Phenothiazine
Synonym(s):10H-Phenothiazine;Phenothiazine;PTZ
- CAS NO.:92-84-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H9NS
- Molecular Weight: 199.27
- MDL number: MFCD00005015
- EINECS: 202-196-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
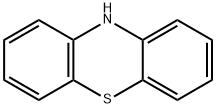
What is Phenothiazine?
Description
Phenothiazine was initially synthesized in 1883 by Bernthsen. It was the basis for the development of other drugs including the phenothiazine class of antipsychotics or neuroleptics. Phenothiazines are the largest class of neuroleptics and include agents such as chlorpromazine, thioridazine, and prochlorperazine. In 1933, a derivative of phenothiazine, promethazine, was synthesized. It was found to have much more significant sedative and antihistaminic effects than previous derivatives of phenothiazine and it was used to induce sedation for surgical patients. After promethazine was developed, a series of agents, including chlorpromazine, was synthesized and tested in France at a military hospital by the French physician Laborit. Laborit found that chlorpromazine induced calm in patients and had other effects that might be useful clinically. Chlorpromazine, known colloquially as ‘Laborit’s drug’ was released into the market in 1953 after a trial published in 1952 showed efficacy in treatment of psychosis in 38 individuals who received daily injections of chlorpromazine. Chlorpromazine is the prototypical drug for the phenothiazine class of antipsychotics. The phenothiazines are classified as low-potency antipsychotics and have more side effects at standard doses than the newer agents used as neuroleptics. For example, they are more anticholinergic and have more extrapyramidal effect than newer agents.
Description
Phenothiazine, a heterocyclic compound that contains ring nitrogen and sulfur atoms, was first made in 1883 when A. Bernthsen fused diphenylamine with sulfur. By 1954, its chemistry was rich enough to be described in?Chemical Reviews?.?Phenothiazine and its derivatives (notably chlorpromazine, or Thorazine) are marketed as antipsychotic and antihistaminic drugs.
Chemical properties
yellow or pale green powder
Chemical properties
Phenothiazine is a greenish-yellow to greenish-gray crystalline substance. Slight odor and taste.
The Uses of Phenothiazine
Phenothiazines are neuroleptic agents that affect a variety of receptors including dopaminergic receptor sites. Phenothiazines are used to treat psychosis including schizophrenia; violent, agitated, disturbed behavior; and mania secondary to bipolar disorder. Other uses include treatment of pain, headache, hiccups, acute severe anxiety, idiopathic dystonia, withdrawal, taste disorders, leishmaniasis, acute intermittent porphyria, and alleviation of nausea and vomiting. Phenothiazines allow smoother induction of anesthesia, potentiate anesthetic agents, and treat behavioral symptoms secondary to Alzheimer disease and senile dementia. Some phenothiazines exert an antipruritic effect and are useful for the treatment of neurodermatitis and pruriginous eczema, and relieve psychogenic itching.
The Uses of Phenothiazine
A key component of antipsychotic and antihistaminic drugs.
The Uses of Phenothiazine
Employed in the preparation of carbazoles and piperazines,1 and charge-transfer semiconducting complexes.2
The Uses of Phenothiazine
A rigid, tricyclic thiazine useful as an electron donor.
The Uses of Phenothiazine
Insecticide; manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
What are the applications of Application
Phenothiazine is a rigid, tricyclic thiazine useful as an electron donor
Definition
ChEBI: The 10H-tautomer of phenothiazine.
brand name
Nemazine (Parke-Davis).
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthesis, p. 506, 1974 DOI: 10.1055/s-1974-23359
General Description
Light green to steel-blue powder. Acquires a greenish-brown tint under exposure to sunlight.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenothiazine is slowly decomposed by sunlight. . Organosulfides are incompatible with acids, diazo and azo compounds, halocarbons, isocyanates, aldehydes, alkali metals, nitrides, hydrides, and other strong reducing agents. Reactions with these materials generate heat and in many cases hydrogen gas. Many of these compounds may liberate hydrogen sulfide upon decomposition or reaction with an acid.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Phenothiazine are not available, but Phenothiazine is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. An insecticide. Large doses, i.e., heavy exposure, may cause hemolytic anemia and toxic degeneration of the liver. Can cause skin irritation and photosensitization. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes it emits hghly toxic fumes of SOx and NOx.
