Chenodeoxycholic acid
Synonym(s):3α,7α-Dihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid;5β-Cholanic acid-3α,7α-diol;Chenodiol
- CAS NO.:474-25-9
- Empirical Formula: C24H40O4
- Molecular Weight: 392.57
- MDL number: MFCD00064142
- EINECS: 207-481-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
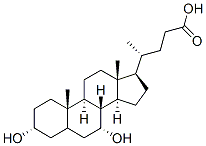
What is Chenodeoxycholic acid?
Absorption
Chenodiol is well absorbed from the small intestine.
Toxicity
Hepatotoxic.
Description
Chenodeoxycholic acid is the first agent to be introduced into the US market for the treatment of radiolucent gallstones. Large scale clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of this agent. Chenodeoxycholic acid reduces the biliary concentration of cholesterol relative to that of bile acids and phospholipid, reducing the saturation and thus the lithogenicity of the bile. Success rates in dissolving gallstones are in the range of 50-70% within 4-24 months of treatment. Continuation of the drug after stone dissolution may be required to prevent reoccurrence. Chenodeoxycholic acid is the 7α-isomer of ursodeoxycholic acid which was introduced into the European market in 1978.

chenodeoxycholic acid structure
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Rowell (USA)
History
Chenodeoxycholic acid was isolated in 1924 from goose gall by Adolf Windaus and human gall by Heinrich Wieland.Its complete structural configuation was elucidated by Hans Lettre at the University of Gottingen.
In 1968, William Admirand and Donald Small at Boston University Medical School established that in patients with gallstones their bile was saturated with cholesterol, sometimes even exhibiting microcrystals, whereas this was not the case in normal people.It was then found that biliary levels of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid were lower in patients with cholesterol gallstones than in normal people. Leslie Thistle and John Schoenfield at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, then administered individual bile salts by mouth for four months and found that chenodeoxycholic acid reduced the amount of cholesterol in the bile.This led to a national collaborative study in the United States, which confirmed the effectiveness of chenodeoxycholic acid in bringing about dissolution of gallstones in selected patients. However, recent developments such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy and endoscopic biliary techniques have curtailed the role of chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholelithiasis.
The Uses of Chenodeoxycholic acid
Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid that induces apoptosis through protein kinase C signaling pathways.It is a major bile acid in many vertebrates, occurring as the N-glycine and/or N-taurine conjugate. With other bile acids, forms mixed micelles with lecithin in bile which solubilize cholesterol and thus facilitates its excretion.Bile acids are essential for solubilization and transport of dietary lipids, are the major products of cholesterol catabolism, and are physiological ligands for farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that regulates genes involved in lipid metabolism.They are also inherently cytotoxic, as physiological imbalance contributes to increased oxidative stress. Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis.
- Chenodeoxycholic acid is widely utilized in therapeutic applications. It is applied in medical therapy to dissolve gallstones. It is employed in the treatment of cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis. It is used to treat constipation and cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis. It acts as a urea receptor in supramolecular chemistry which can contain anions. It is a staining additive commonly used with ruthenium or organic photo-sensitizers in the preparation of staining solutions for dye solar cells.
- Chenodeoxycholic Acid is a staining additive commonly used with ruthenium or organic photo-sensitizers in the preparation of staining solutions for Dye Solar Cells. This co-adsorbent will prevent dye aggregation on the semiconductor surface, reducing losses in the solar cell's operation.
- Chenodeoxycholic Acid is a white solid added with the dye powder to the solvent while preparing staining solutions. The concentration of co-adsorbent is typically 10 fold the dye concentration.
- Chenodeoxycholic acid has been used in a study to assess its effects as a long-term replacement therapy for cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX).
- It has also been used in a study to investigate its effects on the small-intestinal absorption of bile acids in patients with ileostomies.
- Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) is a hydrophobic primary bile acid that activates nuclear receptors involved in cholesterol metabolism.EC50 concentrations for activation of FXR range from 13-34 μM.In cells, CDCA also binds to bile acid binding proteins (BABP) with a reported stoichiometry of 1:2.CDCA toxicity is linked to increased cellular glutathione levels and increased oxidative stress. Exposure of cells to excess CDCA contributes to liver and intestinal cancers.
The Uses of Chenodeoxycholic acid
anticholithogenic, antilipemic agent
The Uses of Chenodeoxycholic acid
A major bile acid in many vertebrates, occurring as the N-glycine and/or N-taurine conjugate. With other bile acids, forms mixed micelles with lecithin in bile which solubilize cholesterol and thus fa cilitates its excretion. Fcilitates fat absorption in the small intestine by micellar solubilization of fatty acids and monoglycerides. Anticholelithogenic. Epimeric with Ursodiol.
The Uses of Chenodeoxycholic acid
An apoptosis inducer via PKC-dependent signalling pathway.
Background
Chenodeoxycholic acid (or Chenodiol) is an epimer of ursodeoxycholic acid (DB01586). Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally found in the body. It works by dissolving the cholesterol that makes gallstones and inhibiting production of cholesterol in the liver and absorption in the intestines, which helps to decrease the formation of gallstones. It can also reduce the amount of other bile acids that can be harmful to liver cells when levels are elevated.
