Calcitriol
Synonym(s):Calcitriol;(1α,3β,5Z,7E)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-1,3,25-triol monohydrate;1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol;1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol monohydrate;1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
- CAS NO.:32222-06-3
- Empirical Formula: C27H44O3
- Molecular Weight: 416.64
- MDL number: MFCD00867079
- EINECS: 250-963-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
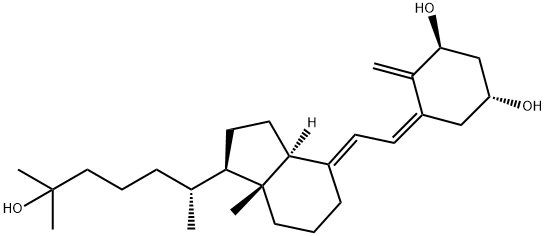
What is Calcitriol?
Absorption
Upon administration, calcitriol is rapidly absorbed from the intestines. When a single oral dose of 0.5 mcg of calcitriol was administered, the mean serum concentrations of calcitriol rose from a baseline value of 40.0±4.4 (SD) pg/mL to 60.0±4.4 pg/mL at 2 hours, and declined to 53.0±6.9 at 4 hours, 50±7.0 at 8 hours, 44±4.6 at 12 hours and 41.5±5.1 at 24 hours . Following administration of single doses of 0.25 to 1.0 mcg of calcitriol, the peak plasma concentrations were reached within 3 to 6 hours . In a pharmacokinetic study, the oral bioavailability was 70.6±5.8% in healthy male volunteers and 72.2±4.8% in male patients with uraemia .
Toxicity
LD50 (oral, rat) = 620 μg/kg; LD50 (intraperitoneal, rat) > 5 mg/kg .
Symptoms of calcitriol toxicity mirrors the early and late signs and symptoms of vitamin D intoxication associated with hypercalcemia . Early signs include weakness, headache, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, muscle pain, bone pain and metallic taste. Late signs are characterized by polyuria, polydipsia, anorexia, weight loss, nocturia, conjunctivitis (calcific), pancreatitis, photophobia, rhinorrhea, pruritus, hyperthermia, decreased libido, elevated BUN, albuminuria, hypercholesterolemia, elevated SGOT and SGPT, ectopic calcification, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias and, rarely, overt psychosis .
Description
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D and is also a kind of hormones in the body. It plays an important role in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus concentration. It can increase the blood calcium level by increasing the intestinal absorption of calcium and can also increase the release of the bone calcium release for increasing the blood calcium levels. This study was first conducted and reported by Michael F. Holick in 1971. The basic principle of action model of calcitriol in many cases is through binding with the vitamin D receptor (the VDR), e.g., the ligand-receptor complex forming between calcitriol and its receptor in the intestinal epithelial cells cytoplasm can be transferred to the nucleus for being as the transcriptional factor in promoting the expression of calcium-binding protein. The increased level of calcium-binding proteins can help the cell to actively transport of more calcium ions, thereby increasing the calcium absorption level. Calcium absorption while maintaining electrical neutrality also requires transporting anions, mainly the absorption of inorganic phosphate ions, so calcitriol also promote the absorption of phosphorus.
Clinically, this drug can be used in the treatment of hypocalcemia, hypoparathyroidism (adult), osteomalacia, rickets (infants), chronic kidney disease, renal osteodystrophy, osteoporosis, as well as the prevention of glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis.

Calcitriol-dimensional molecular structure
The above information is edited by the chemicalbook of Dai Xiongfeng.
Description
Calcitriol, or 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, is the biologically active metabolite of vitamin D3. Its existence and activity were first described by several research groups in the early 1970s. It improves calcium transport in the blood and absorption of calcium from the blood to bones. More recently,?Calcitriol’s role in immune system defenses?was elucidated by C. Geisler and co-workers.
