5-Aminosalicylic acid
Synonym(s):5-Amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid;5-Aminosalicylic acid;5-AS;Mesalamine
- CAS NO.:89-57-6
- Empirical Formula: C7H7NO3
- Molecular Weight: 153.14
- MDL number: MFCD00007877
- EINECS: 201-919-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-27 15:38:00
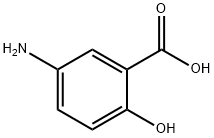
What is 5-Aminosalicylic acid?
Absorption
Depending on the formulation administered, prescribing information for orally administered delayed-released tablets of 2.4g or 4.8g of mesalazine given once daily for 14 days to healthy volunteers was to found to be about 21% to 22% of the administered dose while prescribing information for an orally administered controlled-release capsule formulation suggests 20% to 30% of the mesalazine in the formulation is absorbed. In contrast, when mesalamine is administered orally as an unformulated 1-g aqueous suspension, mesalazine is approximately 80% absorbed.
Toxicity
Mesalazine caused no increase in the incidence of neoplastic lesions over controls in a two-year study of Wistar rats fed up to 320 mg/kg/day of mesalazine admixed with diet (about 1.7 times the recommended human intra-rectal dose of CANASA, based on body
surface area). Mesalazine was not mutagenic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma cell (TK+/-) forward mutation test, or the mouse micronucleus test.
No effects on fertility or reproductive performance of the male and female rats were observed at oral mesalamine doses up to 320 mg/kg/day (about 1.7 times the recommended human intra-rectal dose of mesalazine, based on body surface area).
Description
Fisalamine is an intestinal metabolite of sulfasalazine useful in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and to a lesser degree in the management of Crohn’s disease. Administered as a suppository, it appears to lack the hypersensitivity-type side effects of sulfasalazine.
Description
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), also known as mesalazine or mesalamine, is a metabolite and potential pharmacologically active component of sulphasalazine, a drug used in the treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. However, the mechanism by which this drug works has not been established. In whole blood assays, 5-ASA proves to be a weak, non-selective inhibitor of both COX-1 and COX-2 with IC50 values of 410 and 61 μM, respectively. In ionophore-stimulated colonic mucosal cells, 1 mM 5-ASA does not inhibit prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production, but does reduce leukotriene B4 (LTB4) synthesis approx. 50%. In ionophore-stimulated human leukocytes, 400 μM 5-ASA reduces LTB4 production approximately 20%. 5-ASA does not inhibit 15-hydroxy PGDH at concentrations up to 50 μM.
Chemical properties
Off-White to pink crystals, melting point about 280 ℃ (decomposition). Soluble in hydrochloric acid, slightly soluble in hot water, and slightly bath in cold water or ethanol. In the manufacture of light-sensitive paper, azo and sulfur dyes.
Originator
Radcliffe Infirmary (United Kingdom)
The Uses of 5-Aminosalicylic acid
5-Aminosalicylic acid is used in the preparation of gastrointestinal anti-inflammatory agents. It is a metabolite of sulfasalazine. It acts as a drug involved in the treatment of Crohn?s disease and ulcerative colitis. Further, it is used to make dyes and light-sensitive papers.
Indications
Mesalazine is indicated for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis in adults and patients 5 years or older.. Mesalazine is also indicated for the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis in adults and maintenance of remission of Crohn's ileocolitis.
Background
An anti-inflammatory agent, structurally related to the salicylates and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like acetylsalicylic acid, which is active in inflammatory bowel disease . Although demonstrably effective in treating and maintaining remission for ulcerative colitis, mesalazine has historically faced a number of issues regarding its lack of stability as a pharmaceutical agent.
Definition
ChEBI: Mesalamine is a monohydroxybenzoic acid that is salicylic acid substituted by an amino group at the 5-position. It has a role as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is an aromatic amine, an amino acid, a member of phenols, a monocarboxylic acid and a monohydroxybenzoic acid. It is functionally related to a salicylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a mesalaminate(1-).
