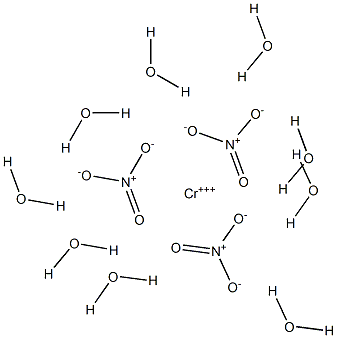
Chromic nitrate
- CAS NO.:13548-38-4
- Empirical Formula: CrH18N3O18
- Molecular Weight: 400.15
- MDL number: MFCD00149659
- EINECS: 236-921-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
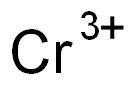
What is Chromic nitrate?
Absorption
Chromium compounds are both absorbed by the lung and the gastrointestinal tract. Oral absorption of chromium compounds in humans can range between 0.5% and 10%, with the hexavalent (VI) chromium more easily absorbed than the trivalent (III) form . Absorption of chromium from the intestinal tract is low, ranging from less than 0.4% to 2.5% of the amount consumed . Vitamin C and the vitamin B niacin is reported to enhance chromium absorption .
Most hexavalent Cr (VI) undergoes partial intragastric reduction to Cr (III) upon absorption, which is an action mainly mediated by sulfhydryl groups of amino acids . Cr (VI) readily penetrates cell membranes and chromium can be found in both erythrocytes and plasma after gastrointestinal absorption of Cr (IV). In comparison, the presence of chromium is limited to the plasma as Cr (III) displays poor cell membrane penetration . Once transported through the cell membrane, Cr (VI) is rapidly reduced to Cr (III), which subsequently binds to macromolecules or conjugate with proteins. Cr (III) may be bound to transferrin or other plasma proteins, or as complexes, such as glucose tolerance factor (GTF).
Toxicity
Oral LD50 for Cr (VI) is 135 - 175 mg/kg in mouse and 46 - 113 mg/kg in rat . Oral LD50 for Cr (III) in rat is >2000 mg/kg . LD50 of chromium (III) oxide in rats is reported to be > 5g/kg . Other LD50 values reported for rats include: 3.5 g/kg (CI 3.19-3.79 g/kg) for chromium sulphate; 11.3 g/kg for chromium (III) acetate; 3.3 g/kg for chromium nitrate; and 1.5 g/kg for chromium nitrate nonahydrate .
Acute overdose of chromium is rare and seriously detrimental effects of hexavalent chromium are primarily the result of chronic low-level exposure . In case of overdose with minimal toxicity following acute ingestion, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive . There is no known antidote for chromium toxicity.
Hexavalent chromium is a Class A carcinogen by the inhalation route of exposure and Class D by the oral route . The oral lethal dose in humans has been estimated to be 1-3 g of Cr (VI); oral toxicity most likely involves gastrointestinal bleeding rather than systemic toxicity . Chronic exposure may cause damage to the following organs: kidneys, lungs, liver, upper respiratory tract . Soluble chromium VI compounds are human carcinogens. Hexavalent chromium compounds were mutagenic in bacteria assays and caused chromosome aberrations in mammalian cells. There have been associations of increased frequencies of chromosome aberrations in lymphocytes from chromate production workers . In human cells in vitro, Cr (VI) caused chromosomal aberrations, sister chromatid exchanges and oxidative DNA damage .
Description
Chromium nitrate is a crystalline substance, variously stated to be green brown or purple and existing in various hydrated forms. Molecular weight =238.03; 400.21(nonahydrate); Freezing/Melting point =60-100℃, depending on the degree of hydration. Hazard Identification (basedon NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 1, Flammability 0,Reactivity 0. Soluble in water
Chemical properties
Chromium nitrate is a crystalline substance, variously stated to be green brown or purple and existing in various hydrated forms.
The Uses of Chromic nitrate
Catalyst, corrosion inhibitor.
Indications
Indicated for use as a supplement to intravenous solutions given for total parenteral nutrition (TPN), to maintain chromium serum levels and to prevent depletion of endogenous stores and subsequent deficiency symptoms .
