Rofecoxib
Synonym(s):4-[4-(Methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-3-phenyl-2(5H)-furanone
- CAS NO.:162011-90-7
- Empirical Formula: C17H14O4S
- Molecular Weight: 314.36
- MDL number: MFCD00935806
- EINECS: 803-260-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
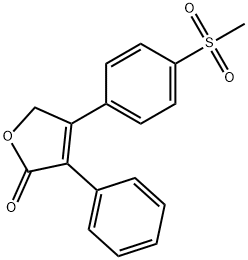
What is Rofecoxib?
Absorption
The mean oral bioavailability of rofecoxib at therapeutically recommended doses of 12.5, 25, and 50 mg is approximately 93%.
Toxicity
No overdoses of rofecoxib were reported during clinical trials. Administration of single doses of rofecoxib 1000 mg to 6 healthy volunteers and multiple doses of 250 mg/day for 14 days to 75 healthy volunteers did not result in serious toxicity.
Description
Rofecoxib ts a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) launched in Mexico, its first market, for the management of acute pain and the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) and primary dysmenorrhea. Rofecoxib can be obtained by several different ways; one example is by arylation of a 4-bromofuranone with a phenylboronic acid under Suzuki conditions. Rofecoxib is a highly selective inhibitor of COX-2, the inducible isoform of cyclooxygenase and therefore exhibits a potent antiinflammatory activity without concomitant gastric or renal toxicities linked to the non-specific COX-1/2 inhibitors. In several clinical studies in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis, Rofecoxib was evaluated at 12.5-50 mg doses once daily: it demonstrated efficacy for all primary and secondary endpoints at doses considerably weaker than those for classical non-specific NSAIDs, with good tolerance and less adverse effects. Selective COX-2 inhibitors potentially have a large spectrum of activity including new indications such as Alzheimer's disease, colorectal cancer, irritable bowel disease or urinary incontinence.
Chemical properties
Off-White (Pale Yellow) Crystalline Powder
Originator
Merck (US)
The Uses of Rofecoxib
Rofecoxib has been used in high performance bioaffinity chromatography.
The Uses of Rofecoxib
A selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor. Use as an anti-inflammatory, analgesic.
The Uses of Rofecoxib
antipsychotic
The Uses of Rofecoxib
Labeled Rizatriptan, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Rizatriptan by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
What are the applications of Application
Vioxx is a selective Cox-2 inhibitorthat has anti-inflammatory properties
Indications
For the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain in adults, and primary dysmenorrhea, as well as acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without auras.
Background
Rofecoxib is used for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain in adults, and primary dysmenorrhea, as well as acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without auras. Rofecoxib is a solid. This compound belongs to the stilbenes. These are organic compounds containing a 1,2-diphenylethylene moiety. Stilbenes (C6-C2-C6 ) are derived from the common phenylpropene (C6-C3) skeleton building block. The introduction of one or more hydroxyl groups to a phenyl ring lead to stilbenoids. Rofecoxib has a half-life of 17 hours and its mean oral bioavailability at therapeutically recommended doses of 125, 25, and 50 mg is approximately 93%. The proteins that rofecoxib target include elastin and prostaglandin G/H synthase 2. Cytochrome P450 1A2, Cytochrome P450 3A4, Cytochrome P450 2C9, Cytochrome P450 2C8, and Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 are known to metabolize rofecoxib. On September 30, 2004, Merck voluntarily withdrew rofecoxib from the market because of concerns about increased risk of heart attack and stroke associated with long-term, high-dosage use.
Definition
ChEBI: A butenolide that is furan-2(5H)-one that is substituted by a phenyl group at position 3 and by a p-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl group at position 4. A selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, it was used from 1999 to 2004 for the tr atment of ostoarthritis, but was withdrawn following concerns about an associated increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Indications
Rofecoxib is approved for the treatment of osteoarthritis, dysmenorrhea, and acute pain. The most common adverse reactions to rofecoxib are mild to moderate GI irritation (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain). Lower extremity edema and hypertension occur relatively frequently (about 3.5%). It is not metabolized by CYP2C9, so rofecoxib should not be subject to some of the interactions seen with celecoxib. However, its metabolism is increased by the coadministration of rifampin, which acts as a nonspecific inducer of hepatic metabolism.
brand name
Vioxx (Merck).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Rofecoxib is derived from furanone and has the ability to cross human placenta. Along with anti-inflammatory action, it possesses analgesic and antipyretic properties. Cytosolic hepatic enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of rofecoxib. It is known to cause oligohydramnios and ductus arteriosus constrictions. Rofecoxib inhibits the action of CYP1A2 (cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2). It might be associated with aseptic meningitis. Rofecoxib is known to ameliorate the risk of colorectal adenoma, but might contribute to toxicity.