Preparation
Preparation by reduction of m-nitrobenzoic acid with Zn dust and HCl.
What are the applications of Application
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) has been used to synthesize 5-formyl-aminosalicylate-inulin to quantify its release during in vitro digestion and fermentation and compare the in vitro fermentation properties of the conjugated inulin to native inulin. It is also used in cell adhesion assay to study its effects on E-cadherin glycosylation and membranous turnover. This compound is used to evaluate its effects on the neutrophilic inflammation index (NII) phenotype to study the effectiveness of the high cholesterol diet-gut inflammation (HCD-GI) platform. 5-Aminosalicylic acid is a peroxidase substrate suitable for use in ELISA procedures. This substrate produces a soluble end product that is brown in color and can be read spectrophotometrically at 450 nm. The reaction may be stopped with 3 N NaOH and read at 550 nm.
Manufacturing Process
Procedure A: To 5-nitrosalicylic acid potassium salt (55 g, 246 mmol) dissolved in water (200 mL) was added potassium hydroxide pellets to reach pH 11.5. To this solution 2 g of Raney nickel were added. The mixture was heated-up to reflux and hydrazine hydrate (40 mL, 80% in water, 64 mmol) was added dropwise during 3-4 hrs. The reflux was maintened until HPLC showed the disappearance of the starting material and the complete reduction of 5-nitrosalicylic acid (3-4 hrs). The hot mixture was filtered under nitrogen and the solution was collected. The solution was cooled to 40°C and the pH was adjusted to 2.3 by addition of 35% HCl aqueous solution. The precipitation of 5-aminosalicylic acid occurred. The solution was cooled at 0°C, and after standing at this temperature for 2 hr, the precipitate was filtered, washed with water, and dried at 60-70°C. 5-Aminosalicylic acid was obtained in 89% yield.
Procedure B: To 5-nitrosalicylic acid potassium salt (55 g, 246 mmol) dissolved in water (200 mL) was added potassium hydroxide pellets to reach pH 11.5. The solution was charged in a stainless steel autoclave and 2 g of Raney nickel are added. Hydrogen was introduced into the autoclave reaching a pressure of 8 atm. The mixture was heated-up to 100°C. The temperature was maintained until HPLC-test 5-aminosalicylic acid showed the disappearance of the starting material and the complete reduction of 5- aminosalicylic acid (6-8 hrs). Hydrogen was purged and replaced by nitrogen. The hot mixture was filtered under nitrogen, the filtrate was cooled to 40°C, and the pH was adjusted to 2.3 by addition of 35% HCl aqueous solution. The precipitation of the 5-aminosalicylic acid occurred. The solution was cooled at 0°C, and after standing at this temperature for 2 hr, the precipitate was filtered, washed with ion depleted water, and dried at 60-70°C.
brand name
SALOFALK
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
General Description
Odorless white to pinkish crystals or purplish-tan powder. Aqueous solutions acidic (pH approximately 4.1 at 0.8 mg/L water) .
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to moisture. Water insoluble.
Reactivity Profile
5-Aminosalicylic acid is incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizers.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 5-Aminosalicylic acid are not available; however, 5-Aminosalicylic acid is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Biochem/physiol Actions
5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is a first-line medicine, used to treat inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis (UC). It has a high-efficiency rate in maintenance and induction of remission. 5-ASA is an active component of sulfasalazine and also consists of the carbohydrate polymer, inulin. It might exhibit anti-oxidant activity to lessen tissue injury. 5-ASA is vital for the prevention of T cell activation and proliferation. It negatively regulates cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways and lowers the formation of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. 5-ASA stimulates the membranous expression of E-cadherin and boosts intercellular adhesion.
Pharmacokinetics
Mesalazine is one of the two components of sulphasalazine, the other being sulphapyridine. It is the latter responsible for most of the side effects associated with sulphasalazine therapy, while mesalazine is known to be the active moiety in the treatment of ulcerative colitis .
