Ammonium thioglycolate
Synonym(s):Thioglycolic acid ammonium salt
- CAS NO.:5421-46-5
- Empirical Formula: C2H7NO2S
- Molecular Weight: 109.15
- MDL number: MFCD00137451
- EINECS: 226-540-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:52
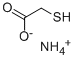
What is Ammonium thioglycolate ?
Description
Ammonium thioglycolate, also known as perm salt, is the chemical compound with the formula HSCH2CO2NH4. Being the salt of a weak acid and weak base, ammonium thioglycolic acid exists in solution as an equilibrium mixture of the salt itself as well as the free carboxylic acid thioglycolic acid (HSCH2CO2H) and ammonia : HSCH2COO- + NH4+ ? HSCH2COOH + NH3.
Chemical properties
Clear colorless solution with characteristic odor
The Uses of Ammonium thioglycolate
Ammonium thioglycolate is contained in permanent waves solutions and causes contact dermatitis in hairdressers.
The Uses of Ammonium thioglycolate
Solutions of various strengths are used for hair waving and for hair removal.
The Uses of Ammonium thioglycolate
acts as a reducing agent in permanent-waving formulations for hair treatment and in shrink-resistant treatment of wool.
Definition
ChEBI: Ammonium thioglycolate is an organic ammonium salt having thioglycolate(1-) as the counterion. Also known as perm salt, it has use in perming hair. It has a role as a reducing agent and an allergen. It contains a thioglycolate(1-).
General Description
Colorless to faint pink liquid with a repulsive, skunk-like odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Ammonium thioglycolate may be sensitive to heat. Ammonium thioglycolate is incompatible with acids.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Ammonium thioglycolate are not available. Ammonium thioglycolate is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Contact allergens
This substance is contained in “basic” permanent waves solutions and causes contact dermatitis in hairdressers.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. An allergen; can cause contact dermatitis. Emits hydrogen sulfide. See also SULFIDES. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic NOx, SOx, and NH3.
Chemical concepts related to perms
When discussing the chemistry of perms, one should consider two chemical facts. First is the thiol-disulfide equilibrium:
RSH + R'SSR' ? R'SH + RSSR'
where R and R' are organic substituents such as methyl (-CH3), ethyl (-C2H5), or -CH2COO-.
The thiol-disulfide exchange reaction is accelerated by bases such as ammonia, because the base generates some thiolate anion (RS- ), which attacks the disulfide. Thus the ammonia plays multiple roles (and more, see below) in this application.
The second chemical fact is that polar molecules are less volatile than nonpolar ones. So the glycolate substituent makes the thiol nonvolatile and hence non-odorous. An added advantage is that the glycolate confers some solubility in water. One could almost certainly use HSCH3 and ammonia to give a perm, but there would be serious olfactory consequences.
The actual chemistry of perms
A solution containing ammonium thioglycolate contains a lot of free ammonia, which swells hair, rendering it permeable. The thioglycolic acid in the perm solution reduces the disulfide cystine bonds in the cortex of the hair. In a sense, the thioglycolate removes crosslinks. After washing, the hair is treated with a mild solution of hydrogen peroxide, which oxidizes the cysteines back to cystine. These new chemical bonds impart the structural rigidity necessary for a successful perm. The rigidification process is akin to the vulcanization of rubber, where commonly polysulfide linkages are used to crosslink the polymer chains. However, not as many disulfide bonds are reformed as there were before the permanent. As a result, the hair is weaker than before the permanent was applied and repeated applications over the same spot may eventually cause strand breakage.
Properties of Ammonium thioglycolate
| Melting point: | 139-139.5 °C |
| Boiling point: | 115℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
| Density | 1.22 |
| vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 25℃ |
| form | Solution |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 1.245 (25℃) |
| Odor | strong skunk-like odor |
| Water Solubility | Miscible |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C2H4O2S.H3N/c3-2(4)1-5;/h5H,1H2,(H,3,4);1H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5421-46-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid, 2-mercapto-, ammonium salt (1:1) (5421-46-5) |
Safety information for Ammonium thioglycolate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H301:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium thioglycolate
| InChIKey | JYAVWXRMOOCSOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C([O-])(=O)CS.[NH4+] |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 AMMONIUM THIOGLYCOLATE 99%View Details
AMMONIUM THIOGLYCOLATE 99%View Details -
 Ammonium Thioglycolate 99%View Details
Ammonium Thioglycolate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium Thioglycolate 5421-46-5 99%View Details
Ammonium Thioglycolate 5421-46-5 99%View Details
5421-46-5 -
 Ammonium Thioglycolate (ca. 60% in Water) CAS 5421-46-5View Details
Ammonium Thioglycolate (ca. 60% in Water) CAS 5421-46-5View Details
5421-46-5 -
 Ammonium thioglycollate, 59% CAS 5421-46-5View Details
Ammonium thioglycollate, 59% CAS 5421-46-5View Details
5421-46-5 -
 Ammonium thioglycolate solution CAS 5421-46-5View Details
Ammonium thioglycolate solution CAS 5421-46-5View Details
5421-46-5 -
 Ammonium Thioglycolate, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
Ammonium Thioglycolate, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
5421-46-5 -
 Ammonium ThioglycolateView Details
Ammonium ThioglycolateView Details
5421-46-5
