Bortezomib
Synonym(s):;Bortezomib - CAS 179324-69-7 - Calbiochem;
- CAS NO.:179324-69-7
- Empirical Formula: C19H25BN4O4
- Molecular Weight: 384.24
- MDL number: MFCD09056737
- EINECS: 605-854-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-29 14:06:09
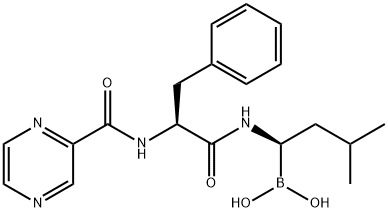
What is Bortezomib?
Absorption
Following intravenous administration of 1 mg/m2 and 1.3 mg/m2 doses, the mean Cmax of bortezomib were 57 and 112 ng/mL, respectively. In a twice-weekly dosing regimen, the Cmax ranged from 67 to 106 ng/mL at the dose of 1 mg/m2 and 89 to 120 ng/mL for the 1.3 mg/m2 dose. In patients with multiple myeloma, the Cmax of bortezomib followig subcutaneous administration was lower than that of intravenously-administered dose; however, the total systemic exposure of the drug was equivalent for both routes of administration. There is a wide interpatient variability in drug plasma concentrations.
Toxicity
The Lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) in mouse was 5 mg/kg/14D following intraperitoneal administration of an intermittent dose and 1.6 mg/kg/12D following subcutaneous administration of a continuous dose.
The therapeutic dose of bortezomib is individualized in each patient to prevent overdose. Fatal outcomes occurred in humans following the administration of more than twice the recommended therapeutic dose of bortezomib. The symptoms from overdose included the acute onset of symptomatic hypotension and thrombocytopenia. As there is no known antidote for bortezomib overdosage, monitoring of vital signs and appropriate supportive care should be initiated when drug overdosage is suspected. In monkeys and dogs, increased heart rate, decreased contractility, hypotension, and death were observed with the intravenous dose as low as two times the recommended clinical dose on a mg/m2 basis. A case of a slight increase in the corrected QT interval leading to death occurred in dog studies.
Description
Bortezomib (trade name Velcade) is a boronic acid that was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2003 as the first drug to treat multiple myeloma, a type of white blood cell cancer. It is a proteazome blocker that is also used to treat mantle cell lymphoma. Bortezomib is a high affinity proteasome inhibitor (Ki = 0.6 nM). Inhibits growth of multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (IC50 values in <50 nM range); induces apoptosis in MM cell lines and MM patient derived cells, including p53 mutant cell lines. Decreases adherence of MM cells lines to bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). Acts synergistically with dexamethasone. Also cytotoxic in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line (IC50 = 50 nM).
Chemical properties
Yellow Solid
Originator
Millenium (LeukoSite, Proscript) (US)
The Uses of Bortezomib
A potent, highly selective and reversible inhibitor of the 20S proteasome, Bortezomib is used as an antineoplastic agent, which controls the growth of cancer cells. It is also useful in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
The Uses of Bortezomib
Bortezomib is the first proteasome inhibitor to be approved b the US FDA for multiple myeloma, a blood cancer. A reversible inhibitor of the 26S proteasome-a barrel-shaped multiprotein particle found in the nucleus and cytosol of all eukaryotic cells. T
What are the applications of Application
Bortezomib is a selective and robust 26S proteasome inhibitor and is a boronic acid dipeptide derivative
Background
Bortezomib is a dipeptide boronic acid derivative and proteasome inhibitor used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. The 26S proteasome is a protein complex that degrades ubiquitinated proteins in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: reversible inhibition of the 26S proteasome, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of cancer cells, is thought to be the main mechanism of action of bortezomib. However, multiple mechanisms may be involved in the anticancer activity of bortezomib.
Bortezomib was first synthesized in 1995. In May 2003, bortezomib became the first anticancer proteasome inhibitor that was approved by the FDA under the trade name VELCADE. Phase I, II, III, and IV clinical trials are undergoing to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of bortezomib in leukemia, myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and solid tumours.
Indications
Bortezomib is indicated for the treatment of adults with multiple myeloma or mantle cell lymphoma.
Definition
ChEBI: L-Phenylalaninamide substituted at the amide nitrogen by a 1-(dihydroxyboranyl)-3-methylbutyl group and at Nalpha by a pyrazin-2-ylcarbonyl group. It is a dipeptidyl boronic acid tha reversibly inhibits the 26S proteasome.
brand name
Velcade (Millennium).
Mechanism of action
Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor. The proteasomal system plays a vital role in cellular protein turnover, which is essential for the homeostasis of cells. Bortezomib reversibly binds to the chymotrypsin-like subunit of the 26S proteasome, resulting in its inhibition and preventing the degradation of various pro-apoptotic factors. The accumulation will eventually activate the programmed cell death via caspase-mediated pathways in the neoplastic cells that are usually dependent on the suppression of pro-apoptotic pathways for their proliferation and survival.
