Vitamin D2
Synonym(s):Ergocalciferol;Calciferol;Ercalciol;Ergosterol irradiated;Irradiated ergosterol
- CAS NO.:50-14-6
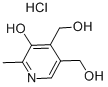
- Empirical Formula: C28H44O
- Molecular Weight: 396.65
- MDL number: MFCD00166988
- EINECS: 200-014-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:40
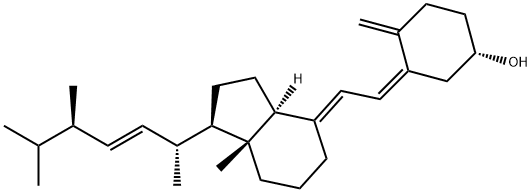
What is Vitamin D2?
Absorption
Ergocalciferol is absorbed in the intestine and carried to the liver in chylomicrons. Its intestinal absorption does not present limitations unless the presence of conditions related to fat malabsorption. However, for absorption to take place, the presence of bile is required.
Toxicity
The reported LD50 for orally administered ergocalciferol in the rat is of 10 mg/kg. Overdosage with this agent is reported to produce hypervitaminosis characterized by hypercalcemia, renal impairment, calcification of soft tissues, a decline in the rate of linear growth and increase in bone mineralization.
Once an overdose state is registered, immediate withdrawal of vitamin D is required along with a calcium diet, generous intake of fluids and symptomatic treatment. The administration of loop diuretics is an option to increase renal calcium excretion. On the other hand, dialysis and administration of citrates, sulfates, phosphates, corticosteroids, EDTA and mithramycin are recommended.
There haven't been long term studies analyzing the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential of ergocalciferol or its effects in fertility.
Description
Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium and has central roles in bone formation and maintenance, hypertension, cancer and immunity. Vitamin D may be obtained from many dietary sources, including eggs and fish, and is synthesized in the skin by the conversion of 7-
Chemical properties
Ergocalciferol is an odorless white crystalline solid
The Uses of Vitamin D2
Vitamin d2 is fat-soluble, and is stable unless oxidized. It is necessary for growth and maintenance of teeth and bones and the normal utilization of calcium and phosphorus; it is used medicinally in the treatment of rickets and as a dietary supplement. Its sources include fish liver and vitamin d-fortified milk.
The Uses of Vitamin D2
The synthetic form of vitamin D. Prepared from ergosterol by UV irradiation in a suitable solvent. Commercial solutions are usually made with propylene glycol or sesame oil. Antirachitic
The Uses of Vitamin D2
antirachitic vitamin; LD50 (rat) 56 mg/kg po
The Uses of Vitamin D2
Rodenticide.
The Uses of Vitamin D2
Vitamin D2 is formed by photochemical cleavage of ergosterin, which is a side-product of many fermentation processes. Microorganisms usually contain up to 3 percent of ergosterin.
Background
Ergocalciferol is an inactivated vitamin D analog. It is synthesized by some plants in the presence of UVB light. The production of ergocalciferol was prompted by the identification of dietary deficiency, more specifically vitamin D, as the main causative factor for the development of rickets. Ergocalciferol was isolated for the first time from yeast in 1931 and its structure was elucidated in 1932.
Ergocalciferol is considered the first vitamin D analog and is differentiated from cholecalciferol by the presence of a double bond between C22 and C23 and the presence of a methyl group at C24. These modifications reduce the affinity of ergocalciferol for the vitamin D binding protein resulting in faster clearance, limits its activation, and alters its catabolism.
The first approved product containing ergocalciferol under the FDA records was developed by US Pharm Holdings and was FDA approved in 1941.
Indications
Ergocalciferol is indicated for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism, refractory rickets, and familial hypophosphatemia.
Hypoparathyroidism is the result of inadequate parathyroid hormone production that occurs due to the presence of damage or removal of the parathyroid glands. This condition produces decreased calcium and increased phosphorus levels.
Rickets is a condition produced due to a deficiency in vitamin D, calcium or phosphorus. However, this condition can also be related to renal diseases. It is characterized to present weak or soft bones.
Familial hypophosphatemia is characterized by the impaired transport of phosphate and an altered vitamin D metabolism in the kidneys. The presence of this condition can derive in the presence of osteomalacia, bone softening and rickets.
What are the applications of Application
Vitamin D2 is a cell differentiation inducer and DNA polymerase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A vitamin D supplement and has been isolated from alfalfa.
brand name
Deltalin (Lilly); Drisdol(Sanofi Aventis).
General Description
Odorless white crystals. Used as a dietary supplement and food additive.
Reactivity Profile
Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert them to aldehydes or ketones. Alcohols exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior. They may initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides.
Health Hazard
Vitamin D2 poisoning disturbs calcium metabolism and causes kidney damage. Vitamin D2 in a single acute ingestion presents no toxic hazards. Daily ingestion in excess of 5000 units/day in children or 7500 units/day in adults will produce toxic symptoms associated with hypervitaminosis D. Those with hypercalcemia are at a greater risk.
Fire Hazard
Shows signs of decomposition when stored for a few days at room temperature.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol (vitamin D3) are the two form of vitamin D which are activated in vivo by hydroxylation. Vitamin D2 and D3 may be used in a wide range of studies to assess their effects on function such as immune function and calcium homeostasis.