Description
Calcitriol is synthesized from 7-
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Powder
Originator
Rocaltrol,Roche,US,1978
The Uses of Calcitriol
Calcitriol (1α,25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3) is synthesized from 7-dehydrocholesterol in humans via a non-enzymatic photochemical reaction with 290-310 nm UV light in the skin. Hydroxylation of the resulting cholecalciferol in the liver produces 25-hydroxy Vitamin D3, the principal circulating form of Vitamin D. A second, tightly regulated hydroxylation in the kidney produces calcitriol. Plasma calcitriol levels range from 10-70 pg/ml and are influenced by numerous dietary and hormonal factors. The main physiologic effects of calcitriol are to increase the absorption of calcium at the level of the intestinal epithelium, and to increase the mineralization of bone via the direct stimulation of osteoblasts.[Cayman Chemical]
The Uses of Calcitriol
The biologically active form of vitamin D3. Calcium regulator; vitamin (antirachitic); antihyperparathyroid; antineoplastic; antipsoriatic
The Uses of Calcitriol
Calcium regulator, anti-psoriatic
The Uses of Calcitriol
Vitamin medicines; it can be used for treating the renal bone malnutrition of patients with chronic renal failure;
Indications
Used to treat vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency, refractory rickets (vitamin D resistant rickets), familial hypophosphatemia and hypoparathyroidism, and in the management of hypocalcemia and renal osteodystrophy in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing dialysis. Also used in conjunction with calcium in the management and prevention of primary or corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis.
What are the applications of Application
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 is also known as Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3, and an activator of PKC and VDR
Background
Calcitriol is an active metabolite of vitamin D with 3 hydroxyl (OH) groups and is commonly referred to as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, or 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. It is produced in the body after series of conversion steps of 7-dehydrocholesterol from exposure to UV light. 7-dehydrocholesterol is converted to Vitamin D3 (vitamin D3) in the skin, which is then converted to Calcifediol in the liver and kidneys. Calcifediol undergoes hydroxylation to form calcitriol via 1α-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) activity . Calcitriol is considered to be the most potent metabolite of vitamin D in humans . Renal production of calcitriol is stimulated in response to PTH, low calcium and low phosphate . Calcitriol plays a role in plasma calcium regulation in concert with parathyroid hormone (PTH) by enhancing absorption of dietary calcium and phosphate from the gastrointestinal tract, promoting renal tubular reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys, and stimulating the release of calcium stores from the skeletal system. In addition to promoting fatty acid synthesis and inhibiting lipolysis, calcitriol has been demonstrated to increase energy efficiency by suppressing UCP2 expression, which is modulated by signaling pathways of classical nuclear receptors (nVDR), where calcitriol acts as a natural ligand . There is also evidence that calcitriol modulates the action of cytokines and may regulate immune and inflammatory response, cell turnover, cell differentiation .
Administered orally and intravenously, calcitriol is commonly used as a medication in the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism and resultant metabolic bone disease, hypocalcemia in patients undergoing chronic renal dialysis, and osteoporosis. It is also available in topical form for the treatment of mild to moderate plaque psoriasis in adults. Calcitriol is marketed under various trade names including Rocaltrol (Roche), Calcijex (Abbott) and Decostriol (Mibe, Jesalis).
Definition
ChEBI: Calcitriol is a hydroxycalciol that is calcidiol in which the pro-S hydrogen of calcidiol is replaced by a hydroxy group. It is the active form of vitamin D3, produced fom calciol via hydoxylation in the liver to form calcidiol, which is subsequently oxidised in the kidney to give calcitriol. It has a role as a bone density conservation agent, an antipsoriatic, an immunomodulator, an antineoplastic agent, a calcium channel modulator, a nutraceutical, a calcium channel agonist, a metabolite, a hormone, a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a hydroxycalciol, a member of D3 vitamins and a triol.
