Acetylsalicylic acid
Synonym(s):O-Acetylsalicylic acid;2-Acetoxybenzoic acid;Acetylsalicylic acid;ASA;Aspirin
- CAS NO.:50-78-2
- Empirical Formula: C9H8O4
- Molecular Weight: 180.16
- MDL number: MFCD00002430
- EINECS: 200-064-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-10 14:44:25
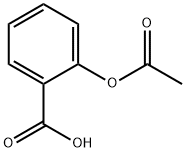
What is Acetylsalicylic acid?
Absorption
Absorption is generally rapid and complete following oral administration but absorption may be variable depending on the route, dosage form, and other factors including but not limited to the rate of tablet dissolution, gastric contents, gastric emptying time, and gastric pH .
Detailed absorption information
When ingested orally, acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly absorbed in both the stomach and proximal small intestine. The non-ionized acetylsalicylic acid passes through the stomach lining by passive diffusion. Ideal absorption of salicylate in the stomach occurs in the pH range of 2.15 - 4.10. Intestinal absorption of acetylsalicylic acid occurs at a much faster rate. At least half of the ingested dose is hydrolyzed to salicylic acid in the first-hour post-ingestion by esterases found in the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma salicylate concentrations occur between 1-2 hours post-administration .
Toxicity
Lethal doses
Acute oral LD50 values have been reported as over 1.0 g/kg in humans, cats, and dogs, 0.92 g/kg - 1.48 g/kg in albino rats, 1.19 g/kg in guinea pigs, 1.1 g/kg in mice, and 1.8 g/kg in rabbit models .
Acute toxicity
Salicylate toxicity is a problem that may develop with both acute and chronic salicylate exposure .
Multiple organ systems may be affected by salicylate toxicity, including the central nervous system, the pulmonary system, and the gastrointestinal system. Severe bleeding may occur. In the majority of cases, patients suffering from salicylate toxicity are volume-depleted at the time of presentation for medical attention. Fluid resuscitation should occur immediately and volume status should be monitored closely. Disruptions in acid-base balance are frequent in ASA toxicity .
Description
Aspirin(ASA), or more formally, acetylsalicylic acid, was first identified and prepared by C. F. Gerhardt in 1853. By 1899, Bayer was manufacturing it and selling it worldwide. It was the leading over-the-counter pain remedy until the 1950s, when acetaminophen and then ibuprofen began to take away much of its market. In the 1980s, the discovery that aspirin is an anticlotting agent strengthened its sales because many people take it to lower the chance of heart attack or stroke.
Chemical properties
Acetylsalicylic acid is a white crystalline solid with a slightly bitter taste. It is odorless but hydrolyzes in moist air to give an acetic acid odor. Acetylsalicylic acid may be effective at preventing certain types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. The main undesirable side effects of aspirin taken by mouth are gastrointestinal ulcers, stomach bleeding, and tinnitus, especially in higher doses. In children and adolescents, aspirin is no longer indicated to control flu - like symptoms or the symptoms of chickenpox or other viral illnesses, because of the risk of Reye's syndrome.
History
The use of Acetylsalicylic acid goes back thousands of years, and there are numerous accounts of the medicinal properties of plants from the Salix (willow) and Myrtaceae (Myrtle) families. Writings from ancient civilizations indicate the use of willow bark in Mesopotamia and myrtle leaves in Egypt as medicines existing several thousand years b.c.e. Hippocrates (460–377 b.c.e. ) and the ancient Greeks used powdered willow bark and leaves to reduce fever (antipyretic) and as a pain reliever (analgesic). Willow and oil of wintergreen was used as medications by native Americans.
The chemical responsible for the medicinal properties in willow and oil of wintergreen are forms of salicylates, a general name to describe compounds containing the general structure of salicylic acid. Willows (genus Salix) contain salicin and oil of wintergreen contains methyl salicylate. Although the use of willow bark and oil of wintergreen as an accepted antipyretic and analgesic has occurred for at least 2,000 years, by the 19th century medicines were starting to be synthesized in chemical laboratories.
The Uses of Acetylsalicylic acid
Acetylsalicylic acid's original use as an analgesic, an antipyretic, and to reduce inflammation continues to this day. Acts as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase which results in the inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. Acetylsalicylic acid also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of arterial and venous thrombosis. More recently there is some evidence that aspirin lessens the chance of heart attacks as a result of its effect as a blood "thinner."
Background
Also known as Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causes. Acetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. This drug also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of blood clots stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI) .
