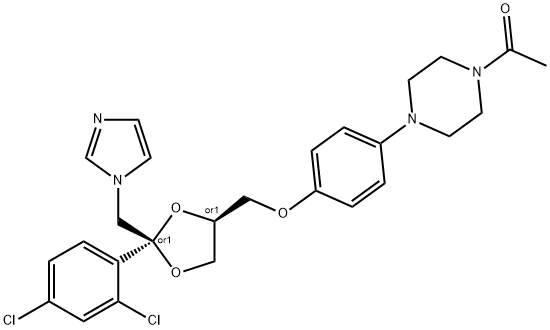
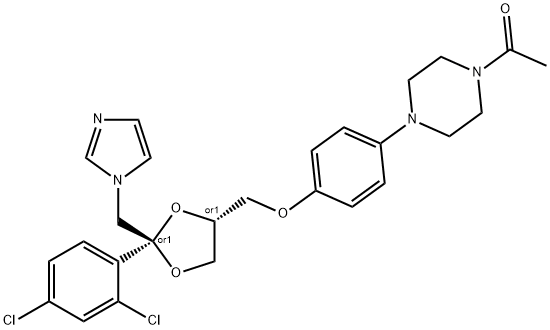
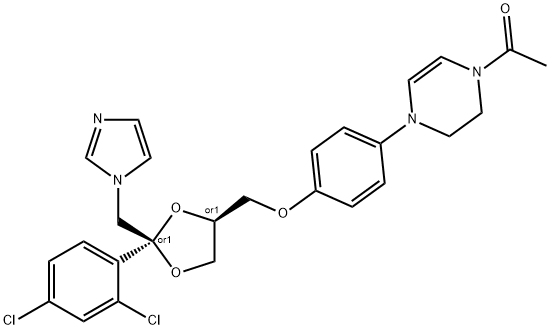
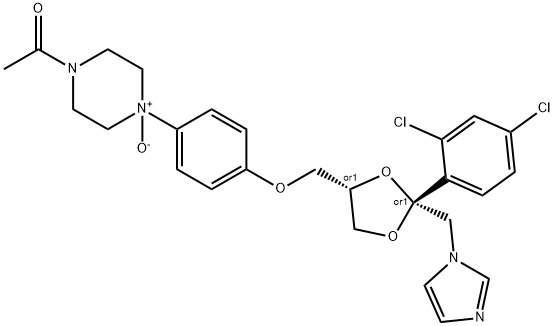
Ketoconazole
Synonym(s):(±)-cis-1-Acetyl-4-(4-[(2-[2,4-dichlorophenyl]-2-[1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl]-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)-methoxy]phenyl)piperazine;cis-1-Acetyl-4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazine, R-41400, CYP17A1 Inhibitor I;Ketoconazole;Ketoconazole - CAS 65277-42-1 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:65277-42-1
- Empirical Formula: C26H28Cl2N4O4
- Molecular Weight: 531.43
- MDL number: MFCD00058579
- EINECS: 265-667-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is Ketoconazole?
Absorption
Ketoconazole requires an acidic environment to become soluble in water. At pH values above 3 it becomes increasingly insoluble with about 10% entering solution in 1 h. At pH less than 3 dissolution is 85% complete in 5 min and entirely complete within 30 min. A single 200 mg oral dose produces a Cmax of 2.5-3 mcg/mL with a Tmax of 1-4 h. Administering ketoconazole with food consistently increases Cmax and delays Tmax but literature is contradictory regarding the effect on AUC, which may experience a small decrease. A bioavailablity of 76% has been reported for ketoconazole.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include acute liver injury, which may include both hepatocellular and cholestatic injury, accompanied by anorexia, fatigue, nausea, and jaundice. In case of overdose, gastric lavage with activated charcoal may be used if within one hour of ketoconazole ingestion otherwise provide supportive care. If the patient shows signs of adrenal insufficiency, administer 100 mg hydrocortisone once together with saline and glucose infusion and monitor the patient closely. Blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte balance should be monitored over the next few days.
Description
Ketoconazole (Nizoral), an orally effective broadspectrum antifungal agent, blocks hydroxylating enzyme systems by interacting with cytochrome P450 at the heme iron site to inhibit steroid and/or androgen synthesis in adrenals, gonads, liver, and kidney. The most sensitive site of action appears to be the C17-20 lyase reaction involved in the formation of sex steroids. This explains the greater suppressibility of testosterone production than with cortisol. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage and 11β/18-hydroxylase are secondary sites of inhibition.
