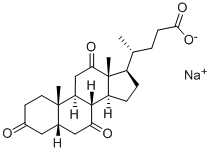
Dehydrocholic acid
Synonym(s):(5β)-3,7,12-Trioxocholan-24-oic acid;3,7,12-Trioxo-5β-cholanic acid;5β-Cholanic acid-3,5,12-trione;5β-cholanic acid-3,7,12-trione;5?-cholanic acid-3,7,12-trione
- CAS NO.:81-23-2
- Empirical Formula: C24H34O5
- Molecular Weight: 402.53
- MDL number: MFCD00066410
- EINECS: 201-335-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
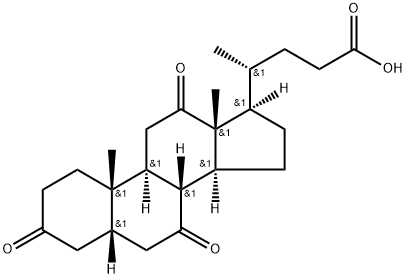
What is Dehydrocholic acid?
Absorption
The duodenal experiment indicates that dehydrocholic acid is absorbed from the proximal small intestine .
Toxicity
Oral LD50, intravenous LD50, and intramuscular LD50 in rat is 4000 mg/kg, 750 mg/kg, and 1500 mg/kg, respectively . Oral LD50, subcutaneous LD50, and intravenous LD50 in mouse is 3100 mg/kg, 1620 mg/kg, and 1492 mg/kg, respectively . There have been no reports of overdose with dehydrocholic acid.
Chemical properties
white to off-white amorphous powder
Originator
Dehydrocholic Acid,New Zealand Pharmaceuticals Limited (NZP)
The Uses of Dehydrocholic acid
Dehydrocholic Acid is a derivative of Cholic Acid (C432600). a choleretic produced by, and isolated from liver cells.
The Uses of Dehydrocholic acid
antibacterial
Background
Dehydrocholic acid is a synthetic bile acid that was prepared from the oxidation of cholic acid with chromic acid . It has been used for stimulation of biliary lipid secretion. The use of dehydrocholic acid in over-the-counter products has been discontinued by Health Canada.
What are the applications of Application
Dehydrocholic acid is used in the production of chenodeoxycholic acid by bioconversion
Indications
No approved therapeutic indications.
Definition
ChEBI: 3,7,12-trioxo-5beta-cholanic acid is an oxo-5beta-cholanic acid in which three oxo substituents are located at positions 3, 7 and 12 on the cholanic acid skeleton. It has a role as a gastrointestinal drug. It is an oxo-5beta-cholanic acid, a 7-oxo steroid, a 12-oxo steroid and a 3-oxo-5beta-steroid. It is a conjugate acid of a 3,7,12-trioxo-5beta-cholan-24-oate.
Manufacturing Process
A.) Oxidation of cholic acid:
A solution, consisting of 15.40 g of cholic acid and 18.75 g of anhydrous
sodium acetate in a solvent mixture of 20 ml of ethyl acetate, 30 ml of glacial
acetic acid, and 30 ml of water, was prepared. This solution was cooled to
20°C. Chlorine gas was bubbled into the solution with vigorous stirring while
the reaction temperature was maintained at 20°C. The chlorine was delivered
at a constant rate of about 2.5 g per hour over a 4-hour period. The total
amount of chlorine gas was 9.80 g which corresponds to about 3.68 moles per
mole of cholic acid, or approximately a 23% excess. The solution temperature
was maintained in the range of 16° to 20°C during the entire addition of
chlorine. Initially the cholic acid solution was very dark-colored. As the
reaction progressed, the solution became pale yellow and a precipitate of
sodium chloride deposited. A considerable amount of product and sodium
chloride precipitated during the latter stages of the reaction so that the final
reaction mixture was a heavy slurry which was difficult to stir. After the
addition of chlorine was complete, the slurry was aged one hour with stirring
at 20°C. The excess chlorine was then discharged by dropwise addition of
10% aqueous sodium sulfite until the solution gave a negative test to starchiodide paper. The semi-crystalline slurry was then diluted with water to raise
the total volume to 225 ml. The water was added dropwise with stirring over
a 1-hour period. The ethyl acetate was then distilled off at 65-88°C. The
resulting crystalline slurry was cooled to below 70°C and filtered through a
sintered-glass funnel of medium porosity. The filter cake was washed until the
filtrate gave a negative halide test with silver nitrate solution and then was
sucked partially dry on the funnel. Drying was completed in a drier at 110°C
for 3 hours. The product was crude pale tan dehydrocholic acid. Yield 14.3
(95%); M.P. 225-231°C.
