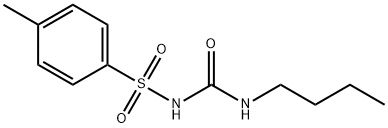
CHLORPROPAMIDE
Synonym(s):1-(p-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-3-propylurea
- CAS NO.:94-20-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H13ClN2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 276.74
- MDL number: MFCD00079004
- EINECS: 202-314-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
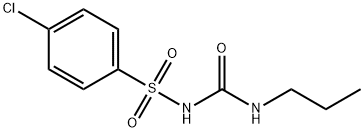
What is CHLORPROPAMIDE?
Absorption
Readily absorbed from the GI tract. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 2-4 hours and the onset of action occurs within one hour. The maximal effect of chlorpropamide is seen 3-6 hours following oral administration.
Toxicity
IPN-RAT LD50 580 mg/kg
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
Originator
Diabinese ,Pfizer, US,1958
The Uses of CHLORPROPAMIDE
Chlorpropamide is a sulfonylurea derivative. Chlorpropamide is a long acting hyopglycemic agent. Chlorpropamide is used in the treatment of diabetes metilus type 2. Chlorpropamide acts to increase the secretion of insulin and is not effective in patients who do not have pancreatic beta cell function.
The Uses of CHLORPROPAMIDE
antidiabetic
The Uses of CHLORPROPAMIDE
For treatment of NIDDM in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Background
Chlorpropamide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the sulfonylurea class of insulin secretagogues, which act by stimulating β cells of the pancreas to release insulin. Sulfonylureas increase both basal insulin secretion and meal-stimulated insulin release. Medications in this class differ in their dose, rate of absorption, duration of action, route of elimination and binding site on their target pancreatic β cell receptor. Sulfonylureas also increase peripheral glucose utilization, decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis and may increase the number and sensitivity of insulin receptors. Sulfonylureas are associated with weight gain, though less so than insulin. Due to their mechanism of action, sulfonylureas may cause hypoglycemia and require consistent food intake to decrease this risk. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased in elderly, debilitated and malnourished individuals. Chlorpropamide is not recommended for the treatment of NIDDM as it increases blood pressure and the risk of retinopathy (UKPDS-33). Up to 80% of the single oral dose of chlorpropramide is metabolized, likely in the liver; 80-90% of the dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug and metabolites. Renal and hepatic dysfunction may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
What are the applications of Application
Chlorpropamide is a derivitized sulfonyl urea compound
Indications
For treatment of NIDDM in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-sulfonylurea that is urea in which a hydrogen attached to one of the nitrogens is substituted by 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl group and a hydrogen attached to the other nitrogen is substituted by propyl group. Chlorpropamide is a hypogly aemic agent used in the treatment of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus not responding to dietary modification.
Manufacturing Process
A solution of 54 g (0.64 mol) of propyl isocyanate in 60 ml of anhydrous
dimethylformamide was added to a cold, well-stirred suspension of 81 g (0.42
mol) of dry p-chlorobenzenesulfonamide in 210 ml of anhydrous triethylamine
during the course of 20 to 30 minutes. The mildly exothermic reaction was
completed by allowing it to stand at room temperature for about 5 hours. The
reaction mixture was then slowly added to 3 liters of cold 20% acetic acid
during the course of about one hour, constant agitation being maintained
throughout the addition.
After the addition was complete, the desired product, which had crystallized
out, was filtered and washed well with about 2 liters of cold water. The crude
material was then dissolved in 1 liter of cold 5% sodium carbonate and the
resulting solution was immediately filtered from an insoluble gum. The product
was then reprecipitated, by slowly adding the filtrate to 3 liters of 20% acetic
acid. The precipitate, which is very nearly pure N-(p-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-
N'-propylurea, was then dried and subsequently recrystallized from about 800
ml of benzene to give a 59% yield of pure product, MP 129.2 to 129.8°C.
brand name
Diabinese (Pfizer); Glucamide (Teva).
