Pimecrolimus
Synonym(s):33-epi-chloro-33-desoxyascomycin;Picrolimus
- CAS NO.:137071-32-0
- Empirical Formula: C43H68ClNO11
- Molecular Weight: 810.45
- MDL number: MFCD00901792
- EINECS: 603-999-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 14:25:50
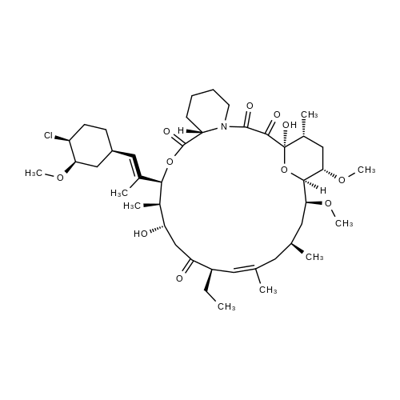
What is Pimecrolimus?
Absorption
Because of the low systemic absorption of pimecrolimus following topical application the calculation of standard pharmacokinetic measures such as AUC, Cmax, half-life, etc. cannot be reliably done.
Toxicity
Side effects include burning sensation, irritation, pruritus, erythema, and skin infections, at the application site.
Description
Pimecrolimus is an ascomycin macrolactam derivative, developed as a topical formulation (1% cream) for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis for patients aged two years and over in whom the use of conventional therapies is inadvisable. Pimecrolimus is an inflammatory cytokine inhibitor that works by selectively targeting T-cells in the skin. It inhibits in vitro the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines after antigen-specific or non-specific stimulation in T cells and mast cells. Pimecrolimus binds specifically to cytosolic receptor macrophilin-12 at nanomolar concentrations leading to inhibition of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphatase, calcineurin. Pimecrolimus is a chlorine derivative of the known FK-520, from which it can be synthesized. In a pig model of dinitrofluorobenzene-induced allergic contact dermatitis, pimecrolimus was shown to inhibit erythema and induration, had equivalent efficacy compared to clobetasol-17- propionate, but did not cause atrophogenic effects. In a mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis, pimecrolimus given orally was as potent as tacrolimus and more effective than cyclosporin. The agent also decreased the intensity of cutaneous manifestations in an atopic dermatitis model involving hypomagnesemic hairless mice. Both in adults and in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis, treatment with pimecrolimus has demonstrated greater efficiency than conventional treatment in reducing the incidence of disease flares, as well as the use of second-line corticosteroids. Moreover, in a 26 week study, in pediatric patients (2-17 years), from 65% of subjects showing improvement, 85% were cleared of the disease. Oral pimecrolimus administration resulted in an elimination half-life of about 30 to 40 h. It is not metabolized or degraded during skin permeation after topical administration. However, following oral administration, it is metabolized via the liver CYP3A4 pathway and excreted mainly in the feces. Pimecrolimus is well tolerated; no systemic accumulation is seen and the most commonly reported side effect is reaction at the site of application. Moreover, pimecrolimus did not cause skin atrophy in contrast to corticosteroids. At this time, as a replacement therapy for topical corticosteroids, the only competing agent for pimecrolimus is topical tacrolimus (ointment). Preliminary studies demonstrated comparable efficacy and safety between these two agents.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Novartis (USA)
The Uses of Pimecrolimus
Macrolactam ascomycin derivative; inhibits production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by T cells and mast cells. Immunosuppresant Pimecrolimus caused a strong and dose-dependent inhibition of anti-IgE–induced release of histamine from mast cells and basophils (maximally 73% and 82%, respectively, at 500 nmol/L pimecrolimus) and of mast cell tryptase (maximally 75%) and a less pronou.
The Uses of Pimecrolimus
Pimercrolimus (21) is the first non-steroid agent for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis lunched by Novartis. It selectively blocks the production and release of cytokines from T-cells. These cytokines cause inflammation, redness and itching associated with eczema. Long-term therapy with pimecrolimus (21) was more effective than conventional treatment in reducing the incidence of disease flares and the use of corticosteroids. This drug is also safe and effective in pediatric patients and is approved for use in children as young as two years.
The Uses of Pimecrolimus
Pimecrolimus is a semi-synthetic, macrocyclic lactone derived from ascomycin by activation of the 32-hydroxy group with a triflate ester, and nucleophilic substitution with chloride under phase transfer conditions to provide the chloro analogue. Pimecrolimus has been targeted for treatment of inflammatory skin disorders. Like all tacrolimus analogues, pimecrolimus binds to receptor protein, FKBP12. The complex then binds to mTOR preventing it from interacting with target proteins. Pimecrolimus is extensively cited in the literature with over 2,000 citations.
Background
Pimecrolimus is an immunomodulating agent that was first marketed by Novartis under the trade name Elidel. It is now promoted in Canada by Galderma since early 2007. It is currently available as a topic cream used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Indications
For treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
What are the applications of Application
Pimecrolimus is an immunosuppressant asomycin derivative
Indications
Pimecrolimus (SDZ ASM 981, Elidel) is another recently approved macrolide immunosuppressant that acts by inhibiting calcineurin and blocking the release of proinflammatory cytokines from T lymphocytes. The parent compound, ascomycin, was originally isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus var ascomyceticus. Like tacrolimus, pimecrolimus is approved for the topical treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis that is refractory to other therapies.Transient local irritation is a common side effect.