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic nitrate salt consisting of chromium and nitrate in which the ratio of chromium (in the +3 oxidation state) to nitrate is 1:3
Hazard
May ignite organic materials on contact; may be explosive when shocked or heated; powerful oxidizer. Very toxic.
Pharmacokinetics
Trivalent chromium is part of glucose tolerance factor, an essential activator of insulin-mediated reactions. Chromium helps to maintain normal glucose metabolism and peripheral nerve function. Chromium increases insulin binding to cells, increases insulin receptor density and activates insulin receptor kinase leading to enhanced insulin sensitivity . In chromium deficiency, intravenous administration of chromium resulted in normalization of the glucose tolerance curve from the diabetic-like curve typical of chromium deficiency .
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous and ingestion routes. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx and Cr.
Potential Exposure
Chromium nitrate is used in the preparation of chrome catalysts, in textile printing operations; and as a corrosion inhibitor. Used to make other chemicals.
First aid
If chromium nitrate gets into the eyes, removeany contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for atleast 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids.Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and washimmediately with soap and water. Seek medical attentionimmediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, removefrom exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolism
The metabolism of Cr (VI) involves reduction by small molecules and enzyme systems to generate Cr (III) and reactive intermediates. During this process, free radicals can be generated, which is thought to induce damage of cellular components and cause toxicity of chromium . The metabolites bind to cellular constituents .
storage
Color Code—Yellow: Reactive Hazard; Store in alocation separate from other materials, especially flammables and combustibles. Color Code—Blue: HealthHazard/Poison: Store in a secure poison location. Prior toworking with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Chromium nitrate must bestored to avoid contact with strong reducing agents, fuels,and ether since violent reactions occur. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away fromflammable and combustible materials. A regulated, markedarea should be established where this chemical is handled,used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard1910.1045. See OSHA Standard 1910.104 and NFPA 43ACode for the Storage of Liquid and Solid Oxidizers fordetailed handling and storage regulations.
Shipping
UN2720 Chromium nitrate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer
Purification Methods
Filter off the salt and wash it with CCl4 in a closed system under N2, and dry it in vacuo. It is very soluble in H2O, EtOAc and Me2SO but insoluble in *C6H6, CCl4 and CHCl3. The deliquescent powder reacts vigorously with Et2O. [Addison & Chapman J Chem Soc 539 1964.] Cr(VI) ions are carcinogenic as they cause DNA breaks, and Cr(III) ions affect DNA synthesis.
Incompatibilities
This chemical is a strong oxidizer. Contact with reducing agents; fuels, ethers, and other flammable and combustible materials cause a fire and explosion hazard. Violent reaction with many compounds, including reducing agents; alcohols, chemically active metals; combustible materials, strong acids, alkaline earth sulfides, aluminum carbides, aluminum, amines, calcium sulfide, carbides, chlorine trifluoride, glycerin, hydrides, hydrochloric acid, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydroxylamine, magnesium, metal powders, metal sulfides, molybdenum, phenylhydrazine, phosphorous red/friction, phosphorous trichloride, silicon, sulfides, sulfur, sulfur Chromium Nitrate 845 dioxide, sulfur/friction, sulfuric acid, tungsten, hydrogen trisulfide
Waste Disposal
Precipitate chromium as the hydroxide. Dewater the sludge and dispose of in singlepurpose dumps.
Properties of Chromic nitrate
| Melting point: | 60 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1Pa at 20℃ |
| solubility | very soluble in H2O |
| form | Crystalline Chunks |
| color | Dark purple to black |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| Merck | 13,2246 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13548-38-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chromium(III) nitrate (13548-38-4) |
Safety information for Chromic nitrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Chromic nitrate
Chromic nitrate manufacturer
Cosmic Chemicals
Anchor Chemicals Industries
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 13548-38-4 Chromium(III) nitrate 98%View Details
13548-38-4 Chromium(III) nitrate 98%View Details
13548-38-4 -
 13548-38-4 99%View Details
13548-38-4 99%View Details
13548-38-4 -
 CHROMIUM NITRATE CAS 13548-38-4View Details
CHROMIUM NITRATE CAS 13548-38-4View Details
13548-38-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1