Ampicillin
Synonym(s):D- (−)-α-Aminobenzylpenicillin;Ampicillin;Ampicillin trihydrate
- CAS NO.:69-53-4
- Empirical Formula: C16H19N3O4S
- Molecular Weight: 349.4
- MDL number: MFCD00072036
- EINECS: 200-709-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
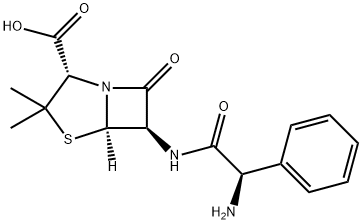
What is Ampicillin?
Description
Ampicillin is an antibacterial antibiotic from the α-aminobenzyl penicillin group, which differs from penicillin by the presence of an amino group that facilitates penetration through the outer membrane of some gram-negative bacteria.
Ampicillin is Semi-synthetic derivative of penicillin that functions as an orally active broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Chemical properties
Ampicillin in anhydrous form occurs as crystals.
Originator
Binotal,Bayer,W. Germany,1962
The Uses of Ampicillin
Labelled Ampicillin. Orally active, semi-synthetic antibiotic; structurally related to penicillin. Antibacterial.
The Uses of Ampicillin
β-lactam antibiotics
The Uses of Ampicillin
Ampicillin caused contact dermatitis in a nurse also sensitized to amoxicillin (with tolerance to oral phenoxymethylpenicillin), and in a pharmaceutical factory worker.
Indications
For treatment of infection (Respiratory, GI, UTI and meningitis) due to E. coli, P. mirabilis, enterococci, Shigella, S. typhosa and other Salmonella, nonpenicillinase-producing N. gononhoeae, H. influenzae, staphylococci, streptococci including streptoc
Background
Ampicillin is a semi-synthetic derivative of penicillin that functions as an orally active broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Definition
ChEBI: A penicillin in which the substituent at position 6 of the penam ring is a 2-amino-2-phenylacetamido group.
Manufacturing Process
α-Carbobenzyloxyaminophenylacetic acid (0.1 mol), which is obtained by the
reaction of equivalent quantities of α-aminophenylacetic acid and benzyl
chlorocarbonate in aqueous sodium hydroxide, dissolved in dry acetone is
stirred and cooled to approximately -5°C. To this there is added dropwise with
continued cooling and stirring a solution of ethyl chlorocarbonate (0.1 mol).
After approximately 10 minutes, the acylating mixture is cooled to about -5°C
and then is slowly added to a stirred ice-cold mixture of 6-aminopenicillanic
acid (0.1 mol), 3% sodium bicarbonate solution (0.1 mol) and acetone. This
reaction mixture is allowed to attain room temperature, stirred for an
additional thirty minutes at this temperature and then is extracted with ether.
The extracted aqueous solution is covered with butanol and the pH adjusted
to 2 by the addition of HCl. The acidified aqueous phase is extracted with
butanol, the pH of the aqueous phase being adjusted to pH 2 each time. The
combined butanol solutions which contain the free acid, α-
carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin, are washed with water, and are then
shaken with water to which sufficient 3% sodium bicarbonate has been added
to bring the aqueous phase to pH 7. The process of washing and shaking is
repeated with fresh water and bicarbonate solution. The combined aqueous
solutions are washed with ether and then are evaporated under reduced
pressure and low temperature. The product, the sodium salt of α-
carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin, is obtained as a yellow solid in a yield of
65%.
A suspension of palladium on barium carbonate (3.7 grams of 30%) in water
(20 ml) is shaken in an atmosphere of hydrogen at room temperature. The
catalyst is then filtered and washed well with water, care being taken that it
does not become dry. A solution of the sodium salt of α-
carbobenzyloxyaminobenzylpenicillin (4 grams) in water (20 ml) is added to
the pretreated catalyst and the suspension is shaken in an atmosphere of
hydrogen at room temperature and pressure for one hour. The catalyst is then filtered off, washed well with water, and the combined filtrate and washings
adjusted to pH 7 with hydrochloric acid. The resulting solution is evaporated in
vacuum at a temperature below 20°C to give α-aminobenzylpenicillin (2.4
grams, 74% yield), which is assayed at approximately 48% pure by the
manometric method.
brand name
Amcill (Parke-Davis); Omnipen (Wyeth-Ayerst); Polycillin (Apothecon); Principen (Apothecon).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Mechanism of action
Ampicillin acts by interfering directly with the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan, which constitutes the major component of the bacterial cell wall, leading to structural instability and death of bacteria.