Manufacturing Process
1α,25-Dihydroxyprecholecalciferol: A solution of 1α,25-
diacetoxyprecholecalciferol (0.712 g, 1.42 mmols), potassium hydroxide (2.0
g, 35.6 mmols) and methanol (40 ml) was stirred at room temperature under
argon for 30 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced
pressure. Water (50 ml) was added to the residue and the mixture was
extracted with methylene chloride (3 x 100 ml). The combined organic
extracts were washed with saturated sodium chloride solution (3 x 50 ml),
dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and evaporated under reduced
pressure to give 0.619 g of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyprecholecalciferol as a thick
oil.
1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol: A solution of 1α,25-dihydroxyprecholecalciferol
[0.619 g in dioxane (30 ml)] was heated under reflux for 30 minutes under an
atmosphere of argon. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified with a Waters Associates liquid
chromatograph model 202 using a 8 foot * 3/8 inch Porasil A column and a
5:1 mixture of ethyl acetate-n-hexane as the eluent to give 0.474 g (80%
yield based on 1α,25-diacetoxyprecholecalciferol) of pure 1α,25-
dihydroxycholecalciferol. Recrystallization from methyl formate afforded 0.340
g of 1α,25-dihydroxcholecalciferol as colorless crystals, MP 113°-114°C.
brand name
Calcijex (Abbott); Rocaltrol (Roche.
Therapeutic Function
Calcium regulator
General Description
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3, also referred as calcitriol, is a calcitrophic hormone. It is the most biologically active metabolite of vitamin D produced in proximal tubular cells in the kidney.
Biological Activity
Active metabolite of vitamin D 3 that activates the vitamin D receptor (VDR). Displays calcemic actions; stimulates intestinal and renal Ca 2+ absorption and regulates bone Ca 2+ turnover. Exhibits antitumor activity; inhibits in vivo and in vitro cell proliferation in a wide range of cells including breast, prostate, colon, skin and brain carcinomas and myeloid leukemia cells.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Biologically active form of vitamin D3 in calcium absorption and deposition. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 has widespread effects on cellular differentiation and proliferation, and can modulate immune responsiveness, and central nervous system function. Recent studies suggest that 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 acts as a chemopreventive agent against several malignancies including cancers of the prostate and colon and shows synergy with other anticancer compounds.
Pharmacokinetics
Calcitriol is a biologically active calcitrophic hormone with anti-osteoporotic, immunomodulatory, anticarcinogenic, antipsoriatic, antioxidant, and mood-modulatory activities. Its main sites of action are the intestine, bone, kidney and parathyroid hormone . Calcitriol is a ligand for the vitamin D nuclear receptor, which is expressed in, but not limited to, gastrointestinal (GI) tissues, bones, and kidneys . As an active form of vitamin D3, calcitriol elevates the plasma levels of calcium by stimulating intestinal calcium uptake, increasing reabsorption of calcium by the kidneys, and possibly increasing the release of calcium from skeletal stores. The duration of pharmacologic activity of a single dose of exogenous calcitriol is expected to be about 3 to 5 days .
In addition to its important role in calcium metabolism, other pharmacological effects of calcitriol have been studied in various conditions including cancer models. Various studies demonstrated expression of vitamin D receptors in cancer cell lines, including mouse myeloid leukemia cells . Calcitriol has been found to induce differentiation and/or inhibit cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo in many cell types, such as malignant cell lines carcinomas of the breast, prostate, colon, skin, and brain, myeloid leukemia cells, and others . In early human prostate cancer trials, administration of 1.5 μg/d calcitriol in male participants resulted in a reduction in the rate of PSA rise in most participants, however it was coincided with dose-limiting hypercalcemia in most participants . Hypercalcemia and hypercalcuria were evident in numerous initial trials, and this may be due to these trials not testing the drug at concentrations that are active in preclinical systems . Findings from preclinical data show an additive or synergistic antineoplastic action of calcitriol when combined with agents including dexamethasone, retinoids, and radiation, as well as several cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs such as platinum compounds .
