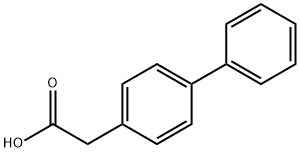
Phenylacetic acid
Synonym(s):α-Toluic acid;α-Tolylic acid;Benzeneacetic acid;PAA;Phenylacetic acid
- CAS NO.:103-82-2
- Empirical Formula: C8H8O2
- Molecular Weight: 136.15
- MDL number: MFCD00004313
- EINECS: 203-148-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:42
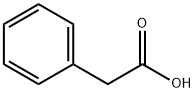
What is Phenylacetic acid?
Toxicity
Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 2250 mg/kg [Mouse].
Chemical properties
white crystals with a honey-like odour
Chemical properties
Phenylacetic Acid occurs in Japanese peppermint
oil, in neroli oil, and in traces in rose oils. It is a volatile aroma constituent
of many foods (e.g., honey). It forms colorless crystals (mp 78°C) that have a
honey odor.
The common route to phenylacetic acid is conversion of benzyl chloride into
benzyl cyanide by reaction with sodium cyanide, followed by hydrolysis. Because of its intense odor, phenylacetic acid is added to perfumes in small quantities
for rounding off blossom odors. Addition to fruit aromas imparts a sweet
honey note.
Chemical properties
Phenylacetic acid has a sweet, animal, honey-like odor in dilute solution. The odor is persistent and disagreeable in concentrated solution. It has a sweet, honey-like flavor at high levels. At low levels, it is a sweetener.
Occurrence
Reported found among the constituents of a few essential oils: tobacco, Rosa centifolia, Bulgarian rose, orange flowers absolute, neroli and Mentha arvensis of Japanese origin; also reported present among the volatile constituents of cocoa. Also reported found in guava, papaya, raspberry, strawberry, cooked potato, tomato, peppermint oil, pepper, rye bread, cheddar cheese, Swiss cheese, Gruyere cheese, boiled mutton, beer, cognac, cider, sherry, grape wines, white wine, sake, cocoa, tea, honey soy protein, passion fruit, starfruit, mango, mushroom, malt, wort, roasted chicory root, naranjilla fruit, choke berry, sea buckthorn and Chinese quince.
The Uses of Phenylacetic acid
Phenylacetic Acid is used in the synthesis of Diclofenac (D436450) and its metabolite 4'-Hydroxydiclofenac (H825225), which is the principal human metabolite of Diclofenac.
The Uses of Phenylacetic acid
Phenylacetic Acid is a flavoring agent that is crystalline (white, glis- tening), with unpleasant, persisting odor resembling geranium leaf and rose when diluted. it is soluble in most fixed oils and glycerin, slightly soluble in water, and insoluble in mineral oil. it is obtained by chemical synthesis. it is also termed a-toluic acid.
The Uses of Phenylacetic acid
Phenylacetic acid?has strong fixative agent and can be directly used in low-or-middle-level soap, cosmetics essences. It is usually to confect the substitute for civetta with indole quinoline type and used in acacia, sweet-scented osmanthus, rose, hosta and other floral essences.
Background
Phenylacetic acid is an organic compound containing a phenyl functional group and a carboxylic acid functional group. It is a white solid with a disagreeable odor. Because it is used in the illicit production of phenylacetone (used in the manufacture of substituted amphetamines), it is subject to controls in countries including the United States and China.
Indications
For use as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia and associated encephalopathy in patients with deficiencies in enzymes of the urea cycle.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is toluene in which one of the hydrogens of the methyl group has been replaced by a carboxy group.
Preparation
By the treatment of benzyl cyanide with dilute sulfuric acid and other processes.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 1 ppm
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 30 ppm: sweet, floral, chocolate, honey and tobacco.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 20, p. 440, 1955 DOI: 10.1021/jo01122a005
Tetrahedron Letters, 26, p. 2027, 1985 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94770-1
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Combustible liquid. Used in production of drugs of abuse. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes
Metabolism
Phenylacetate esterases found in the human liver cytosol. Human plasma esterase also hydrolyze phenylacetate. Phenylacetate hydrolysis involved arylesterase in plasma, both arylesterase and carboxylesterase in liver microsomes and carboxylesterase in liver cytosol. Plasma hydrolysis is less important and overall esterase activity is lower in humans than in the rat.
Metabolism
Phenylacetic acid is conjugated in man and the chimpanzee, but probably in no other species, with glutamine. In most other animals, except the hen, it behaves like benzoic acid, forming glycine and glucuronic acid conjugates. In the hen, it conjugates with ornithine, forming phenacetornithuric acid. Phenacetylglutamine and its addition compound with urea were isolated from human urine alter the administration of phenylacetic acid (Williams, 1959).
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from pet ether (b 40-60o), isopropyl alcohol, 50% aqueous EtOH or hot water (m 77.8-78.2o). Dry it in vacuo. It can be distilled under a vacuum. [Beilstein 9 II 294, 9 III 2169.]
Properties of Phenylacetic acid
| Melting point: | 76-78 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 265 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.081 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | ~4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 97 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5120 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 2878 | PHENYLACETIC ACID |
| Flash point: | 132°C |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | DMF: 1 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/ml |
| pka | 4.28(at 18℃) |
| form | neat |
| color | Leaflets on distillation in vac; plates, tablets from pet ether |
| Specific Gravity | 1.081 |
| Odor | disagreeable odor of geranium |
| PH | 3.7(1 mM solution);3.17(10 mM solution);2.66(100 mM solution) |
| Water Solubility | 15 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,7268 |
| JECFA Number | 1007 |
| BRN | 1099647 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.0(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-82-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzeneacetic acid(103-82-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenylacetic acid (103-82-2) |
Safety information for Phenylacetic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenylacetic acid
Phenylacetic acid manufacturer
Neshiel Agrochem Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
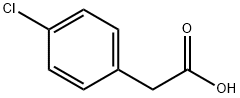
You may like
-
 Phenyl acetic acid, 99% CAS 103-82-2View Details
Phenyl acetic acid, 99% CAS 103-82-2View Details
103-82-2 -
 Phenylacetic acid CAS 103-82-2View Details
Phenylacetic acid CAS 103-82-2View Details
103-82-2 -
 PHENYLACETIC ACID Extra Pure CAS 103-82-2View Details
PHENYLACETIC ACID Extra Pure CAS 103-82-2View Details
103-82-2 -
 Phenylacetic acid CAS 103-82-2View Details
Phenylacetic acid CAS 103-82-2View Details
103-82-2 -
 Tropicamide Related Compound D CAS 103-82-2View Details
Tropicamide Related Compound D CAS 103-82-2View Details
103-82-2 -
 Powder Phenylacetic Acid PAA, Packaging Type: Drum, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
Powder Phenylacetic Acid PAA, Packaging Type: Drum, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
103-82-2 -
 99% Phenyl Acetic Acid, For Perfumery, Packaging Size: 25 KgView Details
99% Phenyl Acetic Acid, For Perfumery, Packaging Size: 25 KgView Details
103-82-2 -
 Phenylacetic Acid, Packaging Type: Drum, Packaging Size: 200View Details
Phenylacetic Acid, Packaging Type: Drum, Packaging Size: 200View Details
103-82-2