B.) Purification of dehydrocholic acid:
To a chromatographic column, packed with 6.67 g of charcoal ("Nuchar C")
with layers of sea sand at either end, 75 ml of acetone was added to wet the
carbon. The column was heated to 40°C, and 25 ml of acetone was drained
off. A solution of 20 g of dry crude dehydrocholic acid in 500 ml of acetone
was poured into a reservoir atop the column and maintained in this reservoir
at 40°C. This solution was then allowed to drop through the column at a
constant rate over a 3-hour period. The column was then washed with 250 ml
of acetone flowing through the column at a constant rate over a 1-hour-period
at 40°C. The column effluent and wash acetone were combined and
concentrated to a residual volume of about 100 ml which resulted in the
formation of a thick slurry. The slurry was cooled with stirring at 0° to 5°C
and aged for 30 min at this temperature. The slurry was filtered and the filter
cake washed with cold acetone. The filter cake of U.S.P. dehydrocholic acid
was sucked partially dry on the filter and then dried at 110°C for 3 hours.
Yield 15 g to 17 g (75% to 85%).
A second crop of crystals was obtained from the combined filtrate and wash
liquid from the first crop filtration. This mixture, which initially had a volume
of about 100 ml, was concentrated to 20 ml. 10 ml of water was added to the
solution and 10 ml of acetone mixed with a small amount of water distilled off.
The residual thick slurry of dehydrocholic acid was cooled to 0-5°C, aged at this temperature with stirring for 30 min, and filtered. The filter cake was
washed with acetone at 0°C, partially dried by suction on the filter, and then
dried for three hours at 110°C. Yield 1 to 2 g (5% to 10%).
brand name
Decholin Sodium (Bayer).
Therapeutic Function
Choleretic, Diuretic, Diagnostic aid
Biochem/physiol Actions
Dehydrocholic acid is an oxidation product of cholic acid by chromic acid that is not present in physiological conditions. When used in animal experiments, it stimulates bile secretion.
Pharmacokinetics
Following infusion of dehydrocholic acid (DHCA) in rats, the secretions of all the endogenous biliary bile acids were decreased within 30-60 minutes of infusion . Phospholipid secretion as well as cholesterol levels were also declined. The bile flow was increased after administration of dehydrocholic acid .
Metabolism
The major site of metabolism is proposed to be the liver. The major metabolite accounting for 70% of total detectable metabolites is dihydroxymonoketo bile acid (3α,7α-dihydroxy-12-keto-5β-cholanoic acid). About 20% of metabolites is monohydroxydiketoacid (3α-hydroxy-7,12-keto-5β-cholanoic acid) and about 10% is cholic acid .
Properties of Dehydrocholic acid
| Melting point: | 238-240 °C |
| Boiling point: | 444.65°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 29 º (c=2, dioxane) |
| Density | 1.0687 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0.013Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | 30.5 ° (C=2, Dioxane) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | ethanol: 10 mg/mL |
| pka | pKa 5.12(H2O
t = 20
c > CMC) (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 65mg/L(30 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,2868 |
| BRN | 3226734 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 81-23-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dehydrocholic acid(81-23-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,7,12-trioxo-, (5.beta.)- (81-23-2) |
Safety information for Dehydrocholic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P403:Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for Dehydrocholic acid
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Dehydrocholic acid 95% CAS 81-23-2View Details
Dehydrocholic acid 95% CAS 81-23-2View Details
81-23-2 -
 Dehydrocholic Acid CAS 81-23-2View Details
Dehydrocholic Acid CAS 81-23-2View Details
81-23-2 -
 Dehydrocholic acid CAS 81-23-2View Details
Dehydrocholic acid CAS 81-23-2View Details
81-23-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8