Interestingly, the results of various studies have demonstrated that long-term use of acetylsalicylic acid may decrease the risk of various cancers, including colorectal, esophageal, breast, lung, prostate, liver and skin cancer . Aspirin is classified as a non-selective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor and is available in many doses and forms, including chewable tablets, suppositories, extended release formulations, and others .
Acetylsalicylic acid is a very common cause of accidental poisoning in young children. It should be kept out of reach from young children, toddlers, and infants .
Indications
Pain, fever, and inflammation
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), in the regular tablet form (immediate-release), is indicated to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation associated with many conditions, including the flu, the common cold, neck and back pain, dysmenorrhea, headache, tooth pain, sprains, fractures, myositis, neuralgia, synovitis, arthritis, bursitis, burns, and various injuries. It is also used for symptomatic pain relief after surgical and dental procedures .
The extra strength formulation of acetylsalicylic acid is also indicated for the management migraine pain with photophobia (sensitivity to light) and phonophobia (sensitivity to sound).
brand name
Aspirin; Compralgyl; Melabon; Rumicine; Salipran; Spalt; Tapal; Zorprin, Acetylin (Bristol Myers Squibb, Germany), Acimetten (Pharmonta, Austria), Adprin (Pfeiffer, USA), Alka Seltzer (Bayer, Austria, Switzerland, Czech Republic), Angettes (Bristol-Myers, UK), Asaped (Sanofi- Winthrop, USA), Aspro (Roche Nicholas, Germany), Colfarit (Bayer Pharma Deutschland, Germany), .
Biological Functions
Acetylsalicylic acid is one of the most important NSAIDs because it decreases pain at predominantly peripheral sites with little cortical interaction and thus has few CNS effects. The prototypical COX-2 inhibitors are celecoxib (Celebrex) and its chemical cousin, rofecoxib (Vioxx). In addition to a role in inflammatory processes,COX-2 seems to play a role in colon cancer and Alzheimer’s disease, providing potential additional uses for COX-2-selective drugs.
Acquired resistance
Acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly absorbed in the stomach and quickly degraded by plasma cholinesterases (half-life, 15–20 min). A once-daily dose of 160 mg of aspirin, which is much lower than dosages needed for its anti-inflammatory/analgesic actions, is sufficient to completely inactivate platelet COX-1 irreversibly. Higher doses of aspirin only contribute to its side effects, especially internal bleeding and upper gastrointestinal irritations.
Air & Water Reactions
Slowly hydrolyzes in moist air. Has been involved in dust cloud explosions. Water insoluble. Solution in water is acid to methyl red indicator.
Reactivity Profile
The active ingredient in common aspirin. Incompatible with oxidizers and strong acids. Also incompatible with strong bases. May react with water or nucleophiles (e.g. amines and hydroxy groups). May also react with acetanilide, amidopyrine, phenazone, hexamine, iron salts, phenobarbitone sodium, quinine salts, potassium and sodium iodides, alkali hydroxides, carbonates, stearates and paracetanol.
Hazard
An allergen; may cause local bleeding espe- cially of the gums; 10-g dose may be fatal. May cause excessive biosynthesis of prostaglandins. Dust dispersed in air is serious explosion risk. Skin and eye irritant.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Blocks the production of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (prostaglandin H synthase), with greater selectivity toward the COX-1 isoform. The antithrombotic effect is due to the inhibition of COX-1 in platelets that blocks thromboxane production and platelet aggregation. Chemopreventive against colorectal and other solid tumors.
Pharmacokinetics
Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts the production of prostaglandins throughout the body by targeting cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) . Prostaglandins are potent, irritating substances that have been shown to cause headaches and pain upon injection into humans. Prostaglandins increase the sensitivity of pain receptors and substances such as histamine and bradykinin. Through the disruption of the production and prevention of release of prostaglandins in inflammation, this drug may stop their action at pain receptors, preventing symptoms of pain. Acetylsalicylic acid is considered an antipyretic agent because of its ability to interfere with the production of brain prostaglandin E1. Prostaglandin E1 is known to be an extremely powerful fever-inducing agent.
