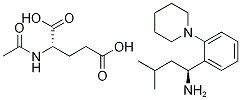
Repaglinide
Synonym(s):(S)-(+)-2-Ethoxy-4-[N-[1-(2-piperidinophenyl)-3-methyl-1-butyl]aminocarbonylmethyl]benzoic acid;Novonorm;Prandin;Repaglinide
- CAS NO.:135062-02-1
- Empirical Formula: C27H36N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 452.59
- MDL number: MFCD00906179
- EINECS: 629-921-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
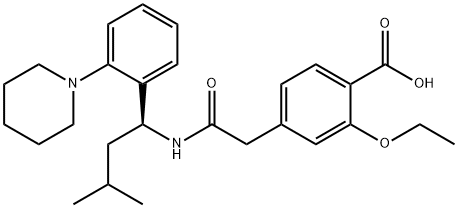
What is Repaglinide?
Absorption
Rapidly and completely absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are observed within 1 hour (range 0.5-1.4 hours). The absolute bioavailability is approximately 56%. Maximal biological effect is observed within 3-3.5 hours and plasma insulin levels remain elevated for 4-6 hours. When a single 2 mg dose of repaglinide is given to healthy subjects, the area under the curve (AUC) is 18.0 - 18.7 (ng/mL/h)^3.
Toxicity
LD50 >1 g/kg (rat) (W. Grell)
Description
Repaglinide was marketed in the US as an orally active hypoglycemic agent in patients with a type Ⅱ diabetes mellitus, to lower blood glucose in synergistic combination with metformin, when hyperglycemia cannot be controlled by diet, exercise or metformin alone. Chiral (S)-repaglinide can be synthesized in several ways, each involving a stereoselective reduction of an imine or enamine group. Repaglinide is a nonsulfonylurea belonging to the meglitinide family, with an insulin-releasing effect mediated by pancreatic betacells, by closing the ATP-sensitive K+ channels that, in turn, increases the cytosolic concentration of Ca++. In several animal models, repaglinide was more efficient than glibenclamide as a dose-dependant promoter of insulin release, but its mechanism of action is probably slightly different. Repaglinide has a rapid onset of action, a short duration of action and a reduced risk of hypoglycemia compared to glyburide.
Description
Repaglinide is a metaglitinide antidiabetic agent that blocks ATP-dependent potassium (Kir6) channels in pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.42 nM for the sulphonylurea receptor SUR1 when co-expressed with Kir6.2). In vivo, repaglinide lowers blood glucose in fasted rats and dogs (ED50s = 10 and 28.3 μg/kg, respectively). Formulations containing repaglinide have been used to control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany)
The Uses of Repaglinide
The R-enantiomer showed only weak hypoglycemic activity. Repaglinide impurity
The Uses of Repaglinide
Non-sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agent. Used as an antidiabetic
The Uses of Repaglinide
antineoplastic
The Uses of Repaglinide
A KIR6 (KATP) channel blocker
Background
Repaglinide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the meglitinide class of short-acting insulin secretagogues, which act by binding to β cells of the pancreas to stimulate insulin release. Repaglinide induces an early insulin response to meals decreasing postprandial blood glucose levels. It should only be taken with meals and meal-time doses should be skipped with any skipped meal. Approximately one month of therapy is required before a decrease in fasting blood glucose is seen. Meglitnides may have a neutral effect on weight or cause a slight increase in weight. The average weight gain caused by meglitinides appears to be lower than that caused by sulfonylureas and insulin and appears to occur only in those na?ve to oral antidiabetic agents. Due to their mechanism of action, meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia although the risk is thought to be lower than that of sulfonylureas since their action is dependent on the presence of glucose. In addition to reducing postprandial and fasting blood glucose, meglitnides have been shown to decrease glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, which are reflective of the last 8-10 weeks of glucose control. Meglitinides appear to be more effective at lowering postprandial blood glucose than metformin, sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones. Repaglinide is extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted in bile. Repaglinide metabolites do not possess appreciable hypoglycemic activity. Approximately 90% of a single orally administered dose is eliminated in feces and 8% in urine.
Indications
As an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
What are the applications of Application
Repaglinide is a KIR6 (KATP) channel blocker
Definition
ChEBI: Repaglinide is a member of piperidines.
brand name
Prandin (Novo Nordisk).
General Description
Repaglinide is 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-[2-(1-piperidinyl)phenyl]butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid(Prandin); approvals for generics are pending. Combinationsare available with metformin in the United States(Prandimet), and the drug may also be coprescribed with oneof the thiazolidinediones (typically pioglitazone or rosiglitazone;see previous discussion). To establish the most clinicallyvaluable dose, the patient is titrated while monitoringblood glucose levels and hemoglobin glycosylation (HbA1c)as an index of longer-term overall control.
