Carfilzomib
- CAS NO.:868540-17-4
- Empirical Formula: C40H57N5O7
- Molecular Weight: 719.92
- MDL number: MFCD11040997
- EINECS: 692-054-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 19:45:46
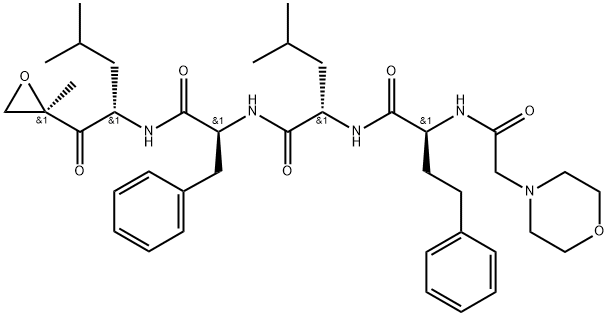
What is Carfilzomib?
Absorption
Cmax, single IV dose of 27 mg/m^2 = 4232 ng/mL; AUC, single IV dose of 27 mg/m^2 = 379 ng?hr/mL; Carfilzomib does not accumulation in the systemic. At doses between 20 and 36 mg/m2, there was a dose-dependent increase in exposure.
Toxicity
Most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) are fatigue, anemia, nausea, thrombocytopenia, dyspnea, diarrhea, and pyrexia. The two dose limiting toxicities are thrombocytopenia and febrile neutropenia. Maximum tolerate dose = 15 mg/m^2
Description
In July 2012, the US FDA approved carfilzomib (also referred to as PR-171) for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma (MM) who have received at least two prior therapies including bortezomib and an immunomodulatory agent and have demonstrated disease progression within 60 days of completion of the last therapy. Carfilzomib binds to and irreversibly inhibits the chymotrypsin-like protease activity of the constitutive proteosome (β5) and immunoproteosome (β5i) via its epoxyketone pharmacophore. Proteosome inhibition results in the accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins and induction of apoptosis through activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic caspase pathways. Carfilzomib inhibits chymotrypsin activity with an IC50 of 6 nM and is less potent an inhibitor of trypsin and caspase (IC50s of 3600 and 2400 nM, respectively). Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis are seen in a variety of hematologic and solid tumor cell lines (e.g.,MM, acutemyeloid leukemia (AML), pancreatic cancer, lung cancer) treated with carfilzomib. The synthesis of carfilzomib is reported in the patent literature and a route to the intermediate epoxy ketone from a Boc-leucine-derived α,β-unsaturated ketone is also described.
Description
Carfilzomib, a selective proteasome inhibitor, is marketed by Onyx Pharmaceuticals under the name Kyprolis. FDA approved the epoxomicin derivative in July 2012 for treating patients with relapsed, refractory multiple myeloma. Work by C. M. Crews and co-workers at Yale University led directly to the development of carfilzomib.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Proteolix Inc. (United States)
The Uses of Carfilzomib
Carfilzomib is a second-generation proteasome inhibitor that is used as a treatment in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma.
Indications
Carfilzomib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one to three lines of therapy in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone; or dexamethasone; or daratumumab and dexamethasone; or daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj and dexamethasone; or isatuximab and dexamethasone. It is also indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received one or more lines of therapy.
Background
Carfilzomib is an injectable antineoplastic agent (IV only). Chemically, it is a modified tetrapeptidyl epoxide and an analog of epoxomicin. It is also a selective proteasome inhibitor. FDA approved carfilzomib in July 2012 for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma as monotherapy or combination therapy.
Definition
ChEBI: Carfilzomib is a synthetic tetrapeptide consisting of morpholin-4-acetyl, L-2-amino-4-phenylbutanoyl, L-leucyl and L-phenylalanyl residues joined in sequence with the C-terminus connected to the amino group of (2<element S)-2-amino-4-methyl-1-[(2R)-2-methyloxiran-2-yl]-1-oxopentan-1-one via an amide linkage. Used for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma.
Pharmacokinetics
Intravenous carfilzomib administration resulted in suppression of proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity when measured in blood 1 hour after the first dose. On Day 1 of Cycle 1, proteasome inhibition in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) ranged from 79% to 89% at 15 mg/m2, and from 82% to 83% at 20 mg/m2. In addition, carfilzomib administration resulted in inhibition of the LMP2 and MECL1 subunits of the immunoproteasome ranging from 26% to 32% and 41% to 49%, respectively, at 20 mg/m2. Proteasome inhibition was maintained for ≥ 48 hours following the first dose of carfilzomib for each week of dosing. Resistance against carfilzomib has been observed and although the mechanism has not been confirmed, it is thought that up-regulation of P-glycoprotein may be a contributing factor. Furthermore, studies suggest that carfilzomib is more potent than bortezomib.
Clinical Use
Carfilzomib is an irreversible inhibitor of the chymotrypsin-like protease in the proteasome and was approved in the U.S. for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Carfilzomib was discovered by Proteolix which was later acquired by Onyx Therapeutics who completed the development of this drug. Carfilzomib is also undergoing clinical evaluation for additional oncology indications such as relapsed solid tumors, lymphoma, prolymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Synthesis
Carfilzomib is an analog of the natural product epoxomicin which was first synthesized in
the laboratories of Professor Crews at Yale University. Subsequent development of the SAR led to the
discovery of YU-101 in which 3 of the amino acids of this pentapeptide were modified to improve the
potency of the molecule. After licensing the molecule to Proteolix, the introduction of the morpholino
group was found to improve the solubility of the drug while maintaining efficient interaction with the
target. The most scalable route to carfilzomib closely resembles the original route developed toward
epoximicin and is described herein.
The synthesis was initiated with the amide coupling of phenyl alanine methyl ester (53) and N-Boc
leucine (54) using standard coupling reagents to afford dipeptide 55 in high yield the Scheme below. Acidic
removal of the amine protecting group followed by a second amide coupling reaction with N-Boc
homophenyl alanine provided tripeptide 56 in 85% yield for the two steps. Acidic removal of the amine
protecting group followed by acylation with chloroacetyl chloride provided |?-chloro amide 57 in 67%
yield. Reaction of 57 with morpholine in the presence of catalytic amounts of potassium iodide
followed by saponification of the methyl ester with lithium hydroxide provided acid 58 in 87% yield for
the two steps. Amide coupling between acid 58 and keto-epoxyamine 59 (whose preparation is
described in the scheme below) using HOBT as the coupling reagent followed by recrystallization of the
resulting product ultimately gave carfilzomib (IX) in 75% yield.

