Ferric nitrate
Synonym(s):Iron(III) nitrate solution
- CAS NO.:10421-48-4
- Empirical Formula: FeN3O9
- Molecular Weight: 241.86
- MDL number: MFCD00011003
- EINECS: 233-899-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
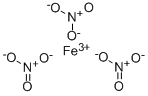
What is Ferric nitrate?
Description
Ferric nitrate is a pale violet, green, or grayish-white, odorless solid in lumpy crystals (like salt).Molecular weight = 241.88; Boiling point = decomposes;Freezing/Melting point = 35 C; 47 C (nonhydrate). Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 2, Flammability 1, Reactivity 3, Oxidizer. Highlysoluble in water.
Chemical properties
Violet crystals. Soluble in water and alcohol.
Chemical properties
Ferric nitrate is a pale violet, green, or grayish-white, odorless solid in lumpy crystals (like salt).
Physical properties
The nonahydrate form occurs as grayish-violet crystal; density 1.68 g/cm3; hygroscopic; decomposes at 47°C; very soluble in water, alcohol and acetone.
The Uses of Ferric nitrate
Dyeing (mordant for buffs and blacks), tanning, analytical chemistry.
General Description
A violet crystalline solid. Noncombustible but Ferric nitrate will accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in the fire or the combustible material is finely divided an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure of the material to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving Ferric nitrate. Ferric nitrate is used for dyeing and tanning, in chemical analysis, and in medicine.It is a strong oxidant and irritant,and a fire hazard when in contact with organic substances.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Ferric nitrate is an oxidizing agent. Mixtures with alkyl esters may explode, owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates. Mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick, 1979 p. 108-109].
Hazard
Dangerous fire risk in contact with organic materials. Strong oxidant and irritant.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Dust irritates eyes and can irritate skin on prolonged contact.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported.A reactive oxidizer.
Potential Exposure
Ferric nitrate is used in textile dyeing, tanning, and weighting silk.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. The symptoms of metal fume fevermay be delayed for 4-12 h following exposure: it may lastless than 36 h.Note to physician: For severe poisoning do not use BAL[British Anti-Lewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol(C3H8OS2)] as it is contraindicated or ineffective in poisoning from iron.
storage
Color Code—Yellow: Reactive Hazard; Store in alocation separate from other materials, especially flammables and combustibles. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from organic materials and other combustible materials or aluminum powder. See OSHAStandard 1910.104 and NFPA 43A Code for the Storage ofLiquid and Solid Oxidizers for detailed handling and storageregulations.
Shipping
UN1466 Ferric nitrate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer.
Incompatibilities
An oxidizer. Keep away from reducing agents, oxidizable materials and combustibles including metal powders, sulfur, and organic materials, combustibles,and easily oxidizable materials. Light sensitive. Aqueous solution is corrosive to metals.
Properties of Ferric nitrate
| Melting point: | 47.2℃ |
| Boiling point: | 125℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
| Density | 1.684 |
| vapor pressure | 0.01Pa at 20℃ |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear pale yellow |
| Water Solubility | g/100g H2O: 82.520 [CRC10] |
| Merck | 13,4057 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10421-48-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferric nitrate (10421-48-4) |
Safety information for Ferric nitrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ferric nitrate
Ferric nitrate manufacturer
Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS)
Cosmic Chemicals
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 10421-48-4 FERRIC NITRATE 99%View Details
10421-48-4 FERRIC NITRATE 99%View Details
10421-48-4 -
 Iron(III) nitrate 99%View Details
Iron(III) nitrate 99%View Details -
 Ferric Nitrate CAS 10421-48-4View Details
Ferric Nitrate CAS 10421-48-4View Details
10421-48-4 -
 Iron(III) nitrate 10421-48-4 98%View Details
Iron(III) nitrate 10421-48-4 98%View Details
10421-48-4 -
 Iron Standard for ICP CASView Details
Iron Standard for ICP CASView Details -
 Iron(III) nitrate 98%View Details
Iron(III) nitrate 98%View Details
10421-48-4 -
 Iron Standard for ICP CASView Details
Iron Standard for ICP CASView Details -
 Iron Standard for AAS CASView Details
Iron Standard for AAS CASView Details