Definition
ChEBI: Pimecrolimus is a lactam and a macrolide.
brand name
Elidel (Novartis);Elide1.
Pharmacokinetics
Pimecrolimus is a chemical that is used to treat atopic dermatitis (eczema). Atopic dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by redness, itching, scaling and inflammation of the skin. The cause of atopic dermatitis is not known; however, scientists believe that it may be due to activation of the immune system by various environmental or emotional triggers. Scientists do not know exactly how pimecrolimus reduces the manifestations of atopic dermatitis, but pimecrolimus reduces the action of T-cells and mast cells which are part of the immune system and contribute to responses of the immune system. Pimecrolimus prevents the activation of T-cells by blocking the effects of chemicals (cytokines) released by the body that stimulate T-cells. Pimecrolimus also reduces the ability of mast cells to release chemicals that promote inflammation.
Synthesis
The syntheses of pimecrolimus (21) appeared in several patent applications. Starting material 178 was prepared by either fermentation or modification of a previously described synthetic method in the literature. Treatment of macrolide 178 with triisopropylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TIPS-triflate) in the presence of lutidine in DCM at 0??C afforded di-protected compound 179 in 94% yield. Selective deprotection of the TIPS group at position 32 using p-TSA in MeOH at rt gave mono-protected macrolide 180 in 88% yield. Reaction of the hydroxyl group at position 32 with o-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride (181) in the presence of DMAP and DIPEA in DCM provided 182 in 78% yield with 20% recovered starting material 180. Displacement of the sulfate with chloride using LiCl in DMF furnished the chlorinated compound, which was treated with aqueous HF to remove the TIPS group to provide pimecrolimus (21).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
A relatively new addition to the human topical armamentarium, pimecrolimus cream may be of benefit in veterinary patients in the
adjunctive treatment of atopic dermatitis, discoid lupus erythematosus, pemphigus erythematosus or foliaceous, pinnal vascular disease,
alopecia areata, vitiligo and for perianal fistulas (terminal phase or maintenance treatment after cyclosporine therapy). Unlike topical
corticosteroids, tacrolimus or pimecrolimus do not have atrophogenic or metabolic effects associated with long-term or large area
treatment.
Pimecrolimus acts similarly as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, namely inhibiting T-lymphocyte activation primarily by inhibiting the
phosphatase activity of calcineurin. It also inhibits the release of inflammatory cytokines and mediators from mast cells and basophils.
Pimecrolimus may not have identical mechanisms of action as tacrolimus, as it did not impair the primary immune response (as did
tacrolimus) in mice after a contact sensitizer was applied. Both drugs did impair the secondary response however. Any clinical significance
associated with this difference is not yet clear.
Metabolism
No drug metabolism was observed in human skin in vitro. Oral administration yielded metabolites produced from O-demethylation and oxygenation reactions.
References
[1]. stuetz a, grassberger m, meingassner jg. pimecrolimus (elidel, sdz asm 981)--preclinical pharmacologic profile and skin selectivity. semin cutan med surg, 2001, 20(4): 233-241.
[2]. zuberbier t, chong su, grunow k, et al. the ascomycin macrolactam pimecrolimus (elidel, sdz asm 981) is a potent inhibitor of mediator release from human dermal mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. j allergy clin immunol, 2001, 108(2): 275-280.
[3]. kalthoff fs, chung j, stuetz a. pimecrolimus inhibits up-regulation of ox40 and synthesis of inflammatory cytokines upon secondary t cell activation by allogeneic dendritic cells. clin exp immunol, 2002, 130(1): 85-92.
Properties of Pimecrolimus
| Melting point: | 135-136 °C |
| Boiling point: | 866.1±75.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.19 |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Sonicated), Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.97±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Pimecrolimus
Computed Descriptors for Pimecrolimus
Pimecrolimus manufacturer
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 137071-32-0 PIMECROLIMUS 99%View Details
137071-32-0 PIMECROLIMUS 99%View Details
137071-32-0 -
 137071-32-0 99%View Details
137071-32-0 99%View Details
137071-32-0 -
 137071-32-0 Pimecrolimus 98%View Details
137071-32-0 Pimecrolimus 98%View Details
137071-32-0 -
 Pimecrolimus 137071-32-0 98%View Details
Pimecrolimus 137071-32-0 98%View Details
137071-32-0 -
 Pimecrolimus 98%View Details
Pimecrolimus 98%View Details
137071-32-0 -
 Pimecrolimus CAS 137071-32-0View Details
Pimecrolimus CAS 137071-32-0View Details
137071-32-0 -
 Pimecrolimus IH/USP CAS No.137071-32-0)View Details
Pimecrolimus IH/USP CAS No.137071-32-0)View Details
137071-32-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
