of 182°F. Dimethyl sulfate is slightly soluble in water and decomposed by water to give sulfuric acid with evolution of heat. Dimethyl sulfate is corrosive to metals and tissue.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Pure Dimethyl sulfate and concentrated aqueous ammonia react extremely violently with one another, as is the case for tertiary organic bases, [NFPA 491M, 1991]. Dimethyl sulfate ignites in contact with unheated barium chlorite, due to the rapid formation of unstable methyl chlorite. The product of methylating an unnamed material at 110°C was alloyed to remain in a reactor for 80 min. before the reactor exploded. This involved a sulfur ester such as Dimethyl sulfate, [MCA Case History No. 1786].
Health Hazard
Dimethyl sulfate is extremely hazardous because of its lack of warning properties and delayed toxic effects. The vapor of this compound is extremely irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract, and contact with the liquid can cause very severe burns to the eyes and skin. Ingestion of dimethyl sulfate causes burns to the mouth, throat, and gastrointestinal tract. The effects of overexposure to dimethyl sulfate vapor may be delayed. After a latent period of 10 hours or more, headache and severe pain to the eyes upon exposure to light may occur, followed by cough, tightness of the chest, shortness of breath, difficulty in swallowing and speaking, vomiting, diarrhea, and painful urination. Fatal pulmonary edema may develop. Systemic effects of dimethyl sulfate include damage to the liver and kidneys. Dimethyl sulfate is listed by IARC in Group 2A ("probable human carcinogen") and is classified as a "select carcinogen" under the criteria of the OSHA Laboratory Standard. Data indicate that dimethyl sulfate does not specifically harm unborn animals; dimethyl sulfate is not a developmental toxin. It is a strong alkylating agent and does produce genetic damage in animals and in bacterial and mammalian cell cultures.
Flammability and Explosibility
Dimethyl sulfate is a combustible liquid (NFPA rating = 2). Toxic dimethyl sulfate vapors are produced in a fire. Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight dimethyl sulfate fires.
Potential Exposure
Tumorigen,Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; Human Data; PrimaryIrritant. Industrial use of dimethyl sulfate is based upon itsmethylating properties. It is used as an alkylating agent; inthe manufacture of methyl esters, ethers, and amines; indyes, drugs, perfume, phenol derivatives, and other organicchemicals; as a solvent in the separation of mineral oils; asan intermediate in the manufacture of sodium acetylide synthesis, as well as many pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least30 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting. Medical observation isrecommended for 2448 h after breathing overexposure, aspulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consideradministering a corticosteroid spray.
Carcinogenicity
Dimethyl sulfate is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogenbased on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Hydrolyzes in water (half-life = 1.2 h) to methanol and sulfuric acid (Robertson and Sugamori, 1966) via the intermediate methyl sulfuric acid (Du Pont, 1999a)
Storage
work with dimethyl sulfate should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent exposure by inhalation, and appropriate impermeable gloves and safety goggles should be worn at all times to prevent skin and eye contact.
Shipping
This compound requires a shipping label of“POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS, CORROSIVE.” Itfalls in Hazard Class 6.1 and Packing Group I.
Incompatibilities
Dimethyl sulfate can react violently with ammonium hydroxide, sodium azide, and strong oxidizers.
Waste Disposal
Excess dimethyl sulfate and waste material containing this substance should be placed in a covered metal container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines.
Properties of Dimethyl sulfate
| Melting point: | -32 °C |
| Boiling point: | 188 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.333 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.7 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 182 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 0.26 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless, oily liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor | Almost odorless |
| Water Solubility | 2.8 g/100 mL (18 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,3282 |
| BRN | 635994 |
| Exposure limits | TLV/PEL-TWA skin 0.1 ppm (0.52 mg/m3 )
(ACGIH, OSHA, NIOSH)
IDLH 10 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 55.0(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable; combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases including ammonia. Moisture-sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 77-78-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 4, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sulfuric acid, dimethyl ester(77-78-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethyl sulfate (77-78-1) |
Safety information for Dimethyl sulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dimethyl sulfate
Dimethyl sulfate manufacturer
Aara Biotech
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
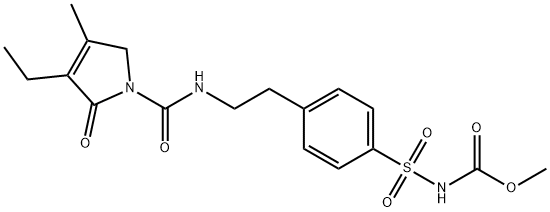
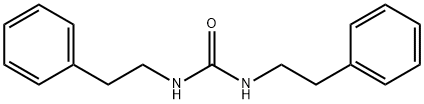
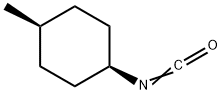
![4-[2-[(3-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrrolin-1-yl)carboxamido]ethyl]benzenesulfonamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/119018-29-0.gif)
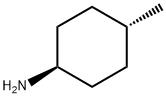
You may like
-
 Dimethyl sulfate 98%View Details
Dimethyl sulfate 98%View Details -
 Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 Dimethyl sulphate CAS 77-78-1View Details
Dimethyl sulphate CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 DIMETHYL SULPHATE For Synthesis CAS 77-78-1View Details
DIMETHYL SULPHATE For Synthesis CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 Dimethyl Sulfate 98% CAS 77-78-1View Details
Dimethyl Sulfate 98% CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
Dimethyl sulfate CAS 77-78-1View Details
77-78-1 -
 Grade: Commercial Dimethyl Sulphate Chemical, For Industrial And Laboratory, Purity: 99View Details
Grade: Commercial Dimethyl Sulphate Chemical, For Industrial And Laboratory, Purity: 99View Details
77-78-1
