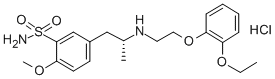
Terbinafine Hydrochloride
Synonym(s):trans-N-(6,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ylyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthylmethylamine hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:78628-80-5
- Empirical Formula: C21H26ClN
- Molecular Weight: 327.89
- MDL number: MFCD00145430
- EINECS: 616-640-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
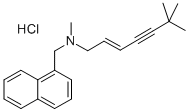
What is Terbinafine Hydrochloride?
Description
Terbinafine hydrochloride is the first orally active allylamine antifungal with 30-fold greater antifungal activity than naftifine. The compound is indicated for the treatment of ringworm and fungal nail infections. Terbinatine hydrochloride acts on a single fungal enzyme, squalene epoxidase, interfering with the biosynthesis of ergosterols in cell membranes. Unlike other antifungal agents, it does not inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Chemical properties
Terbinafine hydrochloride is an off-white crystalline material that is soluble in polar organic solventssuch as methanol, ethanol, and methylene chloride but isonly slightly soluble in water. The highly lipophilic freebase is insoluble in water.
Originator
Sandoz (Switzerland)
The Uses of Terbinafine Hydrochloride
Terbinafine hydrochloride is a synthetic allylamine antifungal. It is used to treat dermatophyte infections of the toenail/fingernail, ringworm and jock itch. It is used in adsorption, partition and stability studies.
The Uses of Terbinafine Hydrochloride
An orally active, antimycotic allylamine related to Naftifine. A specfic inhibitor of squalene epoxidase, a key enzyme in fungal ergosterol biosynthesis. Antifungal.
The Uses of Terbinafine Hydrochloride
Terbinafine hydrochloride may be used as a pharmaceutical reference standard for the determination of the analyte in drug dosage forms by UV spectrophotometry and high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC).
What are the applications of Application
Terbinafine hydrochloride is a squalene monooxygenase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrochloride obtained by reaction of terbinafine with one molar equivalent of hydrogen chloride.
Indications
Terbinafine Hydrochloride is a synthetic allylamine antifungal agent, structurally related to naftifine. It inhibits fungal sterol biosynthesis by inhibiting the enzyme squalene 2,3-epoxidase. The deficiency of ergosterol and concomitant accumulation of squalene within the fungal cell results in cell death. It can be fungicidal or fungistatic, depending on the concentration used, and is effective against dermatophytes, Aspergillus, blastomycosis, and histoplasmosis. It is only minimally effective against Candida.
Manufacturing Process
To prepare terbinafine hydrochloride, N-methyl-1-naphthalene methylamine hydrochloride (29 kg) was added to a reactor containing dimethylformamide (70.4 liters) and water (11 liters). The mixture was stirred for 15 minutes until fully dissolved. Sodium carbonate (11 kg) was added and the reaction mixture was cooled to 13 °C. Then, 1-chloro-6,6-dimethyl-2-heptene-4-yne (22 kg) was slowly added at a temperature range of 11 to 14 °C. The mixture was stirred for 60 minutes at 12-14 °C, then heated to 55 °C and maintained at 60 °C for 5 hours. Thin layer chromatography was used to confirm completion of the reaction. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and water (99 liters) was added. The mixture was extracted three times with dichloromethane (75 liters in total). The organic layer was washed twice with water (88 liters in total) and additional water (18 liters) was added to the organic layer, which was then cooled to 13 °C. The pH of the reaction mass was adjusted to 0.2 by adding 36% aqueous hydrochloric acid (15 liters) and stirring for 30 minutes. The organic layer was separated and washed three times with water (267 liters in total). The final organic layer was transferred to a reactor and the solvent was distilled below 45 °C. Petroleum ether (11.8 liters) was added and the solvent was completely distilled below 50 °C. An additional amount of petroleum ether (68 liters) was added and the mixture was heated to reflux. After 30 minutes of stirring at reflux, the mixture was cooled to 50 °C. The solid formed was allowed to settle for 60 minutes and the top petroleum ether layer was decanted. This decantation process was repeated twice more. Finally, 44 liters of petroleum ether was added, heated to reflux for 30 minutes, and then cooled to 25 °C. The mixture was stirred for 60 minutes at 20-25 °C, centrifuged to collect the solid, and washed twice with petroleum ether (2x16 liters). The solid was then spin-dried for about 60 minutes to obtain 29.3 kg of crude terbinafine hydrochloride as a semi-dry solid.
WO2007096904A2 Improved process for the preparation of terbinafine hydrochloride and novel crystalline form of terbinafine
brand name
Lamisil
Therapeutic Function
Antifungal
General Description
Terbinafine Hydrochloride is a synthetic allylamine derivative structurally related to naftifine, antifungal Terbinafine Hydrochloride blocks ergosterol biosynthesis by inhibition of squalene epoxidase, part of the sterol synthesis pathway for the fungal cell membrane.