Clinical Use
Acetylsalicylic acid is used in the treatment of a number of conditions, including fever, pain, rheumatic fever, and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, pericarditis, and Kawasaki disease.PainAsprin 325 MG for pain In most cases, Acetylsalicylic acid is considered inferior to ibuprofen for the alleviation of pain, because Acetylsalicylic acid is more likely to cause gastrointestinal bleeding . Acetylsalicylic acid is generally ineffective for those pains caused by muscle cramps, bloating, gastric distension, or acute skin irritation.HeadacheAcetylsalicylic acid, either by itself or in combined formulation, effectively treats some types of headache, but its efficacy may be questionable for others.Acetylsalicylic acid or other overthe- counter analgesics are widely recognized as effective for the treatment of tension headache. Acetylsalicylic acid, especially as a component of an acetaminophen/Acetylsalicylic acid/caffeine formulation (e.g., Excedrin Migraine), is considered a first - line therapy in the treatment of migraine, and comparable to lower doses of sumatriptan.FeverLike its ability to control pain, Acetylsalicylic acid's ability to control fever is due to its action on the prostaglandin system through its irreversible inhibition of COX .Heart attacks and strokesFor a subset of the population, Acetylsalicylic acid may help prevent heart attacks and strokes. In lower doses, Acetylsalicylic acid has been known to prevent the progression of existing cardiovascular disease, and reduce the frequency of these events for those with a history of them . ( This is known as secondary prevention.)Post-surgeryAfter percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs), such as the placement of a coronary artery stent, a US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality guideline recommends that Acetylsalicylic acid be taken indefinitely.Frequently, Acetylsalicylic acid is combined with an ADP receptor inhibitor, such as clopidogrel, prasugrel or ticagrelor to prevent blood clots. This is called dual anti-platelet therapy (DAPT).
Side Effects
The most common adverse effects produced by the Acetylsalicylic acid are GI disturbances. Occult blood loss from the GI tract, peptic ulceration, and rarely, severe GI hemorrhage can occur. Because salicylic acid is highly bound to plasma proteins, it may be displaced by other highly protein-bound drugs such as oral anticoagulants, sulfonylureas, phenytoin, penicillins, and sulfonamides. The nonacetylated Acetylsalicylic acid have greatly reduced effects on blood loss and produce fewer adverse GI effects. In addition, they may be somewhat kidney sparing. Acetylsalicylic acid may provoke hypersensitivity reactions and prolonged bleeding time in some individuals. Tinnitus, hearing impairment, blurred vision, and lightheadedness are indicators of toxic dosages. The use of aspirin in conjunction with any other NSAID is not recommended because of the lack of evidence that such combinations increase efficacy and because of the increased potential for an adverse reaction. Acetylsalicylic acid are contraindicated in children with febrile viral illnesses because of a possible increased risk of Reye's syndrome
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and possibly other routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: acute pulmonary edema, body temperature increase, changes in kidney tubules, coma, constipation, dehydration, hematuria, hepatitis, nausea or vomiting, respiratory stimulation, somnolence, tinnitus, decreased urine volume. Implicated in aplastic anemia. A 10 gram dose to an adult may be fatal. A human teratogen. Human reproductive effects by ingestion and possibly other routes: menstrual cycle changes, parturition, various effects on newborn including Apgar score, developmental abnormalities of the cardlovascular and respiratory systems. Experimental animal reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. An allergen; skin contact, inhalation, or ingestion can cause asthma, sneezing, irritation of eyes and nose, hves, and eczema. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Synthesis
Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid (3.2.2), is synthesized by the acetylation of salicylic acid (3.2.1) using acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride [60¨C63].

Potential Exposure
Used as an over-the counter and proprietary pharmaceutical and veterinary drug. Those engagedin manufacture of aspirin or, more likely, in its consumption in widespread use as an analgesic, antipyretic, and antiinflammatory agent
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect, increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs - increased side effects; avoid with
ketorolac - increased risk of side effects and
haemorrhage.
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins enhanced;
possibly increased risk of bleeding with edoxaban,
heparins and coumarins.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlaflaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas
enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib. Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect, hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics; increased risk of toxicity
of acetazolamide with high dose aspirin.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Environmental Fate
The toxicity of Acetylsalicylic acid is multifactorial. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain occur as a result of both local gastric irritation and stimulation of the medullary chemoreceptor trigger zone. Salicylates directly stimulate the respiratory drive in the brain stem, leading to hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. Anion gap metabolic acidosis occurs from a buildup of organic acids as well as the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, which results in an imbalance in ATP consumption and production, resulting in a net buildup of hydrogen ions. Therefore, Acetylsalicylic acid often causes a mixed acid–base status. Furthermore, the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation results in failure to produce ATP despite increased oxygen utilization, which leads to heat production and hyperthermia. Acetylsalicylic acid interferes with glucose metabolism and gluconeogenesis, and can cause profound decreases in cerebrospinal fluid glucose concentrations despite normal blood glucose concentrations.
Metabolism
Acetylsalicylic acid is hydrolyzed in the plasma to salicylic acid. Plasma concentrations of aspirin following after administration of the extended-release form are mostly undetectable 4-8 hours after ingestion of a single dose. Salicylic acid was measured at 24 hours following a single dose of extended-release acetylsalicylic acid .
