Boron carbide
Synonym(s):B 626010;B 626300;Carbon tetraboride
- CAS NO.:12069-32-8
- Empirical Formula: CB4
- Molecular Weight: 55.25
- MDL number: MFCD00011520
- EINECS: 235-111-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
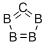
What is Boron carbide?
Description
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate/borax (anhydrous) is a clear, colorless or pale yellow hygroscopic substance with a faint odor of detergent. It is stable and is incompatible with powdered metalsand slightly soluble in water. It is extensively used in the industrial manufacturing of metallurgical fluxes, fiberglass, ceramics, fertilizers, enamels, heat-resistant glass (e.g., Pyrex), and other chemicals. It decomposes on heating or on burning producing toxic fumes including sodium oxide, reacts with strong oxidants, and in fire gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases).
Chemical properties
hard, black, shiny crystal(s), -325 mesh with 99.5% purity; rhomb; hardness 9.3 Mohs; less brittle than most ceramics; does not burn in oxygen flame; used as an abrasive; Knoop hardness ~27GPa; produced by reducing B2O3 with carbon at 1400°C–2300°C; used in crucible form as a container for molten salts except molten caustic and as a 99.5% pure sputtering target for producing semiconductor and wear-resistant films [KIR78] [HAW93] [MER06] [CER91]
Physical properties
Black hard crystal; density 2.50 g/cm3; hardness 9.3 Mohs; melts at 2,350°C; vaporizes above 3,500°C; insoluble in water and acid; inert to most chemicals at ordinary temperatures; rapidly attacked by hot alkalies.
Physical properties
Hard black shiny crystals, fourth hardest material known after diamond, cubic boron nitride, and boron oxide. Does not burn in an O flame if temperature is 2 maintained below 983°C. Maximum operating temperature 2000°C (inert, reducing) or 600°C (oxidizing). Not attacked by hot HF or chromic acid. Used as abrasive, crucible container for molten salts except molten alkali hydroxides. In form of molded shape, used for pressure-blast nozzles, wire-drawing dies, and bearing surfaces for gauges. For grinding and lapping application available mesh sizes cover range 240 to 800.
The Uses of Boron carbide
Boron carbide (B4C) is a hard, black crystal that is used as an abrasive powder and as an additive to strengthen composite parts in aircraft.
The Uses of Boron carbide
Abrasive. In the manufacture of hard and chemicals-resistant ceramics or wear-resistant tools. Finely pulverized B4C can be molded under (considerable) pressure and heat. The resulting products are very wear-resistant, such as pressure-blast nozzle liners, thread guides, extrusion dies, and all types of extremely accurate plug, snap, and ring gages.
The Uses of Boron carbide
Boron carbide is a hard boron-carbon ceramic material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders, neutron absorber, cutting tools and dies and in brake linings of vehicles. It acts as an antioxidant additives in magnesia-carbon bricks. It is used as a precursor in the production of boron containing materials such as titanium boride.
Definition
boron carbide: A black solid, B4C,soluble only in fused alkali; it is extremelyhard, over 9? on Mohs’scale; rhombohedral; r.d. 2.52; m.p.2350°C; b.p. >3500°C. Boron carbideis manufactured by the reduction ofboric oxide with petroleum coke inan electric furnace. It is used largelyas an abrasive, but objects can alsobe fabricated using high-temperaturepowder metallurgy. Boron nitride isalso used as a neutron absorber becauseof its high proportion ofboron–10.
Preparation
Boron carbide is prepared by reduction of boric oxide either with carbon or with magnesium in presence of carbon in an electric furnace at a temperature above 1,400°C. When magnesium is used, the reaction may be carried out in a graphite furnace and the magnesium byproducts are removed by treatment with acid.
What are the applications of Application
Unlike natural minerals and rocks abrasives, boron carbide is a artificial electric-furnace abrasivescould uses in the encasement of spent nuclear waste, special optic fibers, high-gloss paints for the auto industry , and high-intensity electromagnets.
Origin
Boron carbide is an artificial abrasive introduced in 1934 by the Norton Company under the name "Norbide." Washington Mills was the only producer of boron carbide in the United States in 2004.
Industrial uses
Boron carbide (B4C) is produced by the hightemperature(about 1371 to 2482°C) interactionof boric oxide, B2O3, and carbon in an electricalresistance-type furnace. It is a black, lustroussolid. It is used extensively as an abrasive,because its hardness approaches that of the diamond.It is also used as an alloying agent, particularlyin molybdenum steels.
Additionally, it is used in drawing dies andgauges, or into heat-resistant parts such as nozzles.The composition is either B6C or B4C; theformer is the harder but usually contains anexcess of graphite difficult to separate in thepowder. It can be used thus as a deoxidizingagent for casting copper, and also for lapping,since the graphite acts as a lubricant. Borofluxis B4C with flake graphite, used as a casting flux.B4C parts are fabricated by hot pressing,sintering, and sinter-HIPing (HIP = hot-isostaticpress). Industrially, densification is carriedout by hot pressing (2100 to 2200°C, 20to 40 MPa) in argon. The best properties areobtained when pure fine powder is densifiedwithout additives. Pressureless sintering to highdensity is possible using ultrafine powder, withadditives (notably carbon). Less expensive thanhot pressing, sintering also can be used for morecomplex shapes.
Special part formulations include bondingB4C with fused sodium silicate, borate frits,glasses, plastics, or rubbers to lend strength,hardness, or abrasion resistance. B4C-based cermets and MMC (especially Al/B4C, Mg/B4C, Ti/B4C), and CMCs (e.g., TiB2/B4C) haveunique properties, including superior ballisticperformance, that make these materials suitablefor highly specialized applications. Hightemperaturestrength, light weight, corrosionresistance, and hardness make these compositesespecially attractive. B4C shapes can bereaction-bonded using SiC as the bondingphase. B4C–C mixtures are formed, thenreacted with silicon to create the SiC bond. SiCalso can be used as a sintering aid for B4C, andvice versa.
Properties of Boron carbide
| Melting point: | 2450°C |
| Boiling point: | 3500°C |
| Density | 2.51 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, acid solutions |
| form | powder |
| color | Black |
| Specific Gravity | 2.51 |
| Resistivity | 4500 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal |
| Merck | 14,1344 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Not flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12069-32-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Boron carbide(12069-32-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Boron carbide (B4C) (12069-32-8) |
Safety information for Boron carbide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Boron carbide
| InChIKey | NOJMLSPGQSYAIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Boron carbide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Boron carbide sputtering target, 76.2mm (3.0 in.) dia. x 3.18mm (0.125 in.) thick CASView Details
Boron carbide sputtering target, 76.2mm (3.0 in.) dia. x 3.18mm (0.125 in.) thick CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details -
 Boron carbide CASView Details
Boron carbide CASView Details