Mesalazine is thought to dampen the inflammatory process through its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, interfere with leukotriene synthesis, and consequent leukocyte migration as well as act as a potent scavenger of free radicals. Regardless of the mode of action, mesalazine appears to be active mainly topically rather than systemically.
Intraperitoneally administered mesalazine at 30 and 340 mg/kg daily had similar efficacy in attenuating colitis as prednisolone 4 to 550 mg/kg daily given intraperitoneally or sulphasalazine 0.34 to 5 mg/kg given orally in immune complex-induced colitis mice. Mesalazine at 5 mmol/L and sulphasalazine 1.5 mmol/L also reversed the increase in water and chloride secretion and decrease the sodium in dinitrochlorbenzene-induced colitis guinea pig.
Clinical Use
Induction and maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route.Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects byingestion: hypermotility, diarrhea, dermatitis, increasedbody temperature. When heated to decomposition it emitstoxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Mesalazine is metabolized both pre-systemically by the intestinal mucosa and systemically in the liver to N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA) principally by NAT-1. Some acetylation also occurs through the action of colonic bacteria.
Metabolism
The absorbed part of mesalazine is almost completely acetylated in the gut wall and in the liver to acetyl-5- aminosalicylic acid. The acetylated metabolite is excreted mainly in urine by tubular secretion, with traces of the parent compound.
Side Effects
Mesalazine is an aminosalicylate, and symptoms of salicylate toxicity include nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, tachypnea, hyperpnea, tinnitus, and neurologic symptoms (headache, dizziness, confusion, seizures). Severe salicylate intoxication may lead to electrolyte and blood pH imbalance and potentially to other organ involvement (e.g., renal and liver).
Mesalazine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Evaluate renal function in all patients prior to initiation and periodically while on Asacol HD therapy. Monitor patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking nephrotoxic drugs for decreased renal function and mesalamine-related adverse reactions.
Purification Methods
It crystallises as needles from H2O containing a little NaHSO3 to avoid aerial oxidation to the quinone-imine. The Me ester gives needles from *C6H6, m 96o, and the hydrazide has m 180-182o (from H2O). [Fallab et al. Helv Chim Acta 34 26 1951, Shavel J Amer Pharm Assoc 42 402 1953, Beilstein 14 IV 2058.]
Properties of 5-Aminosalicylic acid
| Melting point: | 275-280 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 276.03°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3585 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 279-281°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| form | tablets |
| pka | 2.74, 5.84(at 25℃) |
| color | off-white to gray |
| PH | 4.0-4.1 (0.8g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | Non-B uorescence (3.1) to light green B uorescence (4.4) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Decomposition | 279-281 ºC |
| Merck | 14,5904 |
| BRN | 2090421 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, chloroformates, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Major Application | Detergent, hair dyes, prevention of colorectal cancer, treating inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune disorders, gastrointestinal inflammation, chemokine-mediated diseases, mucosal tissue disorder, sleep disorders, rectoanal tenesmus, ulcerative colitis |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 89-57-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Mesalamine(89-57-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy- (89-57-6) |
Safety information for 5-Aminosalicylic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for 5-Aminosalicylic acid
| InChIKey | KBOPZPXVLCULAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
5-Aminosalicylic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Gangwal Healthcare Pvt Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Mesalamine 99%View Details
Mesalamine 99%View Details -
 Mesalazine 99%View Details
Mesalazine 99%View Details -
 Mesalazine 99%View Details
Mesalazine 99%View Details -
 89-57-6 Mesalazine 98%View Details
89-57-6 Mesalazine 98%View Details
89-57-6 -
 89-57-6 Mesalazine 98%View Details
89-57-6 Mesalazine 98%View Details
89-57-6 -
 89-57-6 99%View Details
89-57-6 99%View Details
89-57-6 -
 Mesalamine 99% (HPLC) CAS 89-57-6View Details
Mesalamine 99% (HPLC) CAS 89-57-6View Details
89-57-6 -
 5-aminosalicylic Acid CAS No.89-57-6View Details
5-aminosalicylic Acid CAS No.89-57-6View Details
89-57-6
