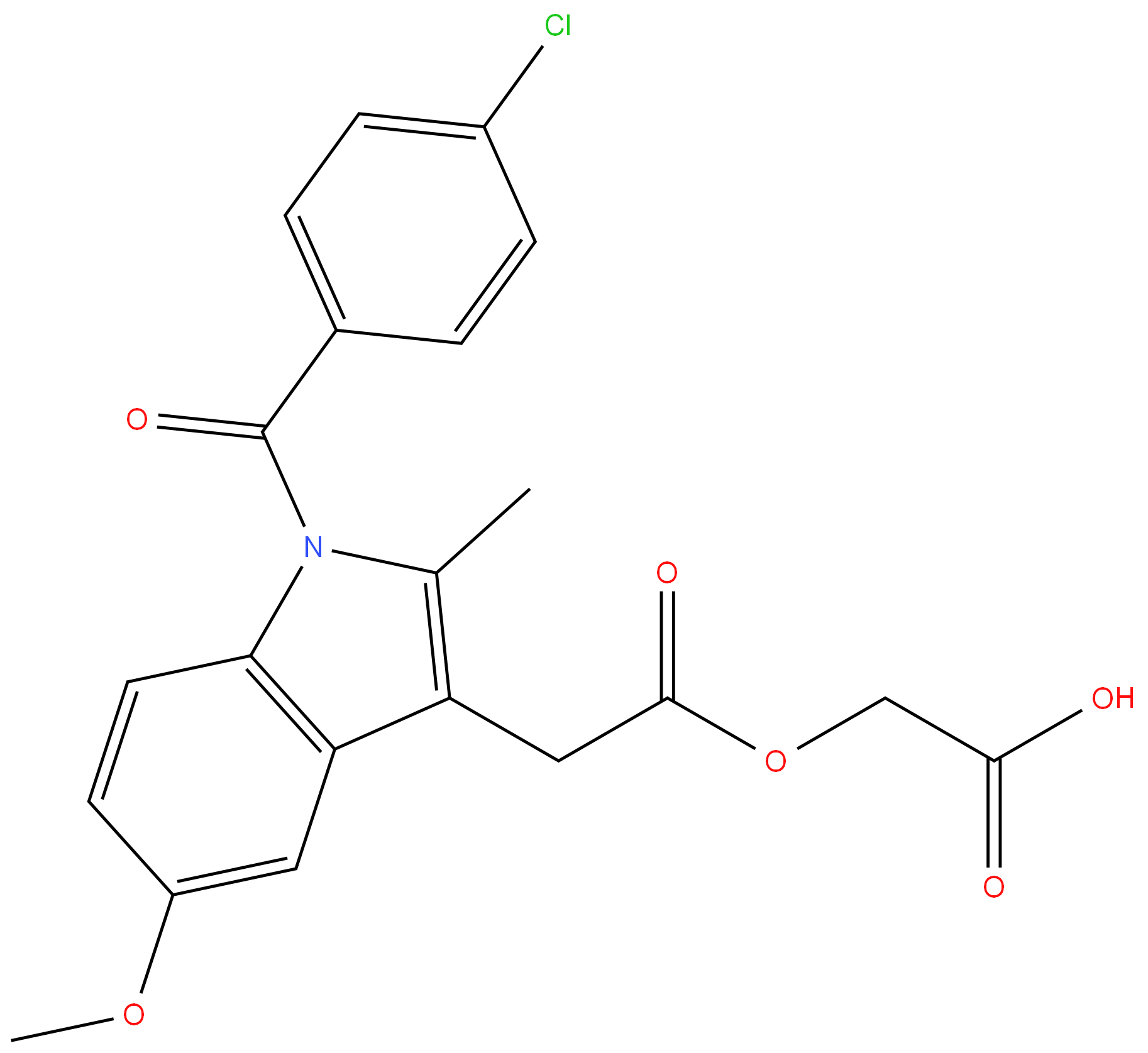
Acemetacin
Synonym(s):1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid carboxymethyl ester
- CAS NO.:53164-05-9
- Empirical Formula: C21H18ClNO6
- Molecular Weight: 415.82
- MDL number: MFCD00151473
- EINECS: 258-403-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
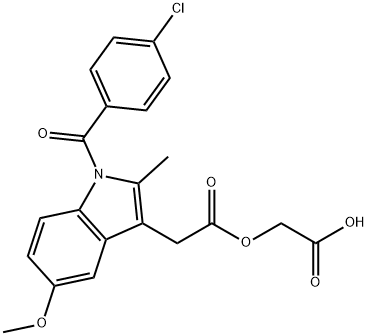
What is Acemetacin?
Absorption
After 8 days of oral administration twice daily of acemetacin there was an age-dependant Cmax of 276.8 ng/ml in elderly compared to 187 ng/ml for younger individuals. There was also a Tmax of 2.5 h and AUC in a range of 483-712 ng h/ml. The bioavailability of acemetacin after repeated doses is aproximately 66% in plasma and 64% in urine.
Toxicity
The pharmacological activity of acemetacin causes blockage of prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandin is one of the mediators of renal blood flow and glomerular filtration thus, acemetacin causes a decreased renal function, transient renal insufficiency, interstitial nephritis and papillary necrosis especially in elderly patients, patients with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis and impaired renal function.