Indications
Chenodiol is indicated for patients with radiolucent stones in well-opacifying gallbladders, in whom selective surgery would be undertaken except for the presence of increased surgical risk due to systemic disease or age. Chenodiol will not dissolve calcified (radiopaque) or radiolucent bile pigment stones.
What are the applications of Application
Chenodeoxycholic acid, free acid is an apoptosis inducer via PKC-dependent signalling pathway
Definition
ChEBI: Chenodeoxycholic acid is a dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid that is (5beta)-cholan-24-oic acid substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 7 respectively. It has a role as a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a bile acid, a dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid and a C24-steroid. It is a conjugate acid of a chenodeoxycholate.
Manufacturing Process
To 1,400 ml of an approximately 50% water/triglycol solution of the
potassium salt of chenodeoxycholic acid, obtained by the Wolff-Kishner
reduction (using hydrazine hydrate and potassium hydroxide) from 50 g of 7-
acetyl-12-ketochenodeoxycholic acid, 220 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid is
added to bring the pH to 2. The solution is stirred and the crude
chenodeoxycholic acid precipitates. The precipitate is recovered and dried to
constant weight at about 60°C. About 36 g of the crude chenodeoxycholic
acid, melting in the range of 126°-129°C, is obtained.
25 g of crude chenodeoxycholic acid so obtained is dissolved in 750 ml of
acetonitrile while stirring and heating. 3 g of activated charcoal is added and
then removed by suction filtering. The resulting liquid filtrate is cooled, the
pure chenodeoxycholic acid crystallizing out. The crystals are recovered by
suction filtering and the recovered crystals dried under vacuum. The yield is
19 g of pure chenodeoxycholic acid with a melting range of 168°-171°C.
brand name
CHEWM
Therapeutic Function
Gallostone dissolving agent
World Health Organization (WHO)
Chenodeoxycholic acid was introduced in 1975 for the treatment of cholelithiasis. It is available in several countries and the World Health Organization is not aware that registration has been refused in any other country.
General Description
Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid synthesized in the liver from cholesterol.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
It acts by reducing levels of cholesterol in the bile, helping gallstones that are made predominantly of cholesterol to dissolve. Chenodeoxycholic acid is ineffective with stones of a high calcium or bile acid content.
Metabolism
Chenodiol is well absorbed from the small intestine and taken up by the liver where it is converted to its taurine and glycine conjugates and secreted in bile. At steady-state, an amount of chenodiol near the daily dose escapes to the colon and is converted by bacterial action to lithocholic acid. About 80% of the lithocholate is excreted in the feces; the remainder is absorbed and converted in the liver to its poorly absorbed sulfolithocholyl conjugates. During chenodiol therapy there is only a minor increase in biliary lithocholate, while fecal bile acids are increased three- to fourfold.
Purification Methods
This major bile acid in vertebrates (~80mg) is chromatographed on silica gel (5g) and eluted with CHCl3/EtOAc (3:2) and crystallised from EtOAc/hexane. It has IR: max 1705 cm-1(CHCl3). It also crystallises from EtOAc, EtOAc/heptane after purifying via the poorly soluble Na and K salt if necessary. [Kametani et al. J Org Chem 4 7 2331 1982, Beilstein 10 IV 1604.]
Properties of Chenodeoxycholic acid
| Melting point: | 165-167 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 437.26°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 12 º (c=1, CHCl3) |
| Density | 0.9985 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4460 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | PRACTICALLY INSOLUBLE |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pKa 4.34 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | PRACTICALLY INSOLUBLE |
| Merck | 13,2062 |
| BRN | 3219887 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 474-25-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chenodiol (474-25-9) |
Safety information for Chenodeoxycholic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Chenodeoxycholic acid
| InChIKey | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-BSWAIDMHSA-N |
Chenodeoxycholic acid manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(2S)-2-[[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)diphenylsilyl]oxy]methyl]-1,3-oxathiolan-5-ol 5-Acetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180601/GIF/202532-88-5.gif)
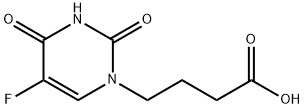
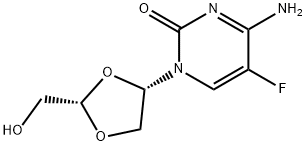
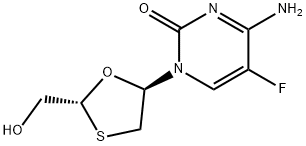
![2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione,5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]-, (2S-cis)- (9CI)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20200119/GIF/145281-92-1.gif)
You may like
-
 474-25-9 Chenodeoxycholic Acid 98%View Details
474-25-9 Chenodeoxycholic Acid 98%View Details
474-25-9 -
 474-25-9 98%View Details
474-25-9 98%View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic acid 95%, CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic acid 95%, CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic acid >98% (HPLC) CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic acid >98% (HPLC) CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic acid, 98% CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic acid, 98% CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic Acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic Acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic Acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic Acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9 -
 Chenodeoxycholic acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
Chenodeoxycholic acid CAS 474-25-9View Details
474-25-9