Glibenclamide
Synonym(s):5-Chloro-N-[4-(cyclohexylureidosulfonyl)phenethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide;Glybenclamide;Glyburide;Glyburide - CAS 10238-21-8 - Calbiochem;N-p-[2-(5-Chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzenesulfonyl-N′-cyclohexylurea
- CAS NO.:10238-21-8
- Empirical Formula: C23H28ClN3O5S
- Molecular Weight: 494
- MDL number: MFCD00056625
- EINECS: 233-570-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
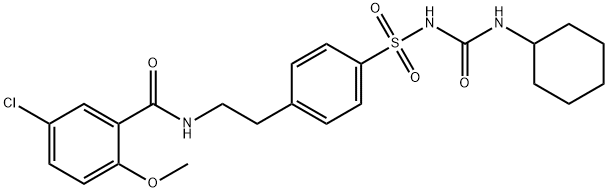
What is Glibenclamide?
Absorption
Elderly patients taking glyburide reached a Cmax of 211-315ng/mL with a Tmax of 0.9-1.0h, while younger patients reached a Cmax of 144-302ng/mL with a Tmax of 1.3-3.0h. Patients taking glyburide have and AUC of 348ng*h/mL.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is >3200mg/kg, in mice is >1500mg/kg, in rabbits is >10,000mg/kg, and in guinea pigs is >1500mg/kg.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with hypoglycemia. Mild hypoglycemia should be treated with oral glucose and adjustments to drug doses or meal schedules. Severe hypoglycemia may present with coma, seizure, and neurological impairment. This should be treated immediately in hospital with intravenous glucose and monitoring for 24-48 hours.
Description
Glyburide (10238-21-8) is a second generation oral hypoglycemic agent. Acts via ATP-dependent K+ channel (Kir6, KATP) block.1?Inhibits Kir6 currents in the pancreas, causing an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and insulin secretion. Glyburide also inhibits recombinant CFTR Cl- channels with an IC50 of 20 μM.2?Cell permeable.
Chemical properties
White or almost white, crystalline powder
Originator
Daonil,Hoechst,Germany
The Uses of Glibenclamide
Glyburide (Glibenclamide) is a sulfonylurea compound that modulates insulin production. Sulfonylureas bind to ATP-dependent K+ channels in beta cells of the pancreas, depolarizing them and stimulating the release of Ca2+, which in turn stimulates insulin production. Glyburide (Glibenclamide) is an ATP-dependent K+ channel (KIR6, KATP) and CFTR Cl- channel blocker. This compound inhibits recombinant CFTR Cl- channels (IC50 = 20 ?M).
The Uses of Glibenclamide
antihyperglycemic
The Uses of Glibenclamide
Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea with hypoglycemic activity. Glyburide is an antidiabetic.
The Uses of Glibenclamide
An ATP-dependent KIR6 and CFTR Cl- channel blocker
What are the applications of Application
Glyburide (Glibenclamide) is an ATP-dependent KIR6 and CFTR Cl- channel blocker
Background
Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea used to treat patients with diabetes mellitus type II. It is typically given to patients who cannot be managed with the standard first line therapy, metformin. Glyburide stimulates insulin secretion through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells, raising intracellular potassium and calcium ion concentrations.
Glyburide was granted FDA approval on 1 May 1984. A formulation with metformin was granted FDA approval on on 31 July 2000.
Indications
Glyburide is indicated alone or as part of combination product with metformin, as an adjunct to diet and exercise, to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-sulfonylurea that is acetohexamide in which the acetyl group is replaced by a 2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl group.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 10.2 g of 4-(β-(2-ethoxy-5-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)- benzenesulfonamide in 12.5 ml of 2 N sodium hydroxide solution and 30 ml acetone are added dropwise, at 0-5°C, 3.3 g of cyclohexyl isocyanate. The whole is stirred for 3 hours, diluted with water and methanol, undissolved matter is separeted by filtration. The filtrate is acidified with dilute hydrochloric acid. The 4-(β-(2-ethoxy-5-chlorobenzamido)ethyl)- benzenesulfonyl)-N'-cyclohexylurea which precipitates in the form of crystals melts after recrystallization from methanol at 168-170°C.
brand name
Micronase (Pharmacia & Upjohn).
Therapeutic Function
Oral hypoglycemic
General Description
Glyburide (glibenclamide) is 5-chloro-N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide; this compound can also be named asthe urea—see preceding discussion (Diabeta, Glynase,generic). Some tablet formulations contain micronized drug(formerly Micronase, now only generic). Combinations areavailable with metformin in the United States (Glucovance,generic; tablets, mg glipizide/mg metformin as hydrochloride:1.25/250, 2.5/500, 5/500).
General Description
Similar to glipizide, glyburide, 1-[[p-[2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl]-phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea(DiaBeta, Micronase, Glynase), is a second-generationoral hypoglycemic agent. The drug has a half-life eliminationof 10 hours, but its hypoglycemic effect remains for upto 24 hours.