Mechanism of action
Rofecoxib is excreted primarily in the urine (72%) as metabolites. Less than 1% is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug, whereas approximately 14% is excreted in the feces as unchanged drug. Although the metabolism of rofecoxib has not been fully determined, the microsomal cytochrome P450 system appears to play only a minor role—a major difference in the metabolic routes of rofecoxib and celecoxib. The major metabolic route appears to form reduction of the dihydrofuranone ring system by cystolic enzymes to the to cis- and trans- dihydro derivatives. Also isolated is the glucuronide of a hydroxy derivative that results from CYP2C9 oxidative metabolism. None of the isolated metabolites of rofecoxib possess pharmacological activity as COX-1 or COX-2 inhibitors.
Pharmacokinetics
Rofecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, is classified as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Unlike celecoxib, rofecoxib lacks a sulfonamide chain and does not require CYP450 enzymes for metabolism. Like other NSAIDs, rofecoxib exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activity. NSAIDs appear to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis via the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX), which are responsible for catalyzing the formation of prostaglandins in the arachidonic acid pathyway. There are at least two isoenzymes, COX-1 and COX-2, that have been identified. Although the exact mechanisms have not been clearly established, NSAIDs exert their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic primarily through the inhibition of COX-2. The inhibition of COX-1 is principally responsible for the negative effects on the GI mucosa. As rofecoxib is selective for COX-2, it may be potentially associated with a decreased risk of certain adverse events, but more data is needed to fully evaulate the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
Rofecoxib has been synthesized by a number of synthetic routes that have been summarized elsewhere. It was the second selective COX-2 inhibitor to be marketed. Rofecoxib is well absorbed from the GI tract on oral administration, with peak plasma levels generally being attained within 2 to 3 hours of dosing. Bioavailability averages 93% following administration of a single dose. The area under the plasma concentration–time curve is increased in patients older than 65 years compared to younger adults and is increased slightly in black and Hispanic patients compared with white patients, but the difference is not considered to be clinically significant.
Clinical Use
Rofecoxib was indicated for the relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis, for the management of acute pain in adults, and for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea.
Side Effects
Rofecoxib causes a significantly lower incidence of upper-gastrointestinal adverse effects (perforations, ulcers, and bleeding) than conventional NSAIDs. Most common adverse events associated with rofecoxib are diarrhoea, headache, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection.
Synthesis
Rofecoxib can be obtained by different synthetic routes, e.g., by condensation of phenylacetic acid with ethyl bromoacetate to ethyl 2-phenylacetoxyacetate, which is then cyclized to a hydroxyfuranone. Subsequently, the hydroxyfuranone reacts with trifluoromethanesulfonic (triflic) anhydride to the corresponding triflate which reacts with LiBr to yield a bromofuranone. The bromofuranone is condensed with 4- (methylsulfanyl)phenylboronic acid to give 4-[4-(methylsulfanyl)phenyl]-3-phenylfuran- 2(5H)-one which is finally oxidized to rofecoxib.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Metabolism of rofecoxib is primarily mediated through reduction by cytosolic enzymes. The principal metabolic products are the cis-dihydro and trans-dihydro derivatives of rofecoxib, which account for nearly 56% of recovered radioactivity in the urine. An additional 8.8% of the dose was recovered as the glucuronide of the hydroxy derivative, a product of oxidative metabolism. The biotransformation of rofecoxib and this metabolite is reversible in humans to a limited extent (< 5%). These metabolites are inactive as COX-1 or COX-2 inhibitors. Cytochrome P450 plays a minor role in metabolism of rofecoxib.
Dosage
Rofecoxib is indicated for relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis (recommended starting dose is 12.5 mg once daily, maximum recommended dose is 25 mg/d), for the management of acute pain in adults and for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea (recommended initial doses are 50 mg once daily, use of rofecoxib for more than 5 d in management of pain has not been studied).
References
1) Chan et al. (1999), Rofecoxib [Vioxx, MK-0966; 4-(4′-methylsulfonylphenyl)-3-phenyl-2-(5H)-furanone]: a potent and orally active cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Pharmacological and biochemical profiles; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 290 551 2) Catalla-Lawson et al. (2013), Effects of specific inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 on sodium balance, hemodynamics and vasoactive eicosanoids; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 289 735
Properties of Rofecoxib
| Melting point: | 207°C |
| Boiling point: | 577.6±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.333±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble5mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| Water Solubility | 9mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8248 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 162011-90-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Rofecoxib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
Computed Descriptors for Rofecoxib
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Rofecoxib CAS 162011-90-7View Details
Rofecoxib CAS 162011-90-7View Details
162011-90-7 -
 Rofecoxib 98% CAS 162011-90-7View Details
Rofecoxib 98% CAS 162011-90-7View Details
162011-90-7 -
 Rofecoxib CAS 162011-90-7View Details
Rofecoxib CAS 162011-90-7View Details
162011-90-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1