Biological Activity
Terbinafine is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent that has activity against T. rubrum, T. metagrophytes, T. verrucosum, E. floccosum, M. canis, A. fumigatus, and S. schenckii (MIC50s = 0.003-0.8 μg/ml). It selectively inhibits C. albicans squalene epoxidase over rat liver epoxidase (IC50s = 0.03 and 77 μM, respectively). Terbinafine (90-120 μM) induces cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase in COLO 205 tumor cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Formulations containing terbinafine have been used in the treatment of nail and skin fungal infections.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Mode of Action: Inhibits squalene epoxidase, preventing biosynthesis of ergosterol.
Antimicrobial spectrum: Antifungal and antimycotic. Fungicidal against dermatopytes and some yeasts; fungistatic against Candida albicans.
Clinical Use
Terbinafine hydrochloride (Lamisil) is available for topical and systemic use (oral tablet) in the treatment of dermatophyte skin and nail infections. Terbinafine also exhibits in vitro activity against filamentous and dimorphic fungi, but its clinical utility in treating infections with these organisms has not yet been established. It is used most commonly in the treatment of onychomycosis; in this setting, terbinafine is superior to griseofulvin and at least equivalent to itraconazole.When given systemically, terbinafine is 99% protein bound and accumulates in fat, skin, and nails, persisting for weeks. Cerebrospinal fluid penetration is less than 10%. Dosage reductions are required with renal or hepatic insufficiency. Although terbinafine has little effect on hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme systems, it does minimally enhance cyclosporine clearance. Oral terbinafine is generally well tolerated but occasionally causes gastric distress and liver enzyme elevation.
Side Effects
Adverse reactions include lens and retinal disturbances (red/green visual perception), metallic taste disturbance that may last up to 4 weeks after medication discontinuation, hepatoxicity, and pancytopenia. Five percent of patients will experience delayed gastric emptying with symptoms of nausea, fullness, and/or dyspepsia. Terbinafine does not appear to have any effect on the cytochrome P-450 systems (Check baseline CBC and LFTs; repeat if taken for >6 weeks).
Synthesis
Terbinafine is produced from olefin metathesis of 1,3-dichloropropene and neohexene followed by reaction with N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Terbinafine may be useful for treating dermatophytic and other fungal infections in dogs and cats. It may also be useful for treating birds for systemic mycotic (e.g., aspergillosis) infections.
The Uses of Terbinafine Hydrochloride
Terbinafine hydrochloride (Lamisil) is a synthetic allylamine antifungal. It is highly lipophilic in nature and tends to accumulate in skin, nails, and fatty tissues. Like other allylamines, terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting the fungal squalene monooxygenase (also called squalene epoxidase), an enzyme that is part of the fungal cell wall synthesis pathway.
Pharmacodynamics
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal that inhibits squalene epoxidase (also known as squalene monooxygenase) to prevent the formation of ergosterol and cause an accumulation of squalene, weakening the cell wall of fungal cells. Terbinafine distributes into tissues and has a long terminal elimination half life, so the duration of action is long. Overdose with terbinafine is rare, even above the therapeutic dose, so the therapeutic index is wide. Patients taking oral terbinafine should have liver function tests performed prior to treatment to reduce the risk of liver injury.
Indication
Terbinafine hydrochloride is indicated to treat fungal skin and nail infections caused by Trichophyton species, Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum, and Tinea species. Terbinafine hydrochloride also treats yeast infections of the skin caused by Candida species and Malassezia furfur.
Properties of Terbinafine Hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 204-208°C |
| storage temp. | 15-25°C |
| solubility | methanol: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,9156 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25N.ClH/c1-21(2,3)15-8-5-9-16-22(4)17-19-13-10-12-18-11-6-7-14-20(18)19;/h5-7,9-14H,16-17H2,1-4H3;1H/b9-5+; |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78628-80-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Terbinafine Hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Terbinafine Hydrochloride
| InChIKey | BWMISRWJRUSYEX-SZKNIZGXSA-N |
| SMILES | C12C=CC=CC1=CC=CC=2CN(C)C/C=C/C#CC(C)(C)C.Cl |
Terbinafine Hydrochloride manufacturer
Besil Chem LLP
Pharma Links
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Terbinafine Hydrochloride 98%View Details
Terbinafine Hydrochloride 98%View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
Terbinafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine HCl 97% CAS 78628-80-5View Details
Terbinafine HCl 97% CAS 78628-80-5View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine Hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
Terbinafine Hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
Terbinafine hydrochloride CAS 78628-80-5View Details
78628-80-5 -
 Terbinafine Hydrochloride Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
Terbinafine Hydrochloride Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
157212-55-0