Biological Activity
ATP-dependent K + channel (K ATP ) and CFTR Cl - channel blocker. Inhibits K ATP currents in the pancreas, causing an increase in intracellular Ca 2+ and insulin secretion. Inhibits recombinant CFTR Cl- channels with an IC 50 of 20 μ M.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Selectively blocks ATP-sensitive K+ channels; high affinity binding sites found in brain, pancreatic β cells, and cardiovascular system.
Mechanism of action
This drug belongs to the second-generation sulfonylurea derivatives. Like all of the other oral hypoglycemic drugs examined, it is a β-cell stimulant in pancreas; but on the other hand, it increases the sensitivity to insulin, the degree to which it binds with target cells. At the same time, it differs in that it is easier to tolerate. The hypoglycemic effect sets in at significantly lower doses than with first-generation drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin secretion through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells, raising intracellular potassium and calcium ion concentrations. Glibenclamide has a long duration of action as it is given once daily, and a wide therapeutic index as patients are started at doses as low as 0.75mg but that can increase as high as 10mg or more. Patients taking glyburide should be cautioned regarding an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality as seen with tolbutamide, another sulfonylurea.
Clinical Use
Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
Synthesis
Glyburide, 1-[4-[2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]-phenylsulfonyl]-3- cyclohexylurea (26.2.11), is a second-generation drug that differs from those described above in that it has a more complex structure in the sulfonylamide region of the molecule into which an additional pharmacophore group is added. It is synthesized from 2-methoxy-5-chlorobenzoic acid chloride, which is transformed into an amide 26.2.9 by reacting it with 2-phenylethylamine. This undergoes subsequent sulfonylchlorination by chlorosulfonic acid, and then amination by ammonia, which gives sulfonamide 26.2.10. The resulting sulfonamide is reacted with cylclohexylisocyanate to give the desired glyburide (26.2.11).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: effects enhanced by NSAIDs.
Antibacterials: effects enhanced by chloramphenicol,
sulphonamides, tetracyclines and trimethoprim;
effects possibly enhanced by ciprofloxacin and
norfloxacin; effect reduced by rifamycins.
Anticoagulants: effect possibly enhanced by
coumarins; also possibly changes to INR.
Antifungals: concentration increased by fluconazole
and miconazole and possibly voriconazole.
Bosentan: increased risk of hepatoxicity - avoid.
Ciclosporin: may increase ciclosporin levels.
Lipid-regulating drugs: absorption reduced by
colesevelam; concentration possibly increased by
fluvastatin; possibly additive hypoglycaemic effect
with fibrates.
Sulfinpyrazone: enhanced effect of sulphonylureas.
Metabolism
Glyburide is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4, followed by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A7, and CYP3A5. These enzymes metabolize glyburide to 4-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M1), 4-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2a), 3-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2b), 3-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M3), 2-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M4), and ethylhydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M5). The M1 and M2b metabolites are considered active, along with the parent molecule.
Metabolism
Glibenclamide is metabolised, almost completely, in the
liver, the principal metabolite being only very weakly
active.
About 50% of a dose is excreted in the urine and 50% via
the bile into the faeces.
Storage
Store at RT
References
1) Brogden et al. (1979), Glipizide: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use; Drugs, 18 329 2) Sheppard and Welsh (1992), Effect of ATP-sensitive K+ channel regulators on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride currents; J. Gen. Physiol., 100 573
Properties of Glibenclamide
| Melting point: | 173-175°C |
| Density | 1.1805 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6100 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble2mg/mL |
| form | White solid |
| pka | 5.3(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (5 mg/mL), DMSO (25 mg/mL), chloroform (1:36), methanol (1:250), and DMF. Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4478 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10238-21-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Glyburide(10238-21-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzamide, 5-chloro-N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxy- (10238-21-8) |
Safety information for Glibenclamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Glibenclamide
| InChIKey | ZNNLBTZKUZBEKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Glibenclamide manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![GLIBENCLAMIDE, [CYCLOHEXYL-2,3-3H(N)]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1182488.gif)
You may like
-
 Glibenclamide 98%View Details
Glibenclamide 98%View Details -
 Glibenclamide 98%View Details
Glibenclamide 98%View Details -
 Glyburide 99% (HPLC) CAS 10238-21-8View Details
Glyburide 99% (HPLC) CAS 10238-21-8View Details
10238-21-8 -
 Glibenclamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 10238-21-8View Details
Glibenclamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 10238-21-8View Details
10238-21-8 -
 Glibenclamide 98% CAS 10238-21-8View Details
Glibenclamide 98% CAS 10238-21-8View Details
10238-21-8 -
 Glibenclamide 95.00% CAS 10238-21-8View Details
Glibenclamide 95.00% CAS 10238-21-8View Details
10238-21-8 -
 Glibenclamide, For ClinicalView Details
Glibenclamide, For ClinicalView Details
10238-21-8 -
 Glibenclamide 5mg TabletView Details
Glibenclamide 5mg TabletView Details
10238-21-8