Description
Acemetacin is used in the treatment of pain and restricted mobility resulting from chronic articular rheumatism, degenerative articular disease, gout, and inflammation of muscle, joints, and tendons. Acemetacin causes less gastrointestinal blood loss than indomethacin. Its anti-inflammatory activity results from liberation of the parent compound, indomethacin.
Chemical properties
Light Yellow Solid
Originator
Rantudil ,Bayer ,W. Germany ,1980
The Uses of Acemetacin
Cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
The Uses of Acemetacin
A potent inhibitor of COX-2 found to have anti-tumor activity in the colon
What are the applications of Application
Acemetacin is an anti-inflammatory
Indications
Acemetacin is not FDA, Canada or EMA approved, but in the countries where it is marketed it is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of pain and swelling in acute inflammation of the joints in rheumathoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, low back pain and post-surgical pain. It is also indicated for the treatment of chronic inflammation of the joints in presence of rheumatoid arthritis, treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, treatment of irritation in the joints and spinal column caused by degenerative disorders, treatment of inflammatory soft-tissue rheumatism syndrome and painful swelling and inflammation caused by injury.
Background
Acemetacin is a carboxymethyl ester of indometacin. It is a potent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, derived from the indol-3-acetic acid, whose activity is thought to be mainly through its active metabolite indomethacin. In clinical trials, acemetacin exhibits a better gastric tolerability compared to its active metabolite indometacin. It was developed by E. Merck and Company in Germany as an attempt to provide a safer drug but other than the amelioration on the gastrointestinal effects, the metabolism of acetamicin led to the formation of indomethacin and it kept the same side effects.
Definition
ChEBI: A carboxylic ester that is the carboxymethyl ester of indometacin. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, it is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and low back pain, as well as for postoperative pain and inflammation. Its activ ty is due to both acemetacin and its major metabolite, indometacin.
Manufacturing Process
25.4 g (0.050 mol) of [1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-
indoleacetoxy]-benzyl acetate were dissolved in 400 ml of glacial acetic acid
and hydrogenated on 2.0 g of palladium carbon at room temperature. After
the absorption of hydrogen had finished (1 hour), the catalyst was filtered off,
the filtrate was concentrated by evaporation under vacuum and the compound
was caused to crystallize by adding petroleum ether. The compound melted at
149.5-150.5°C (determined on the micro-Kofler bench); the yield was 19.4 g
which corresponds to 93% of the theoretical yield.
The starting material for the above step may be prepared as follows: 5 g
(0.016 mol) of N1-(p-methoxyphenyl)-p-chlorobenzhydrazide hydrochloride
and 4.75 g (0.018 mol) of benzyl levulinoyloxyacetate were heated in 25 ml of
glacial acetic acid for 3 hours at 80°C. The solvent was then evaporated off
under vacuum. The residue was taken up in chloroform and the solution was
washed neutral by shaking with sodium bicarbonate solution and thereafter
with water. After drying the chloroform solution, this was subjected to
chromatography on aluminium oxide, the eluate was concentrated by
evaporation and the viscous oil remaining as residue was crystallized by
adding ether. The compound melted at 94-95°C. The yield was 4.1 g which
corresponds to 50.7% of the theoretical yield.
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory
Trade name
Acemetacin (Heumann, Stada, Germany), Acemix (Bioprogress, Italy), Altren (Rh?one-Poulenc Rorer, Belgium), Emflex (Merck, UK), Rantudil (Bayer Pharma Deutschland, Germany)
Pharmacokinetics
The effect of acemetacin causes a weak reduction of prostaglandin synthesis which generates an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. The weak inhibition of prostaglandin reduces significantly the damage caused in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown that acemetacin strongly inhibits the release of histamine from mast cells and the generation of hyperthermia. Acemetacin effect also causes changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as inhibition of platelet aggregation.
Clinical Use
Acemetacin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug acting directly and via its major metabolite indomethacin. Acemetacin is used in chronic joint pain as well as in postoperative pain.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous,intraperitoneal, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. Anexperimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductiveeffects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumesof Cl?? and NOx. An anti-inflammatory agent.
Synthesis
alkylation of indomethacin with benzyl bromoacetate in K2CO3/N,N-dimethylformamide gives the corresponding benzyl glycolate ester, which is hydrogenated over 10 % palladium on charcoal in acetic acid to yield acemetacin.
Metabolism
Acemetacin is highly metabolized and degraded by esterolytic cleavage to form its major and active metabolite indometacin. It presents other inactive metabolites made by reaction of O-demethylation, N-desacylation and part of them are also transformed by conjugation with glucuronic acid.
Properties of Acemetacin
| Melting point: | 151.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 565.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.2387 (rough estimate) |
| RTECS | NL3521400 |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 2.60±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Very fine, pale-yellow crystals from pet eth |
| Merck | 14,27 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 53164-05-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Acemetacin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Acemetacin
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Acemetacin 98%View Details
Acemetacin 98%View Details -
 Acemetacin CAS 53164-05-9View Details
Acemetacin CAS 53164-05-9View Details
53164-05-9 -
 Acemetacin CAS 53164-05-9View Details
Acemetacin CAS 53164-05-9View Details
53164-05-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8