4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
Synonym(s):4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid;Homoanisic acid
- CAS NO.:104-01-8
- Empirical Formula: C9H10O3
- Molecular Weight: 166.17
- MDL number: MFCD00004345
- EINECS: 203-166-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-28 21:36:36
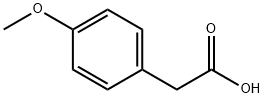
What is 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid?
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystalline powder and
The Uses of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
4-Methoxyphenylacetic Acid is a compound that was found from microbial phenolic metabolites in human feces after the consumption of gin, red wine and dealcholized red wine.
The Uses of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
Preparation of pharmaceuticals, other organic compounds.
The Uses of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid can be used:
- To prepare methyl 4-methoxyphenylacetate by esterification with dimethyl carbonate using mesoporous sulfated zirconia catalyst.
- As a ligand to synthesize pharmacologically important dinuclear gallium(III) and phenyltin(IV) carboxylate metal complexes.
- As a reactant to synthesize hydroxylated (E)-stilbenes by reacting with substituted benzaldehydes via Perkin reaction.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is phenylacetic acid carrying a 4-methoxy substituent. It is used as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals and other organic synthesis. It has been found to inhibit the germination of cress and lettuce seeds.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 51, p. 4354, 1986 DOI: 10.1021/jo00373a005
Tetrahedron Letters, 35, p. 133, 1994 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(94)88182-0
General Description
Pale yellow or off white colored flakes. Severely irritates skin and eyes. May be toxic by ingestion.
Reactivity Profile
Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from EtOH/water, EtOAc/pet ether (m 87o) or *C6H6/pet ether (m 84-86o). [Beilstein 10 III 431, 10 IV 544.] The acid chloride [4693-91-8] has M 184.6, b 143o/10mm, d 254
Properties of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
| Melting point: | 84-86 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 140 °C3 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.1708 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0.071Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5101 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 193°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 6g/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder and Chunks |
| pka | pK1:4.358 (25°C) |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 6 g/L (20 ºC) |
| BRN | 1101737 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 104-01-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzeneacetic acid, 4-methoxy-(104-01-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzeneacetic acid, 4-methoxy- (104-01-8) |
Safety information for 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid
| InChIKey | NRPFNQUDKRYCNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
ASM Organics
New Products
N-Boc-3-pyrrolidinone Carbamic acid, (3-oxocyclobutyl)-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (9CI) 3-(3-PYRIDYL)ACRYLIC ACID 6-chloro-4-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)pyridin-3-amine Milvexian 3-Iodophenylacetic acid Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Lamotrigine Cetirizine Dihydrochloride Clopidogrel Bisulfate/Clopidogrel Hydrogen Sulfate Form-II S-amlodipine Besylate 9-Bromo-7,7-diethyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol methyl 3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridazine-4-carboxylate 2,3-Dimethoxy-7,7-dipropyl-9-(trifluoromethyl)7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol N1-(3,5-diisopropylbiphenyl-4-yl)benzene-1,2-diamine 9-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-methoxy-7,7-dipropyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-5-ol N-(4-bromo-2-chlorobenzyl)propionamide Efinaconazole N-Oxide Impurity 2 Efinaconazole D6 Glycolyl-Phenylalanyl Octreotide Enclomiphene D10 Citrate N-Nitroso Vildagliptin Impurity Vibegron D7 PolycaprolactoneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 104-01-8 4-Methoxy Phenylacetic Acid 99%View Details
104-01-8 4-Methoxy Phenylacetic Acid 99%View Details
104-01-8 -
 4-Methoxyphenylacetic Acid 104-01-8 98%View Details
4-Methoxyphenylacetic Acid 104-01-8 98%View Details
104-01-8 -
 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, 99% CAS 104-01-8View Details
4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, 99% CAS 104-01-8View Details
104-01-8 -
 104-01-8 99%View Details
104-01-8 99%View Details
104-01-8 -
 104-01-8 4-METHOXY PHENYL ACETIC ACID 99%View Details
104-01-8 4-METHOXY PHENYL ACETIC ACID 99%View Details
104-01-8 -
 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid 99%View Details
4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid 99%View Details -
 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid CAS 104-01-8View Details
4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid CAS 104-01-8View Details
104-01-8 -
 4-Methoxyphenylacetic Acid CAS 104-01-8View Details
4-Methoxyphenylacetic Acid CAS 104-01-8View Details
104-01-8