Chemical properties
White or almost white powder.
Originator
Nizoral,Janssen,US,1981
The Uses of Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is used to treat candidiasis, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, oral thrush, candiduria, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, chromomycosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. Ketoconazole is an antifungal agent.
The Uses of Ketoconazole
Inhibits cytochrome P-450 dependent steps in the biosynthesis of steroid hormones in vivo. Antimetastatic and antineoplastic activity. Orally active 5-lipoxygenase and thromboxane synthase inhibitor
The Uses of Ketoconazole
antifungal, PXR/SRC1 & CAR/SRC1 inhibitor
The Uses of Ketoconazole
An inhibitor of CYP proteins, thromboxane synthetase, and 5-LO
Indications
Ketoconazole is used to treat serious fungal or yeast infections, such as candidiasis (thrush, oral thrush), blastomycosis (Gilchrist's disease), coccidioidomycosis (Valley fever, San Joaquin Valley fever), histoplasmosis (Darling's disease), chromoblastomycosis (chromomycosis), or paracoccidioidomycosis (South American blastomycosis, Lutz-Splendore-Almeida disease). This medicine works by killing the fungus or yeast or preventing its growth.
Background
Ketoconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent used in the prevention and treatment of a variety of fungal infections. It functions by preventing the synthesis of ergosterol, the fungal equivalent of cholesterol, thereby increasing membrane fluidity and preventing growth of the fungus. Ketoconazole was first approved in an oral formulation for systemic use by the FDA in 1981. At this time it was considered a significant improvement over previous antifungals, miconazole and clotrimazole, due to its broad spectrum and good absorption. However, it was discovered that ketoconazole produces frequent gastrointestinal side effects and dose-related hepatitis. These effects combined with waning efficacy led to its eventual replacement by triazole agents, fluconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole. Ketoconazole and its predecessor clotrimazole continue to be used in topical formulations.
What are the applications of Application
Ketoconazole is an inhibitor of CYP proteins, thromboxane synthetase, and 5-LO
Definition
ChEBI: (2R,4S)-ketoconazole is a cis-1-acetyl-4-(4-{[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazine which dioxolane moiety has (2R,4S)-configuration. It is an enantiomer of a (2S,4R)-ketoconazole.
Indications
Ketoconazole (Nizoral) is approved for treating dermatophyte infections unresponsive to griseofulvin and for patients unable to tolerate that drug. It is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that in very high doses inhibits several steps in the biosynthesis of both adrenal and gonadal steroids. While the normal antifungal dose is 200 mg/day, testosterone biosynthesis in both the adrenal and testis is completely abolished by doses of 800 to 1,600 mg/day. This drug is used most commonly for large virilizing adrenal tumors that cannot be surgically removed.
brand name
Ketozole (Taro); Nizoral (Janssen); Nizoral (McNeil);Cerozalol;Cetonax;Fetonal;Fungarol;Fungo-hubber;Ketocidin;Ketoisdin;Ketonan;Ketoral;Micoral;Micotek;Micoticum;Nizcrem;Nizoral 2% shampoo;Nizoral 20% cream;Nizovules;Nizshampoo;Oromycosal;Oronazol;Panfungol;Rofenid;Spike;Unidox.
Therapeutic Function
Antifungal
World Health Organization (WHO)
Ketoconazole, an imidazole antifungal agent, was introduced in 1978 for the topical and systemic treatment of a wide variety of fungal infections. Its use by mouth has been associated with hepatotoxicity, including cases of hepatitis, which have usually been reversible on discontinuation of the drug, but some fatalities have also occurred. Ketoconazole is widely marketed.
Antimicrobial activity
The spectrum includes dermatophytes, some dimorphic fungi and Candida spp.
Acquired resistance
Resistance has been documented in patients treated for chronic mucocutaneous candidosis and AIDS patients with oropharyngeal or esophageal candidosis. Some fluconazoleresistant C. albicans and C. glabrata are cross-resistant to ketoconazole.
General Description
Ketoconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent administered through topical or oral means. It is used for the treatment of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, fungal infections of the gastro-intestinal tract, dermatophyte infections, systemic infections, and fungal infections in immuno-compromised patients.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A synthetic dioxolane imidazole available for oral and topical use.
Biological Activity
Antifungal agent; potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450c17.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ketoconazole is an imidazole derivative. It plays an important role in inhibiting the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol in the cell wall of fungi. Ketoconazole has therapeutic effects against dermatophytosis, superficial candidiasis, and paracoccidioidomycosis.