General Description
Repaglinide, (+)-2-ethoxy-4-[N-[3-methyl-1(S)-[2-(1-piperidinyl) phenyl]butyl]carbamoyl-methyl]benzoicacid (Prandin), represents a new class of nonsulfonylureaoral hypoglycemic agents. With a fast onset and ashort duration of action, the medication should be taken withmeals. It is oxidized by CYP 3A4, and the carboxylic acidmay be conjugated to inactive compounds. Less than 0.2%is excreted unchanged by the kidney, which may be an advantagefor elderly patients who are renally impaired. Themost common side effect involves hypoglycemia, resultingin shakiness, headache, cold sweats, anxiety, and changes inmental state.
Biological Activity
K ATP channel blocker that binds with high affinity for SUR1 when co-expressed with Kir6.2 (K d = 0.42 nM). Antidiabetic glucose regulator with hypoglycaemic effect in vivo .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Repaglinide is a potent short-acting insulin secretagogue that acts by closing ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in the plasma membrane of the pancreatic beta cell. It represents a new class of insulin secretagogues, structurally unrelated to sulphonylureas, which were developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Pharmacokinetics
Insulin secretion by pancreatic β cells is partly controlled by cellular membrane potential. Membrane potential is regulated through an inverse relationship between the activity of cell membrane ATP-sensitive potassium channels (ABCC8) and extracellular glucose concentrations. Extracellular glucose enters the cell via GLUT2 (SLC2A2) transporters. Once inside the cell, glucose is metabolized to produce ATP. High concentrations of ATP inhibit ATP-sensitive potassium channels causing membrane depolarization. When extracellular glucose concentrations are low, ATP-sensitive potassium channels open causing membrane repolarization. High glucose concentrations cause ATP-sensitive potassium channels to close resulting in membrane depolarization and opening of L-type calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions stimulates calcium-dependent exocytosis of insulin granules. Repaglinide increases insulin release by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels in a glucose-dependent manner.
Clinical Use
Repaglinide is a nonsulfonylurea insulin secretagogue that was introduced in the United States in 1998 for type 2 diabetes.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: effects enhanced by clarithromycin
and possibly trimethoprim - avoid with
trimethoprim; hypoglycaemic effect antagonised by
rifampicin.
Antifungals: effect possibly enhanced by itraconazole.
Ciclosporin: may increase repaglinide concentration,
possibly enhanced hypoglycaemic effect.
Clopidogrel: avoid concomitant use if possible due to
increased repaglinide exposure.
Cytotoxics: avoid with lapatinib.
Lipid-lowering agents: increased risk of severe
hypoglycaemia with gemfibrozil - avoid.
Metabolism
Repaglinide is rapidly metabolized via oxidation and dealkylation by cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2C9 to form the major dicarboxylic acid derivative (M2). Further oxidation produces the aromatic amine derivative (M1). Glucuronidation of the carboxylic acid group of repaglinide yields an acyl glucuronide (M7). Several other unidentified metabolites have been detected. Repaglinide metabolites to not possess appreciable hypoglycemic activity.
Metabolism
Repaglinide appears to be a substrate for active hepatic
uptake by the organic anion transporting protein
OATP1B1, and undergoes almost complete hepatic
metabolism involving the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes
CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. The glucuronidation of
repaglinide is thought to involve uridine diphosphate
glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes, particularly
UGT1A1.
The metabolites, which are inactive, are excreted in the
bile.
storage
+4°C
Properties of Repaglinide
| Melting point: | 129-130.2 °C |
| Boiling point: | 672.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 +6.97° (c = 0.975 in methanol); D20 +7.45° (c = 1.06 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.137±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 34 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 4.19±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 89.99mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8136 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 135062-02-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Repaglinide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H361:Reproductive toxicity H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Repaglinide
| InChIKey | FAEKWTJYAYMJKF-QHCPKHFHSA-N |
Repaglinide manufacturer
Smilax Laboratories Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 135062-02-1 REPAGLINIDE 0.33% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
135062-02-1 REPAGLINIDE 0.33% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
135062-02-1 -
 135062-02-1 98%View Details
135062-02-1 98%View Details
135062-02-1 -
 Repaglinide 98% CAS 135062-02-1View Details
Repaglinide 98% CAS 135062-02-1View Details
135062-02-1 -
 Repaglinide 135062-02-1 98%View Details
Repaglinide 135062-02-1 98%View Details
135062-02-1 -
 Repaglinide 98%View Details
Repaglinide 98%View Details -
 Repaglinide 98%View Details
Repaglinide 98%View Details -
 Repaglinide CAS 135062-02-1View Details
Repaglinide CAS 135062-02-1View Details
135062-02-1 -
 Repaglinide CAS 135062-02-1View Details
Repaglinide CAS 135062-02-1View Details
135062-02-1