2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide
Synonym(s):(Z)-2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-butenamide;Flucyamide;N-(4-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxycrotoamide;SU 20
- CAS NO.:108605-62-5
- Empirical Formula: C12H9F3N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 270.21
- MDL number: MFCD00910058
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
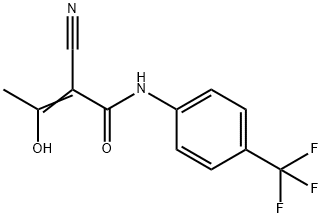
What is 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide?
Description
Teriflunomide (Aubagio®), also known as A77 1726, is an immunosupressant marketed by Sanofi for the teatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). Teriflunomide is the active metabolite of leflunomide, used for treatment of patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, and therefore simultaneously can be used as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.Teriflunomide acts as an inhibitor of the mitochondrial enzyme dihydrorotate dehydrogenase, inhibiting pyrimidine formation, and resulting in reduced B and T cell proliferation.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide
The active metabolite of Leflunomide, 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide can be used as a potent disease-modifying antirheumatic drug used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Definition
ChEBI: Teriflunomide is an enamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of (2Z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxybut-2-enoic acid with the anilino group of 4-(trifluoromethyl)aniline. Used for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. It has a role as an EC 1.3.98.1 [dihydroorotate oxidase (fumarate)] inhibitor, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, a hepatotoxic agent, a drug metabolite and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is a nitrile, an enol, an aromatic amide, an enamide, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes and a secondary carboxamide.
Clinical Use
Immunomodulating agent:
Treatment of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis
Synthesis
Numerous syntheses of teriflunomide have been developed to date, most relying on the use of 4- trifluoromethyl aniline (167). The current optimized method for scale-up synthesis of teriflunomide, developed by Keshav and coworkers, begins with reaction of commercial 4-trifluoromethyl aniline 167 and ethylacetoacetate (168) in refluxing xylenes, providing acetoamidate 169 in 51% yield . The resulting acetoamidate 169 was then treated with H2O2, KBr, and concentrated HCl at room temperature, providing bromide 170 in 67% yield. Bromide 170 was reacted with NaCN in DMSO, generating teriflunomide (XXVI) in 85% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Lipid-lowering agents: effect significantly reduced by
colestyramine - avoid; concentration of rosuvastatin
increased - consider reducing rosuvastatin dose.
Live vaccines: risk of generalised infections - avoid.
Metabolism
Teriflunomide is the active metabolite of leflunomide. It is moderately metabolised and teriflunomide is the only component detected in plasma. The main biotransformation pathway is hydrolysis with oxidation being a minor pathway. Secondary pathways involve oxidation, N-acetylation and sulfate conjugation. Teriflunomide is excreted in the gastrointestinal tract mainly through the bile as unchanged drug and most likely by direct secretion.
storage
Store at +4°C
References
1) Manna et al. (1999), Immunosuppressive leflunomide metabolite (A77 1726) blocks TNF-dependent nuclear factor-kappa B activation and gene expression; J. Immunol., 162 2095 2) Davis et al. (1996), immunosuppressive metabolite of leflunomide is a potent inhibitor of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; Biochemistry, 35 1270 3) Seah et al. (2008), Oxidative bioactivation and toxicity of leflunomide in immortalized human hepatocytes and kinetics of the non-enzymatic conversion to its major metabolite, A77 1726; Drug Metab. Lett., 2 153
Properties of 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide
| Melting point: | 229-232°C |
| Boiling point: | 410.8±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.424±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 30 mg/ml), or in Ethanol (up to 5 mg/ml with warming). |
| form | neat |
| pka | 5.20±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide
2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4'-trifluoromethylphenyl)-crotone amide manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Teriflunomide 99%View Details
Teriflunomide 99%View Details -
 Teriflunomide 98%View Details
Teriflunomide 98%View Details
108605-62-5 -
 Teriflunomide 98%View Details
Teriflunomide 98%View Details
108605-62-5 -
 108605-62-5 99%View Details
108605-62-5 99%View Details
108605-62-5 -
 108605-62-5 98%View Details
108605-62-5 98%View Details
108605-62-5 -
 108605-62-5 99%View Details
108605-62-5 99%View Details
108605-62-5 -
 Leflunomide Related Compound B CAS 108605-62-5View Details
Leflunomide Related Compound B CAS 108605-62-5View Details
108605-62-5 -
 Leflunomide Related Compound B CAS 108605-62-5View Details
Leflunomide Related Compound B CAS 108605-62-5View Details
108605-62-5