Vitamin D deficiency has long been suspected to increase the susceptibility to tuberculosis. The active form of calcitriol, 1,25-(OH)2-D3, has been found to enhance the ability of mononuclear phagocytes to suppress the intracellular growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 1,25-(OH)2-D3 has demonstrated beneficial effects in animal models of such autoimmune diseases as rheumatoid arthritis. Vitamin D appears to demonstrate both immune-enhancing and immunosuppressive effects.
Clinical Use
Vitamin D analogue:
Promotes intestinal calcium absorption
Suppresses PTH production and release
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Calcitriol may be potentially beneficial in the adjunctive treatment of chronic renal disease in dogs and cats but its use is somewhat controversial, particularly the decision on how soon in the course of chronic renal insufficiency it should employed. It may also be of benefit in treating some types of dermatopathies (primary idiopathic seborrhea).
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antiepileptics: the effects of vitamin D may
be reduced in patients taking barbiturates or
anticonvulsants.
Diuretics: increased risk of hypercalcaemia with
thiazides.
Sevelamer: absorption may be impaired by sevelamer
Metabolism
Metabolism of calcitriol involves two pathways . The first pathway involves 24-hydroxylase activity in the kidney; this enzyme is also present in many target tissues which possess the vitamin D receptor such as the intestine. The end product of this pathway is a side chain shortened metabolite, calcitroic acid. The second pathway involves the conversion of calcitriol via the stepwise hydroxylation of carbon-26 and carbon-23, and cyclization to yield ultimately 1a,25R(OH)2-26,23S-lactone D3, which appears to be the major metabolite circulating in humans.
Ohter identified metabolites of calcitriol include 1α, 25(OH)2-24-oxo-D3; 1α, 23,25(OH)3-24-oxo-D3; 1α, 24R,25(OH)3D3; 1α, 25S,26(OH)3D3; 1α, 25(OH)2-23-oxo-D3; 1α, 25R,26(OH)3-23-oxo-D3 and 1α, (OH)24,25,26,27-tetranor-COOH-D3 .
Metabolism
During transport in the blood at physiological concentrations, calcitriol is mostly bound to a specific vitamin D binding protein (DBP), but also, to a lesser degree, to lipoproteins and albumin. At higher blood calcitriol concentrations, DBP appears to become saturated, and increased binding to lipoproteins and albumin occurs. Calcitriol is inactivated in both the kidney and the intestine, through the formation of a number of intermediates including the formation of the 1,24,25-trihydroxy derivatives. It is excreted in the bile and faeces and is subject to enterohepatic circulation.
Storage
Desiccate at -20°C
Properties of Calcitriol
| Melting point: | 119-1210C |
| Boiling point: | 474.91°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +48° (methanol) |
| Density | 1.0362 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4700 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 14 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Do you have solubility information on this product that you would like to share |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 14.43±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
| λmax | 265nm(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,1644 |
| BRN | 7559394 |
| Stability: | Air and Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 32222-06-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Calcitriol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcitriol
| InChIKey | GMRQFYUYWCNGIN-UNVJKIGWSA-N |
Calcitriol manufacturer
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 32222-06-3 98%View Details
32222-06-3 98%View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Calcitriol 99%View Details
Calcitriol 99%View Details -
 32222-06-3 Calcitriol 98%View Details
32222-06-3 Calcitriol 98%View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Calcitriol 99%View Details
Calcitriol 99%View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Calcitriol CAS 32222-06-3View Details
Calcitriol CAS 32222-06-3View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Calcitriol solution CAS 32222-06-3View Details
Calcitriol solution CAS 32222-06-3View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Calcitriol Cas No. 32222 06 3View Details
Calcitriol Cas No. 32222 06 3View Details
32222-06-3 -
 Rocaltrol 0 25 Mcg CapsulesView Details
Rocaltrol 0 25 Mcg CapsulesView Details
32222-06-3