Potential Exposure
Phenothiazine is used as an insecticide; as a base for the manufacture of tranquilizers; as anthelmintic in medicine and veterinary medicine; it is used widely as an intermediate in pharmaceutical manufacture; polymerization inhibitor, antioxidant.
Environmental Fate
Physicochemical Properties
Phenothiazine has the standard formula S(C6H4)2NH and
includes a tricyclic structure that is related to the thiazines.
Thiazines are used in the manufacture of synthetic dies.
Chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine is a white to off-white substance (both the base
and the hydrochloride salt) that is a powder or waxy solid as
a base and a crystalline powder as the hydrochloride. Chlorpromazine
is odorless or has a slightly amine-like odor. It has
a melting point of 56–58 °C and in the basic form is practically
insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and less soluble in chloroform
and ether. It is freely soluble in dilute mineral acids. As
the hydrochloride salt, chlorpromazine is soluble in water, less
soluble in alcohol and chloroform, and insoluble in ether. A
10% aqueous solution has a pH of 3.5–4.5.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from *benzene, toluene, hexane or Me2CO (charcoal) after boiling for 10minutes under reflux. Filter the crystals off and dry them in an oven at 100o, then in a vacuum desiccator over paraffin chips. Also recrystallise it twice from water and dry it in an oven at 100o for 8-10hours. It sublimes at 130o/1mm and has UV with at 253nm in heptane. [Beilstein
Toxicity evaluation
Phenothiazines primarily block postsynaptic neurotransmission by binding to dopamine (D1 and D2), muscarinic, histamine H1, and serotonergic 5-HT2 receptors. Phenothiazines also possess peripheral adrenergic receptor blockade and quinidine-like cardiac effects. Phenothiazines may lower the seizure threshold.
Incompatibilities
Organosulfides are incompatible with strong acids and acid fumes; elevated temperatures; sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides can be produced. Contact with strong reducing agents such as hydrides; azo and diazo compounds, halocarbons, isocyanates can generate heat and may form explosive hydrogen gas
Waste Disposal
Dissolve in combustible solvent and spray into incinerator equipped with afterburner and scrubber. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Phenothiazine
| Melting point: | 184 °C |
| Boiling point: | 371 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.362 |
| vapor pressure | 0.0000647 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6353 |
| Flash point: | 202°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.127mg/l |
| form | Prills or Beads |
| pka | pKa 2.52 (Uncertain) |
| color | Yellow |
| PH | 6 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃)(aqueous suspension) |
| Water Solubility | 2 mg/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7252 |
| BRN | 143237 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 (Skin) NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. May discolour upon exposure to light. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 92-84-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenothiazine(92-84-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenothiazine (92-84-2) |
Safety information for Phenothiazine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenothiazine
| InChIKey | WJFKNYWRSNBZNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phenothiazine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


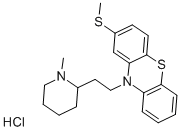
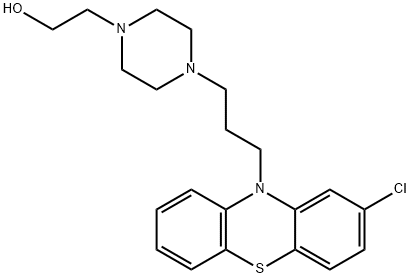
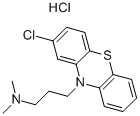
You may like
-
 PHENOTHIAZENE 99%View Details
PHENOTHIAZENE 99%View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine 95% CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine 95% CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine 98% (HPLC) CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine 98% (HPLC) CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine, 98% CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine, 98% CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2 -
 Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
Phenothiazine CAS 92-84-2View Details
92-84-2