Butenafine
- CAS NO.:101828-21-1
- Empirical Formula: C23H27N
- Molecular Weight: 317.47
- MDL number: MFCD00865577
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-17 18:22:24
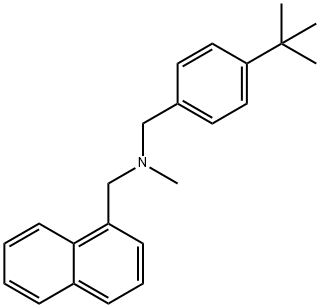
What is Butenafine?
Absorption
The total amount absorbed through the skin into the systemic circulation has not been quantified.
The Uses of Butenafine
Butenafine (Mentax) is a synthetic benzylamine antifungal agent, related structurally and pharmacologically to terbinafine. It is thought to act by inhibiting the enzyme squalene 2,3-epoxidase, resulting in decreased ergosterol and corresponding increase in squalene, with subsequent cell membrane permeability alteration and cell death. It is active against dermatophytes, yeast, and Sporothrix.

Background
Butenafine hydrochloride is a synthetic benzylamine antifungal agent. Butenafine's mechanism of action is believed to involve the synthesis inhibition of sterols. In particular, butenafine acts to inhibit the activity of the squalene epoxidase enzyme that is essential in the formation of sterols necessary for fungal cell membranes.
Indications
For the topical treatment of the following dermatologic infections: tinea (pityriasis) versicolor due to M. furfur, interdigital tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea corporis (ringworm) and tinea cruris (jock itch) due to E. floccosum, T. mentagrophytes, T. rubrum, and T. tonsurans.
Definition
ChEBI: Trimethylamine in which hydrogen atoms attached to different methyl groups are substituted by 1-naphthyl and 4-tert-butylphenyl groups. It is an inhibitor of squalene epoxidase, an enzyme responsible for the creation of sterols needed in funga cell membranes, and is used as its hydrochloride salt for treatment of dermatological fungal infections.
brand name
Lotrimin (Schering); Mentax (Mylan Bertek).
Pharmacokinetics
Butenafine is a synthetic antifungal agent that is structurally and pharmacologically related to allylamine antifungals. The exact mechanism of action has not been established, but it is suggested that butenafine's antifungal activity is exerted through the alteration of cellular membranes, which results in increased membrane permeability, and growth inhibition. Butenafine is mainly active against dermatophytes and has superior fungicidal activity against this group of fungi when compared to that of terbinafine, naftifine, tolnaftate, clotrimazole, and bifonazole. It is also active against Candida albicans and this activity is superior to that of terbinafine and naftifine. Butenafine also generates low MICs for Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus spp. as well.
Metabolism
The primary metabolite in urine was formed through hydroxylation at the terminal t-butyl side-chain.
Properties of Butenafine
| Melting point: | 200-202 °C |
| Boiling point: | 426.1±14.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.032±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 63 mg/mL (198.44 mM);Ethanol: 63 mg/mL (198.44 mM) |
| pka | 7.87±0.50(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | Water: Insoluble |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101828-21-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Butenafine
Computed Descriptors for Butenafine
Butenafine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