General Description
Proteasomes normally function to degrade proteins that areno longer needed by the cell. Such proteins are normallymarked by the addition of ubiquitin, a 76 amino acid proteinthat is added to the -amino group of lysine residues onthe target proteins. The marked proteins are then hydrolyzedby the large barrel-shaped proteasomes to givepeptides of 7 to 8 residues that may be further hydrolyzedand reutilized by the cell. This process serves to regulateprotein levels within the cell, remove defective proteins,and becomes important in maintaining normal signal transduction.Inhibition of the proteasomes results in the buildup of ubiquitylated proteins, which disrupts cell-signalingprocesses and cell growth. The signaling bytranscription factor NF-B (nuclear factor B) appears tobe especially sensitive to bortezomib. NF-B is associatedwith the transcription of antiapoptotic and proliferativegenes but is under the control of IB (inhibitor of NF-B).IB can itself be phosphorylated by IKK (IB kinase),which marks IB for ubiquitylation and destruction allowingNF-B to mediate its antiapoptotic and proliferative effects effects.In the presence of the competitive inhibitor bortezomib(IC50=0.6 nM), the 26S proteasome is inhibitedand the ubiquitylated IkB is still capable of inhibiting NF-kB, preventing its effects.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Bortezomib belong to the class of drugs called proteasome inhibitors and is licensed in the United States and
the United Kingdom for the treatment of multiple myeloma. The drug has been licensed for patients in whom
the myeloma has progressed despite prior treatment or where a bone marrow transplant is not possible or was
not successful. It is marketed under the name Velcade? or Cytomib?. Velcade is administered via injection
and is sold as powder for reconstitution.
Bortezomib was the first drug approved in the new drug class of proteasome inhibitors and boron seems to
be its active element. For the mode of action, it is believed that the boron atom binds with high affinity and
specificity to the catalytic site of 26S proteasome and inhibits its action. Therapy with Bortezomib can lead
to a variety of adverse reactions, including peripheral neuropathy, myelosuppression, renal impairment and
gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances together with changes in taste. Nevertheless, the side effects are in most
cases less severe than with alternative treatment options such as bone marrow transplantation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable: yes
Pharmacokinetics
Bortezomib works to target the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, an essential molecular pathway that regulates intracellular concentrations of proteins and promotes protein degradation. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is often dysregulated in pathological conditions, leading to aberrant pathway signalling and the formation of malignant cells. In one study, patient-derived chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells contained 3-fold higher levels of chymotrypsin-like proteasome activity than normal lymphocytes. By reversibly inhibiting proteasome, bortezomib prevents proteasome-mediated proteolysis. Bortezomib exerts a cytotoxic effect on various cancer cell types in vitro and delays tumour growth in vivo in nonclinical tumour models. Bortezomib inhibits the proteasome activity in a dose-dependent manner. In one pharmacodynamic study, more than 75% of proteasome inhibition was observed in whole blood samples within one hour after dosing of bortezomib.
Clinical Use
Proteasome inhibitor:
Treatment of multiple myeloma for people who have
already tried at least 1 prior therapy and have disease
progression
Synthesis
Although the synthesis of dipeptidyl boronic acids have appeared on several reports, the synthetic details for bortezomib were not revealed. The synthetic route for the preparation of bortezomib is depicted in the scheme.The pinanediol ester of leucine boronic acid (56)was coupled with N-Boc phenylalanine (57) in the presence of TBTU followed by deprotection of the Boc group to provide 58. N-Acylation of 58 then furnished the dipeptide boronate ester 60. Deprotection of the boronic ester functionality was achieved by bi-phase transfer esterification with isobutyl boronic acid. Bortezomib (VI) was isolated by extractive workup.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: potential reduced efficacy with
rifampicin resulting in increased monoclonal IgG
λ – avoid.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine, increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Metabolism
In vitro studies with human liver microsomes and human cDNA-expressed cytochrome P450 isozymes indicate that bortezomib is primarily oxidatively metabolised via cytochrome P450 enzymes, 3A4, 2C19, and 1A2. The major metabolic pathway is deboronation to form two deboronated metabolites that subsequently undergo hydroxylation to several metabolites. Deboronated-bortezomib metabolites are inactive as 26S proteasome inhibitors.
Metabolism
Bortezomib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2C19, and CYP1A2. CYP2D6 and CYP2C9 are also involved in drug metabolism, but to a smaller extent. Oxidative deboronation, which involves the removal of boronic acid from the parent compound, is the main metabolic pathway. Metabolites of bortezomib are pharmacologically inactive and more than 30 metabolites have been identified in human and animal studies.
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Adams et al. (1999), Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents; Cancer Res., 59 2615 2) Williams et al. (2003), Differential effects of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib on apoptosis and angiogenesis in human prostate tumor xenografts; Mol. Cancer Ther., 2 835 3) Richardson et al. (2003), Bortezomib (PS-341): a novel, first-in-class proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of multiple myeloma and other cancers; Cancer Control, 10 361 4) Herve and Ibrahim (2017), Proteasome inhibitors to alleviate aberrant IKBKAP mRNA splicing and low IKAP/hELP1 synthesis in familial dysautonomia; Neurobiol. Dis., 103 113
Properties of Bortezomib
| Melting point: | 122-124°C |
| Density | 1.214 |
| RTECS | ED7771666 |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethanol and methanol. |
| form | solid |
| pka | 9.66±0.43(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic and Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 179324-69-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Bortezomib
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P320:Specific treatment is urgent (see … on this label). P330:Rinse mouth. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Bortezomib
Bortezomib manufacturer
Sumar biotech LLP
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 bortezomib working std 99%View Details
bortezomib working std 99%View Details
179324-69-7 -
 Bortezomib 98%View Details
Bortezomib 98%View Details -
 179324-69-7 98%View Details
179324-69-7 98%View Details
179324-69-7 -
 179324-69-7 Bortezomib 98%View Details
179324-69-7 Bortezomib 98%View Details
179324-69-7 -
 179324-69-7 99%View Details
179324-69-7 99%View Details
179324-69-7 -
 Bortezomib 98% CAS 179324-69-7View Details
Bortezomib 98% CAS 179324-69-7View Details
179324-69-7 -
 Bortezomib CAS 179324-69-7View Details
Bortezomib CAS 179324-69-7View Details
179324-69-7 -
 Bortezomib APIView Details
Bortezomib APIView Details
179324-69-7