Salicylate is mainly metabolized in the liver, although other tissues may also be involved in this process . The major metabolites of acetylsalicylic acid are salicylic acid, salicyluric acid, the ether or phenolic glucuronide and the ester or acyl glucuronide. A small portion is converted to gentisic acid and other hydroxybenzoic acids .
Storage
Store at RT
Purification Methods
Crystallise aspirin twice from toluene, wash it with cyclohexane and dry it at 60o under vacuum for several hours [Davis & Hetzer J Res Nat Bur Stand 60 569 1958]. It has been recrystallised from isopropanol and from diethyl ether/pet ether (b 40-60o). It crystallises from EtOH (m 143-144o), *C6H6 (m 143o), hexane (m 115o and 128o), octane (m 121o), and has m 110o after sublimation. It has pK2 6 3.69(H2O), 4.15(20% aqueous EtOH), 4.47(30% aqueous EtOH) and 4.94(40% aqueous EtOH). It is an analgesic. [Beilstein 10 H 67, 10 II 41, 10 III 102, 10 IV 138.]
Toxicity evaluation
As in humans, the environmental fate of acetylsalicylic acid is pH dependent. Above pH 5.5, acetylsalicylic acid will be the predominant form seen. Anions generally do not volatilize or undergo adsorption to the extent of their neutral counterparts. Although information is limited, aspirin is considered readily biodegradable and is ultimately mineralized to carbon dioxide and water.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, carbonates, moisture. Dust dispersed in air is explosive
Waste Disposal
May be flushed to sewer with large volumes of water.
Properties of Acetylsalicylic acid
| Melting point: | 134-136 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 272.96°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.35 |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 250 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL at 37 °C |
| form | crystalline |
| color | white |
| pka | 3.5(at 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 3.3 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,851 |
| BRN | 779271 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Keep dry. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong acids, various other compounds such as iodides, iron salts, quinine salts, etc. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-78-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 2-(acetyloxy)-(50-78-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aspirin (50-78-2) |
Safety information for Acetylsalicylic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Acetylsalicylic acid
| InChIKey | BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Acetylsalicylic acid manufacturer
New Products
BOC-L-4-HYDROXYPROLINE 2-nitro 3-hydroxy pyridine 2,6-Dichloropyridin-4-amine 2,3 Diamino pyridine 5-Iodo-2-(1-methylethyl)-3(2H)-pyridazinone 1-Azetidinecarboxylic acid, 3-[(3S)-1-(trans-3-carboxy-3-methylcyclobutyl)-3-piperidinyl]-, 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester Tert-Butyl N-[3-(dimethylcarbamoyl)prop-2-en-1-yl]carbamate 1-(difluoromethyl)-N-methylcyclobutan-1-amine 2-(4-Methyl-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1H-benzimidazole 6-(4-iodophenyl)-1-oxa-6-azaspiro[3.3]he Trimethyl(phenylthio)silane Polycaprolactone(2000)-PEG(20000)-Polycaprolactone(2000) Diacrylate Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, PolyoxyethyleneOleylCetylEtherSulfosuccinate Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate or Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate Castor Oil, Ethoxylated, Cremophor EL or PEG-35 Castor Oil Tween 20 or Polysorbate 20 Acetone-d6 (R)-2-Mercaptobutanoic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine 3-(naphthalen-1-ylsulfonyl)-1H-indazol-5-amine methyl 5-amino-3-(1,1-dioxidotetrahydro-2H-1,2-thiazin-2-yl)-2-fluorobenzoate 7-methoxy-8-(2-morpholinoethoxy)-4-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino)benzo[g]quinoline-3-carbonitrile Dimethylaluminum isopropoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Aspirin 98%View Details
Aspirin 98%View Details -
 Acetyl Salicylic Acid / Aspirin 99%View Details
Acetyl Salicylic Acid / Aspirin 99%View Details -
 Acetylsalicylic acid, ≥99% CAS 50-78-2View Details
Acetylsalicylic acid, ≥99% CAS 50-78-2View Details
50-78-2 -
 Acetylsalicylic acid CAS 50-78-2View Details
Acetylsalicylic acid CAS 50-78-2View Details
50-78-2 -
 Acetylsalicylic Acid Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
Acetylsalicylic Acid Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
50-78-2 -
 Aspirin (IP / BP / USP)View Details
Aspirin (IP / BP / USP)View Details
50-78-2 -
 Aspirin API POWDERView Details
Aspirin API POWDERView Details
50-78-2 -
 Aspirin APIView Details
Aspirin APIView Details
50-78-2
