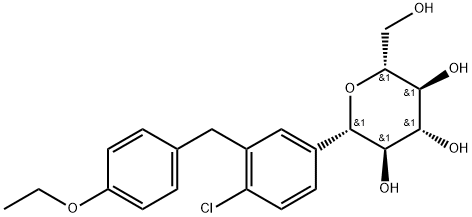
Empagliflozin
- CAS NO.:864070-44-0
- Empirical Formula: C23H27ClO7
- Molecular Weight: 450.91
- MDL number: MFCD22566222
- EINECS: 620-176-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-28 18:20:31
What is Empagliflozin?
Absorption
Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are reached in approximately 1.5 hours (Tmax). At steady-state, plasma AUC and Cmax were 1870 nmol·h/L and 259 nmol/L, respectively, following therapy with empagliflozin 10mg daily and 4740 nmol·h/L and 687 nmol/L, respectively, following therapy with empagliflozin 25mg daily. Administration with food does not significantly affect the absorption of empagliflozin.
Toxicity
Experience with empagliflozin overdose is limited - employ standard symptomatic and supportive measures, as well as gastric decontamination when appropriate. The use of hemodialysis in empagliflozin overdose has not been studied but is unlikely to be of benefit given the drug's relatively high protein-binding.
Description
Empagliflozin is a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Since its mechanism of action is independent of pancreatic islet b-cell function or the degree of insulin resistance. Therefore, SGLT2 inhibitors can be used not only alone, but also in combination with any of the existing glucose-lowering drugs, including insulin.
The Uses of Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is a novel, potent and selective SGLT-2 inhibitor, improves glycaemic control and features of metabolic syndrome in diabetic rats.
Indications
Empagliflozin is indicated for the following conditions:
(1) For improving glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in combination with diet and exercise. It can be used alone or in combination with metformin or linagliptin.
(2) For reducing the risk of cardiovascular death in adult patients with both type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease, either alone or in combination with metformin.
(3) For sustained decline in eGFR, end-stage renal disease, cardiovascular death and risk of hospitalisation in adult patients with chronic kidney disease at risk of progression.
Empagliflozin is not approved for use in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Definition
ChEBI: Empagliflozin is a C-glycosyl compound consisting of a beta-glucosyl residue having a (4-chloro-3-{4-[(3S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy]benzyl}phenyl group at the anomeric centre. A sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor used as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It has a role as a sodium-glucose transport protein subtype 2 inhibitor and a hypoglycemic agent. It is a C-glycosyl compound, an aromatic ether, a tetrahydrofuryl ether and a member of monochlorobenzenes.
Clinical Use
Selective and reversible inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2:Treatment of type 2 diabetes
Side Effects
Empagliflozin had a low incidence of adverse reactions. Compared with the placebo group, the incidence of common adverse reactions was 2%, including urinary tract infection, female reproductive system fungal infection, upper respiratory tract infection, polyuria, dyslipidemia (dose-related low-density lipoprotein increased), arthralgia, fungal infection of male reproductive system, hypoglycemia (the incidence of hypoglycemia increased when empagliflozin was combined with insulin or sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs), nausea. Other adverse reactions less than 2% were common in thirst (polydipsia, polydipsia), hypovolemia, and renal dysfunction.
Synthesis
Commercial 5-iodo-2-chlorobenzoic acid (97) was first converted to the corresponding acid chloride, prior to subjection to commercially available fluorobenzene (98) under Friedel¨CCrafts conditions to generate the desired fluorobenzophenone 99 in 94% yield after isolation by recrystallization from aqueous isopropanol. The fluorobenzophenone (99) was then reacted with commercially available (S)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran (100) and potassium tertbutoxide in THF to afford ethereal benzophenone 101. Next, removal of the ketone functionality within 101 was achieved through the use of 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane (TMDS) in the presence of aluminum chloride in toluene to deliver diaryl iodide 102. This iodide was subsequently converted to the corresponding Grignard reagent and subjected to gluconolactone 103, giving rise to an intermediate lactol which was then sequentially treated with aqueous citric acid, methanolic HCl, and triethylsilyl hydride and aluminum trichloride to ultimately furnish empagliflozin (XIII) in 73% yield across the four-step protocol.

Mechanism of action
Empagliflozin works by inhibiting the sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) found in the proximal tubules in the kidneys. Through SGLT2 inhibition, empagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of glucose and increases urinary excretion of glucose.
Metabolism
Empagliflozin undergoes minimal metabolism. It is primarily metabolized via glucuronidation by 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases 2B7, 1A3, 1A8, and 1A9 to yield three glucuronide metabolites: 2-O-, 3-O-, and 6-O-glucuronide. No metabolite represented more than 10% of total drug-related material.
Metabolism
In vitro studies suggested that the main route of metabolism is glucuronidation by the uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases UGT2B7, UGT1A3, UGT1A8, and UGT1A9Following administration of oral [14C]-empagliflozin solution to healthy volunteers, approximately 96% of the drug-related radioactivity was eliminated in faeces (41%) or urine (54%). The majority of drug-related radioactivity recovered in faeces was unchanged parent drug and approximately half of drug-related radioactivity excreted in urine was unchanged parent drug
storage
-20°C
Mode of action
Empagliflozin is an orally available competitive inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2; SLC5A2) with antihyperglycemic activity. Upon oral administration, empagliflozin selectively and potently inhibits SGLT2 in the kidneys, thereby suppressing the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal tubule. Inhibition of SGLT2 increases urinary glucose excretion by the kidneys, resulting in a reduction of plasma glucose levels in an insulin-independent manner. Inhibition of SGLT2 in the kidneys also suppresses the renal reabsorption of 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5AG). This lowers serum 1,5AG and neutrophil 1,5-anhydroglucitol-6-phosphate (1,5AG6P) levels, which may improve neutropenia and neutrophil dysfunction in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ib (GSD Ib). SGLT2, a transport protein exclusively expressed in the proximal renal tubules, mediates approximately 90% of renal glucose reabsorption from tubular fluid.
pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Empagliflozin
Properties of Empagliflozin
| Boiling point: | 665℃ |
| Density | 1.398 |
| Flash point: | 356℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥20.75 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥7.06 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.23±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Empagliflozin
Computed Descriptors for Empagliflozin
| InChIKey | OBWASQILIWPZMG-QZMOQZSNSA-N |
| SMILES | C1=C(CC2=CC([C@@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O)=CC=C2Cl)C=CC(O[C@H]2CCOC2)=C1 |
Empagliflozin manufacturer
TAGOOR LABORATORIES PVT LTD
Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd
Meenaakshi Molecules Pvt Ltd
Aalidhra Pharmachem Pvt Ltd
Piramal Pharma Solutions
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Empagli ozin 98%View Details
Empagli ozin 98%View Details
864070-44-0 -
 Empagliflozin 98%View Details
Empagliflozin 98%View Details -
 Empagliflozin 864070-44-0 98%View Details
Empagliflozin 864070-44-0 98%View Details
864070-44-0 -
 864070-44-0 Empagliflozin 99%View Details
864070-44-0 Empagliflozin 99%View Details
864070-44-0 -
 Empagliflozin 98%View Details
Empagliflozin 98%View Details -
 Empagliflozin 99%View Details
Empagliflozin 99%View Details -
 Empagliflozin 98% CAS 864070-44-0View Details
Empagliflozin 98% CAS 864070-44-0View Details
864070-44-0 -
 Empagliflozin 98% (HPLC) CAS 864070-44-0View Details
Empagliflozin 98% (HPLC) CAS 864070-44-0View Details
864070-44-0