Mechanism of action
Ketoconazole has little effect on Aspergillus or Cryptococcus. Ketoconazole is highly dependent on low stomach pH for absorption, and antacids or drugs that raise stomach pH will lower the bioavailability of ketoconazole. As with other azoles, it is extensively metabolized by microsomal enzymes. All the metabolites are inactive. Evidence that CYP3A4 plays a significant role in metabolism of ketoconazole is that coadministration of CYP3A4 inducers, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, and rifampin, can cause as much as a 50% reduction in levels of ketoconazole.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: Variable
Cmax 400 mg oral: c. 5–6 mg/L after 2 h
Plasma half-life: 6–10 h
Volume of distribution: 0.36 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: >95%
It is erratically absorbed after oral administration. Absorption
is favored by an acid pH. Food delays absorption, but does not
significantly reduce the peak serum concentration. Absorption
is reduced if it is given with compounds that reduce gastric
acid secretion. Penetration into CSF is generally
poor
and unreliable, although effective concentrations have been recorded with high doses in some cases of active meningitis. It
is extensively metabolized by the liver, and the metabolites are
excreted in the bile. Less than 1% of an oral dose is excreted
unchanged in the urine.
Clinical Use
Ketoconazole remains useful in the treatment of cutaneous and mucous membrane dermatophyte and yeast infections, but it has been replaced by the newer triazoles in the treatment of most serious Candida infections and disseminated mycoses. Ketoconazole is usually effective in the treatment of thrush, but fluconazole is superior to ketoconazole for refractory thrush. Widespread dermatophyte infections on skin surfaces can be treated easily with oral ketoconazole when the use of topical antifungal agents would be impractical. Treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis with topical imidazoles is less expensive.
Side Effects
Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia occur commonly with
ketoconazole, especially when high doses are prescribed.
Epigastric distress can be reduced by taking ketoconazole
with food. Pruritis and/or allergic dermatitis
occurs in 10% of patients. Liver enzyme elevations during
therapy are not unusual and are usually reversible.
Severe ketoconazole-associated hepatitis is rare.
At high doses, ketoconazole causes a clinically significant
reduction in testosterone synthesis and blocks
the adrenal response to corticotropin. Gynecomastia,
impotence, reduced sperm counts, and diminished libido
can occur in men, and prolonged drug use can result
in irregular menses in women. These hormonal effects
have led to the use of ketoconazole as a potential
adjunctive treatment for prostatic carcinoma.
Synthesis
Ketoconazole, cis-1-acetyl-4-[4-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazole- 1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-ylmethyl]phenyl]piperazine (35.2.4), is synthesized from 2,4-dichlorophenacyl bromide, the ketalization of which using glycerol gives cis-2-(2,4- dichlorophenyl)-2-bromoethyl-4-hydroxymethyl-1,3-dioxolane (35.2.1). Acylating the hydroxyl group of this compound with benzoyl chloride, and then alkylating the resulting compound with imidazole gives the derivative (35.2.2). Next, alkaline hydrolysis removes the benzoyl group, and a reaction with methanesulfonyl chloride gives a mesylate (35.2.3). Finally, alkylating the resulting 1-acetyl-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine gives ketoconazole (35.2.4).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Because of its comparative lack of toxicity when compared to amphotericin
B, oral administration, and relatively good efficacy, ketoconazole
has been used to treat several fungal infections in dogs,
cats, and other small species. Ketoconazole is often employed with
amphotericin B to enhance the efficacy of ketoconazole, and by
reducing the dose of amphotericin B, decreasing its risk of toxicity.
See the Dosage section or Pharmacology section for specifics.
Newer antifungal agents (fluconazole, itraconazole) have advantages
over ketoconazole, primarily less toxicity and/or enhanced
efficacy; however, ketoconazole can be significantly less expensive
than the newer agents. Ketoconazole is considered by some to still
be the drug of choice for treating histoplasmosis in dogs.
Use of ketoconazole in cats is controversial and some say it should
never be used that species.
Ketoconazole is also used clinically for the medical treatment of
hyperadrenocorticism in dogs. Ketoconazole
appears to be a viable
option (although relatively expensive) to mitotane, particularly for
palliative
therapy in dogs with large, malignant, or invasive tumors
where surgery is not an option. Ketoconazole is also used frequently
in dogs for stabilization prior to surgery. It is a reversible inhibitor
of steroidogenesis, so it is usually not a viable option for long-term
treatment.