Pharmacokinetics
After the activation of the vitamin D receptor, some of the biological changes produced by ergocalciferol include mobilization and accretion of calcium and phosphorus in the bone, absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the intestine, and reabsorption of calcium and phosphorus in the kidney.
Some other effects known to be produced due to the presence of vitamin D are osteoblast formation, fetus development, induction of pancreatic function, induction of neural function, improvement of immune function, cellular growth and cellular differentiation.
When compared to its vitamin D counterpart cholecalciferol, ergocalciferol has been shown to present a reduced induction of calcidiol and hence, it is less potent.
Ergocalciferol supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease has been shown to generate a significant benefit in lab parameters of bone and mineral metabolism as well as improvement in glycemic control, serum albumin levels and reduced levels of inflammatory markers.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by ingestion: anorexia, nausea or vomiting, and weight loss. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
Used as a nutrient and/or dietary supplement food additive
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolic pathway
Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) is a product made by the UV irradiation of yeast ergosterol. It is a common form of vitamin D and it has very similar biological activity to that of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in the treatment of the vitamin D deficiency diseases (e.g. rickets). The bioactive form of this vitamin is also the 1,25-dihydroxy-derivative and this has equal antirachitic activity to that of the cholecalciferol analogue (Jones et al., 1975).
Metabolism
Ergocalciferol is inactive and hence, the first step in the body is ruled by the conversion of this parent compound to 25-hydroxyvitamin D by the action of CYP2R1 followed by the generation of the major circulating metabolite, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D or calcitrol. The generation of this major metabolite is ruled by the activity of CYP27B1 which is a key 1-hydroxylase and CYP24A1 which is responsible for the 25-hydroxylation.
As part of the minor metabolism, ergocalciferol is transformed into 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the liver by the activity of D-25-hydroxylase and CYP2R1. As well, the formation of 24(R),25dihydroxyvitamin D is performed mainly in the kidneys by the action of 25-(OH)D-1-hydroxylase and 25-(OH)D-24-hydroxylase.
Additionally, there are reports indicating significant activity of 3-epimerase in the metabolism of ergocalciferol which modifies the hydroxy group in C3 from the alpha position to a beta. The epimers formed seemed to have a reduced affinity for the vitamin D plasma proteins and to the vitamin D receptor.
An alternative activation metabolic pathway has been reported and this process is characterized by the activity of CYP11A1 and its hydroxylation in the C-20. This 20-hydroxylated vitamin D seems to have similar biological activity than calcitriol.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3249 Medicine, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
It is converted into its 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl ester and crystallised repeatedly from acetone. The ester is then saponified and the free vitamin is isolated. [Laughland & Phillips Anal Chem 28 817 1956, Beilstein 6 IV 4404.]
Degradation
It is unstable in light and air and in acidic media. It is inactivated within a few days under normal exposure conditions. This is due to oxidation and fragmentation of the triene functionality. Ergocalciferol is slightly more unstable, probably because of the additional alkene group in the side chain. One of the several degradation products of ergocalciferol has been identified as the ketone (8, shown in Scheme 1) formed by the loss of the methano-cyclohexanol function (Stewart et al., 1984).
Toxicity evaluation
Excess vitamin D in the form of 1,25-dihydroxycalciferol results in hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria, due to increased calcium absorption, bone demineralization, and hyperphosphatemia.
Incompatibilities
Dust may be combustible and may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Dispose of contents and container to an approved waste disposal plant. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste drugs and pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffeegrounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator.
Properties of Vitamin D2
| Melting point: | 114-118 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 460.3°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 82 º (c=3, in acetone 25 ºC) |
| Density | 0.9784 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 7 x l0-7 Pa (20 °C), est.) |
| refractive index | 1.5100 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 14 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 200 mg/mL, clear to hazy |
| form | powder |
| pka | 14.74±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | white to yellowish |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +105±2°, c = 4% in ethanol |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, water, methanol, dimethylformamide, and dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| Merck | 14,10018 |
| BRN | 1916682 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-14-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ergocalciferol(50-14-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ergocalciferol (50-14-6) |
Safety information for Vitamin D2
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Vitamin D2
| InChIKey | MECHNRXZTMCUDQ-RKHKHRCZSA-N |
Vitamin D2 manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 50-14-6 Calciferol 98%View Details
50-14-6 Calciferol 98%View Details
50-14-6 -
 50-14-6 99%View Details
50-14-6 99%View Details
50-14-6 -
 Calciferol (Vitamin D2) CAS 50-14-6View Details
Calciferol (Vitamin D2) CAS 50-14-6View Details
50-14-6 -
 Calciferol CAS 50-14-6View Details
Calciferol CAS 50-14-6View Details
50-14-6 -
 Ergocalciferol CAS 50-14-6View Details
Ergocalciferol CAS 50-14-6View Details
50-14-6 -
 Vitamin D2 API Chemical PowderView Details
Vitamin D2 API Chemical PowderView Details
21343-40-8 -
 Vitamin D2 Greater Than 4000 IU By G Organic PowderView Details
Vitamin D2 Greater Than 4000 IU By G Organic PowderView Details
50-14-6 -
 Powder Vitamin D2 100/500 cws, 25 Kg, DrumView Details
Powder Vitamin D2 100/500 cws, 25 Kg, DrumView Details
50-14-6
