Zirconium dioxide
Synonym(s):Zirconia
- CAS NO.:1314-23-4
- Empirical Formula: O2Zr
- Molecular Weight: 123.22
- MDL number: MFCD00011310
- EINECS: 215-227-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:24
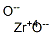
What is Zirconium dioxide ?
Chemical properties
Heavy, white, amorphous powder. Mohs hardness 6.5, refr index 2.2. Insoluble in water and most acids or alkalies at room temperature; soluble in nitric acid and hot concentrated hydrochloric, hydrofluoric, and sulfuric acids. Most heat resistant of commercial refractories; dielectric.
Chemical properties
Zirconium dioxide is a white, amorphous powder, insoluble in water but slightly soluble in acid.
Physical properties
White, heavy, amorphous powder or monoclinic crystals; refractive index 2.13; density 5.68 g/cm3; Mohs hardness 6.5; transforms to tetragonal structure above 1,100°C and cubic form above 1,900°C; melts at 2,710°C and vaporizes at about 4,300°C; insoluble in water; soluble in hydrofluoric acid and hot sulfuric, nitric and hydrochloric acids.
Physical properties
Monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite structure) stable below 1197°C, tetragonal zirconia (rutile structure) stable between 1197 and 2300°C, cubic zirconia (fluorine structure) stable above 2300°C or at lower temperature if stabilized by addition of magnesia, calcia or yttria. Maximum service temperature 2400°C. Zirconia starts to act as an oxygen anion conductor at 1200°C. Highly corrosion resistant to molten metals such as Bi, Hf, Ir, Pt, Fe, Ni, Mo, Pu, and V. Strongly attacked by liquid metals Be, Li, Na, K, Si, Ti, Zr, and Nb. Insoluble in water, but slowly soluble in HCl and HNO3; soluble in boiling concentrated H2SO4 and alkali hydroxides but readily attacked by HF.
The Uses of Zirconium dioxide
Lanthanum-modified lead zirconate titanate (PLZT) fibers with a diameter of around 300 microns were produced by a thermoplastic processing method. The main use of zirconia is in the production of ceramics with other uses including as a protective coating on particles of titanium dioxide pigments, as a refractory material, in insulation, abrasives and enamels. Stabilized zirconia is used in oxygen sensors and fuel cell membranes because it has the ability to allow oxygen ions to move freely through the crystal structure at high temperatures. This high ionic conductivity (and a low electronic conductivity) makes it one of the most useful electroceramics.Zirconium dioxide is also used as the solid electrolyte in electrochromic devices. Zirconia is a precursor to the electroceramic lead zirconate titanate (PZT), which is a high-K dielectric, which is found in myriad components.
The Uses of Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium oxide occurs in nature as the mineral baddeleyite. The oxide has many industrial applications. It is used as a refractory material. It is used in making highly reflective glazes for ceramics, glasses, linings of metallurgical furnaces, crucibles, and laboratory equipment. The oxide is used to produce oxyhydrogen and incandescent lights. Other uses are in producing piezoelectric crystals, heat-resistant fibers, and high-frequency induction coils. The hydrous oxide is used in treating dermatitis resulting from poison ivy.
The Uses of Zirconium dioxide
Instead of lime for the oxyhydrogen light; with earths of the yttrium group in incandescent lighting (Nernst lamps); as pigment, abrasive; manufacture of enamels, white glass, refractory crucibles, and furnace linings.
The Uses of Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium oxide (ZrO2) is the most common compound of zirconium found in nature. It has many uses, including the production of heat-resistant fabrics and high-temperature electrodes and tools, as well as in the treatment of skin diseases. The mineral baddeleyite (known as zirconia or ZrO2) is the natural form of zirconium oxide and is used to produce metallic zirconium by the use of the Kroll process. The Kroll process is used to produce titanium metal as well as zirconium. The metals, in the form of metallic tetrachlorides, are reduced with magnesium metal and then heated to “red-hot” under normal pressure in the presence of a blanket of inert gas such as helium or argon.
General Description
Zirconium(IV) oxide (ZrO2) which is also known as zirconia is a ceramic nanoparticle that can be used as a nano-filler. It can be incorporated in a variety of polymer and metal composites to improve the thermo-mechanical properties of the base material.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
There are several types of zirconia: a pure(monoclinic) oxide and a stabilized (cubic)form, and a number of variations such asyttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconia andnuclear grades. Stabilized zirconia has a highmelting point, about 2760°C, low thermal conductivity,and is generally unaffected by oxidizingand reducing atmospheres and mostchemicals. Yttria- and magnesia-stabilized zirconiasare widely used for equipment and vesselsin contact with liquid metals. Monoclinicnuclear zirconia is used for nuclear fuel elements,reactor hardware, and related applicationswhere high purity (99.7%) is needed.Zirconia has the distinction of being an electricalinsulator at low temperatures, graduallybecoming a conductor as temperaturesincrease.
Carcinogenicity
To simulate the chronic alpha radiation of Thorotrast, the liver of female Wistar rats was exposed to fractionated neutron irradiation at 14-day intervals (0.2Gy per fraction) over 2 years to a total dose of 10.0Gy. Before the start of irradiation, half of the animals received 120 mL of nonradioactive Zirconotrast (ZrO2), which is comparable to Thorotrast in all other physical and chemical properties. The first liver tumor was detected 1 year after the beginning of irradiation. At the end of the life span study, the incidence of irradiated animals with liver tumors was about 40%. In the animals treated additionally with ZrO2, the incidence, time of onset, and overall number of liver tumors were nearly equal, indicating that the fractionated neutron irradiation was the exclusive cause of tumor development. The lifelong-deposited ZrO2 colloid had no influence on tumor induction or development. Histological types of benign and malignant liver tumors seen in this study were the same as those seen in animals treated with Thorotrast.
Properties of Zirconium dioxide
| Melting point: | 2700 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 5000 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 5.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point: | 5000°C |
| solubility | insoluble |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 5.89 |
| PH | 4-5 |
| Resistivity | 2.3 × 10*10 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Crystal Structure | Monoclinic; Tetragonal; Cubic |
| Merck | 14,10180 |
| Dielectric constant | 12.5(0.0℃) |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-23-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Zirconium dioxide(1314-23-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Zirconium oxide (1314-23-4) |
Safety information for Zirconium dioxide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H222:Flammable aerosols H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P211:Do not spray on an open flame or other ignition source. P251:Pressurized container: Do not pierce or burn, even after use. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P410+P412:Protect from sunlight. Do not expose to temperatures exceeding 50 oC/122oF. |
Computed Descriptors for Zirconium dioxide
| InChIKey | RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Zirconium dioxide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Zirconium dioxide 98%View Details
Zirconium dioxide 98%View Details -
 Zirconium (IV) oxide, Yttria stabilized CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium (IV) oxide, Yttria stabilized CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium(IV) oxide CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium(IV) oxide CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium oxide powder, ≥10 µm CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium oxide powder, ≥10 µm CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium oxide spheres, 10 mm dia CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium oxide spheres, 10 mm dia CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium oxide spheres, 5 mm dia CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium oxide spheres, 5 mm dia CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium Dioxide pure CAS 1314-23-4View Details
Zirconium Dioxide pure CAS 1314-23-4View Details
1314-23-4 -
 Zirconium Oxide NanopowderView Details
Zirconium Oxide NanopowderView Details
1314-23-4