Therapeutic Function
Oral hypoglycemic
General Description
White crystalline powder with a slight odor.
General Description
Chlorpropamide is 4-chloro-N-[(propylamino)carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide; or 1-[(p-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl]-3-propylurea; or 1-(p-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-3-propylurea(Diabinese, generic). The p-chlorophenyl moiety is quite resistantto P450-mediated hydroxylations; hence, blood levelsof the drug are sustained for a markedly long length of time,as aliphatic hydroxylation constitutes most of the clearance,and this happens relatively slowly. Although the -hydroxyland (ω–1)-hydroxyl metabolites (the latter formed in muchgreater portion) exert hypoglycemic potencies not much lessthan does the parent drug, elimination of these by conversion to the corresponding glucuronides occurs more rapidly thanhydroxylation of chlorpropamide, so blood levels of thesemetabolites remain low, and thus they probably do not makean appreciable contribution to the hypoglycemic action ofthis drug in clinical application. Removal of the entire propylside chain (oxidative N-dealkylation) also occurs to a significantextent (up to 20% of an orally administered dose), creatingthe inactive metabolite p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea,about 10% of which degrades to the corresponding benzenesulfonamide.
General Description
Chlorpropamide, 1-[(p-chlorophenyl)-sulfonyl]-3-propylurea (Diabinese), is a white, crys-talline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol,and sparingly soluble in chloroform. It will form watersolublesalts in basic solutions. This drug is more resistant toconversion to inactive metabolites than is tolbutamide and, asa result, has a much longer duration of action. One studyshowed that about half of the drug is excreted as metabolites,with the principal one being hydroxylated in the 2-position ofthe propyl side chain.After control of the blood sugar level,the maintenance dose is usually on a once-a-day schedule.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated amide. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for CHLORPROPAMIDE are not available; however, CHLORPROPAMIDE is probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Chlorpropamide, a second-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent, is used with diet to lower blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus type II. Chlorpropamide is twice as potent as the related second-generation agent glipizide.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
While chlorpropamide could potentially be of benefit in the adjunctive treatment of diabetes mellitus in small animals, its use has been primarily for adjunctive therapy in diabetes insipidus in dogs and cats.
Metabolism
Up to 80% of dose is metabolized likely through the liver to to 2-hydroxylchlorpropamide (2-OH CPA), p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea (CBSU), 3-hydroxylchlorpropamide (3-OH CPA), and p-chlorobenzenesulfonamide (CBSA); CBSA may be produced by decomposition in urine. It is unknown whether chlorpropamide metabolites exert hypoglycemic effects.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the urea from aqueous EtOH. [Beilstein 11 IV 119.]
Properties of CHLORPROPAMIDE
| Melting point: | 128 °C |
| Boiling point: | 302°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3046 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa 4.8 (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Light Yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (1:12), acetone (1:5), chloroform (1:9) and solutions of alkali hydroxides. Does not mix well with water. |
| Merck | 14,2186 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 94-20-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chloropropamide (94-20-2) |
Safety information for CHLORPROPAMIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for CHLORPROPAMIDE
CHLORPROPAMIDE manufacturer
Kothari Phytochemicals and Industries Ltd.
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 94-20-2 Chlorpropamide 98%View Details
94-20-2 Chlorpropamide 98%View Details
94-20-2 -
 94-20-2 99%View Details
94-20-2 99%View Details
94-20-2 -
 Chlorpropamide 98% CAS 94-20-2View Details
Chlorpropamide 98% CAS 94-20-2View Details
94-20-2 -
 Chlorpropamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 94-20-2View Details
Chlorpropamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 94-20-2View Details
94-20-2 -
 1-(4-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea CAS 94-20-2View Details
1-(4-Chlorophenylsulfonyl)-3-propylurea CAS 94-20-2View Details
94-20-2 -
 Chlorpropamide CAS 94-20-2View Details
Chlorpropamide CAS 94-20-2View Details
94-20-2 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1