General Description
Ampicillin was synthesized by Beecham Research Laboratories in 1961 and evaluated for its anti-gram-negative activity by Rolinson et al.. It was the first semisynthetic penicillin showing strong activity against gramnegative bacilli. Although it is hydrolyzed by bacterial penicillinase, it is active against Escherichia coli, Shigella, Proteus mirabilis, and Haemophilus influenzae and is used very widely as an oral antibiotic. Ampicillin also is used by injection for serious infections.
Contact allergens
Ampicillin caused contact dermatitis in a nurse also sensitized to amoxicillin (with tolerance to oral phenoxymethylpenicillin) and in a pharmaceutical factory worker. Systemic drug reactions are common. Crossreactivity is regular with ampicillin and can occur with other penicillins.
Pharmacokinetics
Ampicillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Ampicillin has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of Ampicillin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through Ampicillin binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Ampicillin is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Side Effects
Common side effects include rash, nausea, and diarrhea. It should not be used in people who are allergic to penicillin. Serious side effects may include Clostridium difficile colitis or anaphylaxis. While usable in those with kidney problems, the dose may need to be decreased.
Safety Profile
Poison by intracerebral route. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: fever, agranulocytosis, and other blood effects. An experimental teratogen. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NO, and SOx,.
Potential Exposure
Used as an antibiotic.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In dogs and cats, ampicillin is not as well absorbed after oral administration
as amoxicillin and its oral use has largely been supplanted
by amoxicillin. It is used commonly in parenteral
dosage
forms when an aminopenicillin is indicated in all species.
The aminopenicillins, also called the “broad-spectrum” or ampicillin
penicillins, have increased activity
against many strains of
gram-negative aerobes not covered by either the natural penicillins
or penicillinase-resistant penicillins, including some strains of E.
coli, Klebsiella, and Haemophilus.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained onits proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from strongoxidizers and moisture.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
May be incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator.
Properties of Ampicillin
| Melting point: | 198-200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 201.8°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D23 +287.9° (c = 1 in water) |
| Density | 1.2794 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6320 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | NH4OH 1 M: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | solid |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| pka | 2.5 (COOH)(at 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 13.9g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,591 |
| JECFA Number | 85 |
| BRN | 1090925 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be moisture sensitive. Incopmpatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69-53-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 50) 1990 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ampicillin (69-53-4) |
Safety information for Ampicillin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ampicillin
| InChIKey | AVKUERGKIZMTKX-NJBDSQKTSA-N |
Ampicillin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
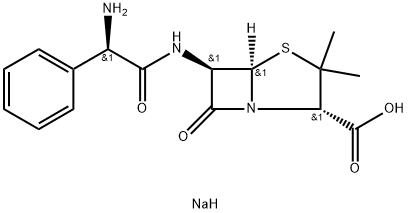
 69-53-4 Piperacillin EP Impurity A 98%View Details
69-53-4 Piperacillin EP Impurity A 98%View Details
69-53-4 -
 69-53-4 98%View Details
69-53-4 98%View Details
69-53-4 -
 Ampicillin 98%View Details
Ampicillin 98%View Details
69-53-4 -
 Ampicillin 96% CAS 69-53-4View Details
Ampicillin 96% CAS 69-53-4View Details
69-53-4 -
 Ampicillin CAS 69-53-4View Details
Ampicillin CAS 69-53-4View Details
69-53-4 -
 Ampicillin CAS 69-53-4View Details
Ampicillin CAS 69-53-4View Details
69-53-4 -
 Ampicillin API PowderView Details
Ampicillin API PowderView Details
69-52-3 -
 Ampicillin API PowderView Details
Ampicillin API PowderView Details
69-52-3
