Zirconium silicate
Synonym(s):Zirconium(IV) silicon oxide
- CAS NO.:10101-52-7
- Empirical Formula: O4SiZr
- Molecular Weight: 183.3071
- MDL number: MFCD00085353
- EINECS: 233-252-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-31 13:32:20
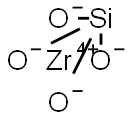
What is Zirconium silicate?
Description
Zircon (ZrSiO4) is an accessory nesosilicate mineral found in granites and, due to its high Mohs hardness of 7.5 and chemical inertness, it concentrates in the weathering products of mother igneous rocks such as in alluvial placer deposits and beach sands. Because of its chemical inertness and high melting point, zircon is wetted less easily by molten metal, producing smoother surfaces on iron, high alloy steel, aluminum, and bronze casting.
Chemical properties
Zirconium silicate is a colorless tetragonal crystals (when pure); presence of impurities forms various colors; density 4.56 g/cm3; hardness 7.5 Mohs; dissociates to ZrO2 and SiO2 above 1,540°C; melts at 2,550°C; insoluble in water, acids, aqua regia, and alkalies; inert in most chemicals. Zirconium silicate is used as an additive to glass, in ceramic tiles, in ultrafiltration membranes, and as a dental abrasive.
The Uses of Zirconium silicate
Zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4) is one form of the mineral whose crystals when polished are known as cubic zircons, which resemble diamond gemstones.
Definition
Zirconium silicate is a naturally occurring silicateof zirconium, ZrSiO4, used as a gemstone.The colour depends in smallamounts of other metals and may bered, brown, yellow, or green. Redgem-quality zircon is sometimescalled jacinth; gem-quality zirconswith other colours are called jargoons.There is also a naturally occurringcolourless variety. Zircongems can be given other colours, ormade colourless, by heat treatment.The colourless varieties (either naturalor treated) are sometimes calledMatura diamonds (after Matura in SriLanka). The name 'zircon' is often erroneouslyapplied to a synthetic formof the oxide cubic zircona, which isused as a diamond substitute.
Preparation
Zirconium silicate occurs in nature as mineral zircon. Ore is mined from natural deposits and concentrated by various techniques (See Zirconium, Recovery). It is separated from sand by electrostatic and electromagnetic methods. Also, the compound can be made by fusion of SiO2 and ZrO2 in an arc furnace, or by reacting a zirconium salt with sodium silicate in aqueous solution.
What are the applications of Application
Zirconium silicate is used for manufacturing refractory materials for applications where resistance to corrosion by alkali materials is required. It is also used in production of some ceramics, enamels, and ceramic glazes. In enamels and glazes it serves as an opacifier. It can be also present in some cements. Another use of zirconium silicate is as beads for milling and grinding. Thin films of zirconium silicate and hafnium silicate produced by chemical vapor deposition. Potential alternative gate dielectric to silica. In Europe in cosmetic creams and powders.
Materials Uses
The largest use of zircon (Zirconium silicate) is as foundry sand, where zircon is used as the basic mold material, as facing material on mold cores, and in ram mixes. Zircon-sand molds have greater thermal shock resistance and better dimensional stability than quartz-sand molds. Zircon grains are usually bonded with sodium silicate.
Properties of Zirconium silicate
| Melting point: | 2550 °C |
| Density | 4,56 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.78-1.99 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, acid solutions |
| form | nanopowder |
| color | Yellow to orange |
| Specific Gravity | 4.56 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water, acids, alkali and aqua regia. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 1: no significant reaction with aqueous systems |
| Merck | 14,10181 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 5(0.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10101-52-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Zirconium silicate(10101-52-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silicic acid (H4SiO4), zirconium(4+) salt (1:1) (10101-52-7) |
Safety information for Zirconium silicate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Zirconium silicate
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Zirconium silicate, 98%+ CAS 10101-52-7View Details
Zirconium silicate, 98%+ CAS 10101-52-7View Details
10101-52-7 -
 ZIRCONIUM SILICATE CAS 10101-52-7View Details
ZIRCONIUM SILICATE CAS 10101-52-7View Details
10101-52-7 -
 ZIRCONIUM SILICATE Extra pure CAS 10101-52-7View Details
ZIRCONIUM SILICATE Extra pure CAS 10101-52-7View Details
10101-52-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4