Because it interferes with the metabolism of cyclosporine, it has
been used to reduce the dosage necessary for cyclosporine in dogs.
Regulations
Due to its hepatotoxic side effects, oral ketoconazole was withdrawn from the European and Australian markets in 2013. The United States imposed strict relabeling requirements and restrictions for prescription, with Canada issuing a risk communication echoing these concerns. Today, oral ketoconazole is only indicated for endemic mycoses, where alternatives are not available or feasible. Meanwhile, topical ketoconazole is effective, safe, and widely prescribed for superficial mycoses, particularly as the first-line treatment for tinea versicolor.
Metabolism
The major metabolite of ketoconazole appears to be M2, an end product resulting from oxidation of the imidazole moiety. CYP3A4 is known to be the primary contributor to this reaction with some contribution from CYP2D6. Other metabolites resulting from CYP3A4 mediated oxidation of the imidazole moiety include M3, M4, and M5. Ketoconazole may also undergo N-deacetylation to M14, , alkyl oxidation to M7, N-oxidation to M13, or aromatic hydroxylation to M8, or hydroxylation to M9. M9 may further undergo oxidation of the hydroxyl to form M12, N-dealkylation to form M10 with a subsequent N-dealkylation to M15, or may form an iminium ion. No metabolites are known to be active however oxidation metabolites of M14 have been implicated in cytotoxicity.
Metabolism
Ketoconazole is extensively degraded by the liver, and very little active drug is excreted in either the urine or bile; the dose need not be modified for renal insufficiency. Adverse reactions to topical ketoconazole are very rare.
storage
Desiccate at +4°C
Precautions
Both rifampin and isoniazid lower plasma ketoconazolelevels, and concomitant administration should be avoided.Phenytoin serum levels should be monitored closelywhen ketoconazole is prescribed.Ketoconazole causes increasesin serum concentrations of warfarin, cyclosporine,and sulfonylureas. Because of its ability to increase serumcyclosporine levels, ketoconazole has been given to cyclosporine-dependent cardiac transplant recipients to reducethe dose of cyclosporine needed and as a cost-savingmeasure.
References
1) Lambert et al. (1986) The effects if ketoconazole on adrenal and testicular steroidogenesis in vitro; Biochem. Pharmacol. 35 3999
2) Sai et al. (2000) Assessment of specificity of eight chemical inhibitors using cDNA-expressed cytochromes P450. Xenobiotica 30 327
3) Loose et al. (1983) Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroidogenesis by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes; J. Clin. Invest. 71 1495
4) Howell et al. (2019) Lung cancer cells survive epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor exposure through upregulation of cholesterol synthesis; FASEB Bioadv. 2 90
5) Beetens et al. (1986) Ketoconazole inhibits the biosynthesis of leukotrienes in vitro and in vivo; Biochem. Pharmacol. 35 883
Properties of Ketoconazole
| Melting point: | 148-152 °C |
| Boiling point: | 753.4±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4046 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -10.5 ° (C=0.4, CHCl3) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | Off-white solid |
| pka | pKa 3.25/6.22(H2O,t =25,I=0.025) (Uncertain) |
| color | white to light yellow |
| optical activity | [α]20/D -1 to 1°, c = 4 in methanol |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, chloroform, water, and methanol. |
| Merck | 14,5302 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 65277-42-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ketoconazole
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Ketoconazole
| InChIKey | XMAYWYJOQHXEEK-OZXSUGGESA-N |
Ketoconazole manufacturer
Piramal Pharma Solutions
Darshan Pharma Chem
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![cis-1-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/67914-61-8.gif)

You may like
-
 Ketoconazole 99%View Details
Ketoconazole 99%View Details -
 Ketoconazole 98%View Details
Ketoconazole 98%View Details -
 65277-42-1 98%View Details
65277-42-1 98%View Details
65277-42-1 -
 Ketoconazole 98%View Details
Ketoconazole 98%View Details -
 Ketoconazole 98%View Details
Ketoconazole 98%View Details -
 Ketoconazole 98%View Details
Ketoconazole 98%View Details -
 Ketoconazole 98% CAS 65277-42-1View Details
Ketoconazole 98% CAS 65277-42-1View Details
65277-42-1 -
 65277-42-1 95-99 %View Details
65277-42-1 95-99 %View Details
65277-42-1