Keto-epoxyamine 59 was prepared from N-Boc leucine (54) as described in the Scheme below. Reaction of
54 with isobutyl chloroformate followed by N,O-dimethylhydroxylamine provided Weinreb amide 60 in
94% yield. Grignard addition of isopropenylmagnesium bromide 60 provided enone 62 in 81% yield.
Epoxidation of 62 with calcium hypochlorite provided a mixture of epoxides giving 41% yield of the desired isomer (presumably isolated by chromatography), and subsequent treatment with TFA liberated
the amine, providing the TFA salt of ketoepoxy amine 59 in 92% yield.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine - increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Metabolism
Carfilzomib was rapidly and extensively metabolized by the liver. The predominant metabolites were the peptide fragments and the diol of carfilzomib which suggests that the main metabolic pathways are peptidase cleavage and epoxide hydrolysis. The cytochrome P450 enzyme system is minimally involved in the metabolism of carfilzomib. All metabolites are inactive.
Metabolism
Carfilzomib was rapidly and extensively metabolised by mainly peptidase cleavage and epoxide hydrolysis. Cytochrome P450 mediated mechanisms played a minor role in overall carfilzomib metabolism. The metabolites have no known biologic activity.
Storage
Store at -20°C
References
1) Bennett and Kirk (2008)?Development of proteasome inhibitors in oncology and autoimmune diseases; Curr. Opin. Drug Disc. Dev.?11?616 2) Hanada?et al.?(1992),?Epoxomicin, a new antitumor agent of microbial origin; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo),?45?174 3) Demo?et al. (2007)?Antitumor activity of PR-171, a novel irreversible inhibitor of the proteasome; Cancer Res.?67?6383 4) Kuhn?et al. (2007),?Potent activity of carfilzomib, a novel, irreversible inhibitor of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, against preclinical models of multiple myeloma; Blood,?110?328
Properties of Carfilzomib
| Melting point: | 204 - 208°C |
| Boiling point: | 975.6±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.161 |
| Flash point: | 543.8℃ |
| storage temp. | -20° |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 80 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 25 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.17±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 1 week. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 868540-17-4 |
Safety information for Carfilzomib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Carfilzomib
Carfilzomib manufacturer
ALS India Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd
Aquigen Bio science Pvt Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
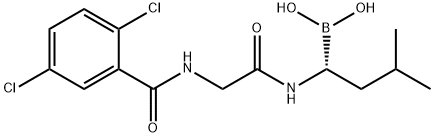

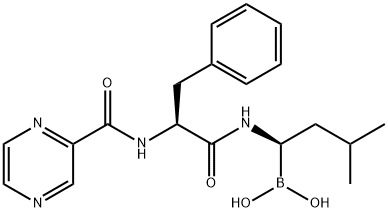
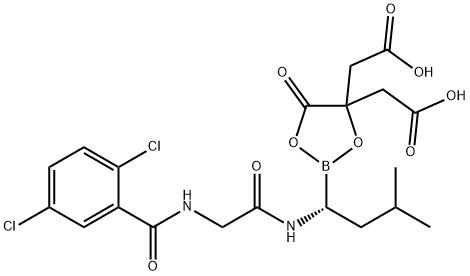

You may like
-
 868540-17-4 98%View Details
868540-17-4 98%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 868540-17-4 99%View Details
868540-17-4 99%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 98%View Details
Carfilzomib 98%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 98%View Details
Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 98%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 98%View Details
Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 98%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 98% (HPLC) CAS 868540-17-4View Details
Carfilzomib 98% (HPLC) CAS 868540-17-4View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 99.66%View Details
Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 99.66%View Details
868540-17-4 -
 Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 99%View Details
Carfilzomib 868540-17-4 99%View Details
868540-17-4
