Vanadium(V) oxide
Synonym(s):vanadium;Vanadium(V) oxide;Divanadium pentaoxide;Divanadium pentoxide;Pentaoxodivanadium
- CAS NO.:1314-62-1
- Empirical Formula: O5V2
- Molecular Weight: 181.88
- MDL number: MFCD00011453
- EINECS: 215-239-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
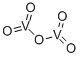
What is Vanadium(V) oxide?
Description
Vanadium pentoxide is a yellow to red colour solid and is odourless. Vanadium pentoxide
dust is the particulate form of a non-combustible, odourless, yellow-orange or dark grey
crystalline solid.
On decomposition by heating, vanadium pentoxide produces toxic fumes. Vanadium
is widely distributed in the Earth’s crust in a wide range of minerals and in fossil fuels.
Vanadium pentoxide, the major commercial product of vanadium, is mainly used in the
production of alloys with iron and aluminium. It is also used as an oxidation catalyst in
the chemical industry and in a variety of minor applications.
Chemical properties
A yellow to rust-brown or orange crystals or powder. Slightly soluble in water and denser than water. Contact may cause severe irritation to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption.
Chemical properties
Vanadium pentoxide dust is an odorless, yellow to red crystal, or powder; or fume (when vanadium is heated). Vanadium pentoxide fume is a finely divided particulate dispersed in air.
The Uses of Vanadium(V) oxide
Vanadium(V) oxide is used in Vacuum deposition, catalysts for conversion of toluene to benzonitrile or propylene to acrylonitrile, as a detector material in bolometers and microbolometer arrays for thermal imaging.
The Uses of Vanadium(V) oxide
As catalyst in the oxidation of SO2 to SO3, alcohol to acetaldehyde, etc.; for the manufacture of yellow glass; inhibiting ultraviolet light transmission in glass; depolarizer; as developer in photography; in form of ammonium vanadate as mordant in dyeing and printing fabrics and in manufacture of aniline black.
The Uses of Vanadium(V) oxide
Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is a reddish-yellow powder extracted from minerals using strong acids or alkalies. In addition to being used as a catalyst for many organic chemical reactions, it is used in photography and in UV-protected windowpanes and to color ceramics and dye cloth.
The Uses of Vanadium(V) oxide
In the production of high-strength steel alloys; catalyst in oxidation reactions; in pesticides; in dyes and inks.
What are the applications of Application
Vanadium(V) oxide is an ammoxidation catalyst
Definition
vanadium pentoxide: A crystalline compound,V2O5, used extensively as a catalyst inindustrial gas-phase oxidationprocesses.
Reactivity Profile
Vanadium pentoxide is acidic in many reactions. Hence, soluble in bases. [Kirk-Othmer]. Can react with ClF3, Li, peroxyformic acid and (Ca+S+H2O). Also reacts with strong acids.
Hazard
The compound is toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and contact. Inhalation can cause asthma, cough, dyspnea, and bronchial constriction. Ingestion can cause gastrointestinal tract disturbances. Other toxic symptoms are skin pallor, greenish-black tongue, and papular skin rash (Lewis, R.J. (Sr) 1996. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9thed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold).
The oral LD50 for V2O5 dust in rats is 10 mg/kg and the inhalation LCLO in rats is 70 mg/m3/2hr.
Health Hazard
Probable oral lethal dose for humans is between 5 and 50 mg/kg or between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person. Toxicity is about the same magnitude as pentavalent arsenic. A person with chronic respiratory disease is at greater risk when exposed to this substance.
Fire Hazard
Container may explode in heat of fire. When heated to decomposition, Vanadium pentoxide emits acrid smoke and fumes of vanadium oxides. Material is not flammable but Vanadium pentoxide may increase the intensity of the fire when in contact with combustible materials. Avoid chlorine trifluoride; lithium; peroxyformic acid; and calcium, sulfur, water complexes. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, intratracheal, and intravenous routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by inhalation: bronchiolar constriction, including asthma, cough, dpspnea, sputum, and conjunctiva irritation. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. A respiratory irritant; causes skin pallor, greenish-black tongue, chest pain, cough, dyspnea, palpitation, lung changes. When ingested it causes gastrointestinal tract disturbances. May also cause a papular skin rash. Mixtures with calcium + sulfur + water may ignite spontaneously. The absorption of V2O5 by inhalation is nearly 100%. Incompatible with ClF3, Li, peroxyformic acid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes of VOx. See also VANADIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
(dust); Suspected reprotoxic hazard, Suspected of causing genetic defects, Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction), (fume) Possible risk of forming tumors, Vanadium pentoxide is an industrial catalyst in oxidation reactions; is used in glass and ceramic glazes; is a steel additive; and is used in welding electrode coatings.
Carcinogenicity
Vanadium pentoxide was not mutagenic in Salmonella strains and did not increase the frequency of micronucleated erythrocytes in mice.9 In other studies vanadium compounds have produced clear evidence of aneuploidy in somatic cells after exposure by several different routes.
Shipping
UN2862 Vanadium pentoxide, nonfused form, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Strong acids; lithium, chlorine trifluoride; peroxyformic acid; combustible substances.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Vanadium pentoxide may be salvaged or disposed of in a sanitary landfill.
Properties of Vanadium(V) oxide
| Melting point: | 690 °C |
| Boiling point: | 3380 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 3.35 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 8 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| Flash point: | 1750°C |
| storage temp. | Poison room |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | turnings |
| color | Orange |
| Specific Gravity | 3.357 |
| PH | 4 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/125 mL |
| Merck | 14,9921 |
| Exposure limits | OSHA: Ceiling 0.5 mg/m3; Ceiling 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 1 mg/m3; STEL 3 mg/m3; Ceiling 0.05 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with chlorine, chlorates, acids, alkali metals, interhalogens. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-62-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 86) 2006 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Vanadium(v) oxide(1314-62-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Vanadium pentoxide (1314-62-1) |
Safety information for Vanadium(V) oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Vanadium(V) oxide
Vanadium(V) oxide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium(V) oxide, Puratronic™ CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide, Puratronic™ CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
Vanadium(V) oxide CAS 1314-62-1View Details
1314-62-1 -
 Vanadium ICP standard CASView Details
Vanadium ICP standard CASView Details -
 Vanadium Standard for AAS CASView Details
Vanadium Standard for AAS CASView Details