Copper dinitrate
- CAS NO.:3251-23-8
- Empirical Formula: CuN2O6
- Molecular Weight: 187.56
- MDL number: MFCD00010967
- EINECS: 221-838-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:02:54
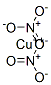
What is Copper dinitrate?
Description
Cupric nitrate is a blue crystalline solid.Molecular weight=187.55; Boiling point=170℃ (decomposes below this point); Freezing/Melting point=115℃.Soluble in water. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 1, Flammability 0,Reactivity 3 (Oxidizer). Soluble in water;solubility=135 g/100 mL (trihydrate).
Chemical properties
Cupric nitrate is a Blue crystalline solid.
The Uses of Copper dinitrate
Light-sensitive papers; analytical reagent; mordant in textile dyeing; nitrating agent; insecticide for vines; coloring copper black; electroplating; production of burnished effect on iron; paints; varnishes, enamels; pharmaceutical preparations; catalyst.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic nitrate salt having copper(2+) as the couterion.
General Description
Obtained as a trihydrate and as a hexahydrate. Both are blue crystalline solids. Used in medicine, as an insecticide, in chemical analysis, in making light sensitive papers. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving Copper dinitrate.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Mixtures of Copper dinitrate with alkyl esters may explode, owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates. Mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick, 1979 p. 108-109]. A finely divided mixture of potassium ferrocyanide and Copper dinitrate exploded when dried at 220°C [Chem. Abst. 77:1343 (1972)]. Noncombustible, but Copper dinitrate will accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities of the material are involved in a fire or the material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion.
Hazard
Oxidizer, causes violent combustion or explosion with organic materials.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes irritation of throat and lungs. Ingestion of large amounts causes violent vomiting and purging, intense pain, collapse, coma, convulsions, and paralysis. Solutions irritate eyes; contact with solid causes severe eye surface injury and skin irritation.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. A severe eye and skin irritant. Potentially explosive reaction above 22OOC with ammonium or potassium hexacyanoferrate(I1). Reaction with ammonia + potassium amide gives explosive product. Violent reaction with acetic anhydride. May ignite on prolonged contact with paper. Concentrated solutions may ipte in contact with tin or aluminum foil. Used as a fungicide, herbicide, and as a catalyst component in solid rocket fuel. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS and NITRATES.
Potential Exposure
Cupric nitrate is used as an insecticide, in paint, varnish, enamel, and in wood preservatives. Metal compounds are often used in “hot” operations in the work-place. These may include, but are not limited to, welding, brazing, soldering, plating, cutting, and metallizing. At the high temperatures reached in these operations, metals often form metal fumes which have different health effects and exposure standards than the original metal compound and require specialized controls.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.
Note to physician: In case of fume inhalation, treat for pulmonary edema. Give prednisone or other corticosteroid orally to reduce tissue response to fume. Positive pressureventilation may be necessary. Treat metal fume fever withbed rest, analgesics, and antipyretics. The symptoms ofmetal fume fever may be delayed for 4-12 h followingexposure: it may last less than 36 h.
Shipping
UN1479 Oxidizing solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from weak aqueous HNO3 (0.5mL/g) by cooling from room temperature. The anhydrous salt can be prepared by dissolving copper metal in a 1:1 mixture of liquid NO2 and ethyl acetate and purified by sublimation [Evans et al. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 75 1023 1979]. The hexahydrate dehydrates to the trihydrate at 26o, and the anhydrous salt sublimes between 150 and 225o, but melts at 255-256o and is deliquescent.
Incompatibilities
A strong oxidizer. Aqueous solution is acidic; incompatible with bases. Violent reaction with potassium hexacyanoferrate; ammonia and potassium amide mixtures; acetic anhydrides, cyanides, ethers. Forms explosive materials with nitromethanes, sodium hypobromite; acetylene; chemically active metals, such as potassium, sodium, etc. May ignite on contact with aluminum foil or tin. Risk of spontaneous combustion with combustibles (wood, cloth, etc.) organics, or reducing agents and readily oxidizable materials. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill. Add slowly to water; stir in excess soda ash. Let stand, then neutralize. Decant solution and flush to sewer; landfill sludge
Properties of Copper dinitrate
| Melting point: | 115°C |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| solubility | soluble in dioxane; reacts with ethyl ether |
| form | blue-green orthorhombic crystals |
| color | blue-green orthorhombic crystals, crystalline;
hygroscopic |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| Merck | 13,2671 |
| Stability: | Stable. Oxidant. Incompatible with combustible materials. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3251-23-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric nitrate (3251-23-8) |
Safety information for Copper dinitrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P220:Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Copper dinitrate
Copper dinitrate manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Copper Nitrate 98%View Details
Copper Nitrate 98%View Details -
 Copper(II) nitrate 98%View Details
Copper(II) nitrate 98%View Details
3251-23-8 -
 3251-23-8 Copper(II) nitrate 98%View Details
3251-23-8 Copper(II) nitrate 98%View Details
3251-23-8 -
 3251-23-8 98%View Details
3251-23-8 98%View Details
3251-23-8 -
 Cupric Nitrate CAS 3251-23-8View Details
Cupric Nitrate CAS 3251-23-8View Details
3251-23-8 -
 copper nitrate CASView Details
copper nitrate CASView Details -
 Copper Standard for AAS CASView Details
Copper Standard for AAS CASView Details -
 Copper Standard for IC CASView Details
Copper Standard for IC CASView Details
