Barium carbonate
Synonym(s):Barium carbonate
- CAS NO.:513-77-9
- Empirical Formula: CBaO3
- Molecular Weight: 197.34
- MDL number: MFCD00003448
- EINECS: 208-167-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-17 10:13:59
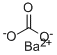
What is Barium carbonate?
Description
Barium carbonate has the molecular formula of BaCO3 and the molecular weight of 197.3359 g/mol. Its CAS number is 513-77-9. Barium carbonate has only one stable form (aragonite-type structure) and temperature of precipitation has no effect on crystal form, unlike that of calcium or magnesium carbonates.
Chemical properties
Barium carbonate, BaCO3, also known as witherite, is a white powder that is soluble in acids,with the exception of sulfuric acid.It has a melting point of 174°C and is used in television picture tubes, rodenticide, optical glass and ceramic flux.

Barium oxide, BaO, is manufactured by decomposition of barium carbonate.
Physical properties
White powder; orthorhombic crystal system; density 4.286 g/cm3; refractive index 1.60; hardness 3.50 Mohs; melts at 811°C; insoluble in water (c. 25 mg/L at 25°C); Ksp 2.0 x 10-9.
Occurrence
Barium carbonate is found in nature as mineral witherite. The compound has many major commercial applications in brick, glass, ceramics, oil-drilling, photographic and chemical industries. It is mixed with wet clay to immobilize many water-soluble salts in making uniform red bricks. In the glass industry, barium is added to glass as barium carbonate or barium oxide to improve the refractive index of optical glass; also to promote sintering and lower the viscosity of melted glass to make glass bead formation easy. It is used in the manufacture of television picture tubes and photographic paper. Another important application involves its use as a fluxing ingredient in ceramic industry for enamels, glazes and ceramic bodies. Barium carbonate is used in oil-well drilling to insolubilize gypsum and inhibit coagulation; in ferrous metallurgy for steel carburizing; in chlor-alkali cells for treating salt brines to remove sulfates; and to make ferrite, and barium titanate. Many barium salts are prepared from barium carbonate.
The Uses of Barium carbonate
Barium carbonate has many major commercial applications in brick, glass, ceramics, oil-drilling, photographic and chemical industries. It is mixed with wet clay to immobilize many water-soluble salts in making uniform red bricks. In the glass industry, barium is added to glass as barium carbonate or barium oxide to improve the refractive index of optical glass and also to promote sintering and lower the viscosity of melted glass to make glass bead formation easy. It is used in the manufacture of television picture tubes and photographic paper. Another important application involves its use as a fluxing ingredient in ceramic industry for enamels, glazes and ceramic bodies. Barium carbonate is used in oil well drilling to insolubilize gypsum and inhibit coagulation; in ferrous metallurgy for steel carburizing; in chloralkali cells for treating salt brines to remove sulfates; and to make ferrites, and barium titanate. Many barium salts are prepared from barium carbonate.
The Uses of Barium carbonate
Preparation of barium standard solution. It is used in ceramic glazes, cement, bricks and in rat poison.
The Uses of Barium carbonate
Rat poison; in ceramics, paints, enamels, marble substitutes, rubber; manufacture of paper, barium salts, electrodes, optical glasses; as an analytical reagent.
What are the applications of Application
Barium carbonate is a barium preparation employed as an active component of rodenticides
Definition
barium carbonate: A white insolublecompound, BaCO3; r.d. 4.43. It decomposeson heating to give bariumoxide and carbon dioxide:
BaCO3(s) → BaO(s) + CO2(g)
The compound occurs naturally asthe mineral witherite and can be preparedby adding an alkaline solutionof a carbonate to a solution of a bariumsalt. It is used as a raw materialfor making other barium salts, as aflux for ceramics, and as a raw materialin the manufacture of certaintypes of optical glass.
Definition
witherite is a mineral form of bariumcarbonate, BaCO3.
Preparation
Barium carbonate is made commercially from barium sulfide either by treatment with sodium carbonate or ammonium carbonate at 60 to 70°C or by passing CO2 gas through a soluble Ba2+ solution at 40 to 90°C.
General Description
Barium carbonate is a white powder. Barium carbonate is insoluble in water and soluble in most acids, with the exception of sulfuric acid. Barium carbonate has a specific gravity of 4.275. Barium carbonate is toxic by ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Barium carbonate is insoluble in water and soluble in most acids, with the exception of sulfuric acid.
Reactivity Profile
Salts, basic, such as Barium carbonate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
Hazard
A poison.
Health Hazard
(INGESTION ONLY): excessive salivation, vomiting, severe abdominal pain, and violent purging with watery and bloody stools; a slow and often irregular pulse and a transient elevation in arterial blood pressure; tinnitus, giddiness and vertigo; muscle twitchings, progressing to convulsions and/or paralysis; dilated pupils with impaired accommodation; confusion and increasing somnolence, without coma; collapse and death from respiratory failure and cardiac arrest.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: stomach ulcers, muscle weakness, paresthesias and paralysis, hypermotility, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, lung changes. Experimental reproductive effects. Incompatible with BrF3 and 2- furanpercarboxylic acid. See also BARIUM COMPOUNDS (soluble).
Properties of Barium carbonate
| Melting point: | 811 °C |
| Boiling point: | 1450 °C |
| Density | 4.43 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.02g/l |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 4.43 |
| PH | 7-8 (0.016g/l, H2O, 16℃) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 0.002 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Decomposition | 1300°C |
| Merck | 14,969 |
| BRN | 7045119 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.59 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 513-77-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Barium carbonate (513-77-9) |
Safety information for Barium carbonate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Barium carbonate
Barium carbonate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 BARIUM CARBONATE 99%View Details
BARIUM CARBONATE 99%View Details -
 BARIUM CARBONATE 99%View Details
BARIUM CARBONATE 99%View Details -
 Barium Carbonate (SQ) CAS 513-77-9View Details
Barium Carbonate (SQ) CAS 513-77-9View Details
513-77-9 -
 Barium carbonate CAS 513-77-9View Details
Barium carbonate CAS 513-77-9View Details
513-77-9 -
 Barium carbonate 99%View Details
Barium carbonate 99%View Details -
 BARIUM CARBONATE 98%View Details
BARIUM CARBONATE 98%View Details -
 Barium Carbonate extrapure AR CAS 513-77-9View Details
Barium Carbonate extrapure AR CAS 513-77-9View Details
513-77-9 -
 Barium carbonate 98% CAS 513-77-9View Details
Barium carbonate 98% CAS 513-77-9View Details
513-77-9
