Pyridoxine
Synonym(s):Pyridoxine, Vitamin B6;Pyridoxol;Pyridoxol (pyridoxine);Vitamin B6
- CAS NO.:65-23-6
- Empirical Formula: C8H11NO3
- Molecular Weight: 169.18
- MDL number: MFCD00006335
- EINECS: 200-603-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
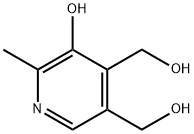
What is Pyridoxine?
Absorption
The B vitamins are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, except in malabsorption syndromes. Pyridoxine is absorbed mainly in the jejunum. The Cmax of pyridoxine is achieved within 5.5 hours.
Toxicity
Oral Rat LD50 = 4 gm/kg. Toxic effects include convulsions, dyspnea, hypermotility, diarrhea, ataxia and muscle weakness.
Chemical properties
crystalline solid
Physical properties
It is one kind of B vitamins, containing pyridoxine or pyridoxal or pyridoxamine. Appearance: colorless crystals at room temperature. Solubility: soluble in water and ethanol. Stability: stable in acid liquor but easily destroyed in alkali liquor. Pyridoxol is resistant to high temperature, but pyridoxal and pyridoxamine are not.
History
The discovery of vitamin was tortuous and legendary. After fat-soluble A and water soluble B were discovered by the year of 1915, the discovery of vitamins entered
into a rapid developed period. In separation process of riboflavin by Kuhn and his
colleagues, they noticed the unusual relationship between growth-promoting activ ity and fluorescence of extracts. Then they supposed that the existence of no fluorescent substances were very necessary for growth-promoting activity of
riboflavin. And they considered this phenomenon as the evidence of a second chem ical existence in the thermostable complex. At last, they named this substance as
vitamin B6 .
Vitamin B6 is widely distributed in foods, including meats, whole-grain products
(especially wheat), vegetables, and nuts. In the cereal grains, vitamin B6 is concen trated primarily in the germ and aleuronic layer. Thus, the refining of grains in the
production of flours, which removes much of these fractions, results in substantial
reductions of vitamin B6 content. The chemical forms of vitamin B6 tend to vary
among foods between plant and animal origin: plant tissues contain most pyridox ine (the free alcohol form, pyridoxol), whereas animal tissues contain most pyri doxal and pyridoxamine.
The Uses of Pyridoxine
pyridoxine HCL is a skin-conditioning agent that is also widely used in hair products.
The Uses of Pyridoxine
antibacterial
The Uses of Pyridoxine
Vitamin B6, a water-soluble vitamin with a solubility of 1 g in 5 ml of water. It functions in the utilization of protein and is an essential nutrient in enzyme reactions. It is necessary for proper growth. During processing, there is a loss due to leaching of the vitamin in water. It is destroyed by high temperatures, high irradiation, and exposure to light. During storage, loss increases with temperature and storage time. It is found in liver, eggs, and meats.
Background
Pyridoxine is the 4-methanol form of vitamin B6, an important water-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in many foods. As its classification as a vitamin implies, Vitamin B6 (and pyridoxine) are essential nutrients required for normal functioning of many biological systems within the body. While many plants and microorganisms are able to synthesize pyridoxine through endogenous biological processes, animals must obtain it through their diet.
More specifically, pyridoxine is converted to pyridoxal 5-phosphate in the body, which is an important coenzyme for synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters (serotonin, norepinephrine), sphingolipids, and aminolevulinic acid. It's important to note that Vitamin B6 is the collective term for a group of three related compounds, pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine, and their phosphorylated derivatives, pyridoxine 5'-phosphate, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate. Although all six of these compounds should technically be referred to as vitamin B6, the term vitamin B6 is commonly used interchangeably with just one of them, pyridoxine .
Vitamin B6, principally in its biologically active coenzyme form pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, is involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions, including the metabolism of amino acids and glycogen, the synthesis of nucleic acids, hemogloblin, sphingomyelin and other sphingolipids, and the synthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) .
Pyridoxine is used medically for the treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and for the prophylaxis of isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy (due to Isoniazid's mechanism of action which competitively inhibits the action of pyridoxine in the above-mentioned metabolic functions). It is also used in combination with Doxylamine (as the commercially available product Diclectin) for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy.
Indications
Pyridoxine is indicated for the treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and for the prophylaxis of Isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy. It is also approved by Health Canada for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy in a combination product with Doxylamine (as the commercially available product Diclectin).
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxymethylpyridine with hydroxymethyl groups at positions 4 and 5, a hydroxy group at position 3 and a methyl group at position 2. The 4-methanol form of vitamin B6, it is converted intoto pyridoxal phosphate which is a coenzyme f r synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters, sphingolipids and aminolevulinic acid.
Indications
Vitamin B6 deficiency
brand name
Hexa-Betalin (Lilly).
World Health Organization (WHO)
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is listed in theWHO Model List of Essential Drugs.
General Description
The discovery of vitamin B6 is generally ascribed to Paul Gy?rgy who first realized there was a vitamin that was distinctly different from vitamin B2 in 1934. Pyridoxine (PN) is the C4 hydroxymethyl derivative, pyridoxal (PL) is the C4 formyl derivative and pyridoxamine (PM) is the C4 aminomethyl derivative of 5-(hydroxymethyl)- 2-methylpyridin-3-ol). Each of these are also converted to their corresponding 5'-phosphate derivatives referred to as pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP), pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), and pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP), respectively . Because of their ability to interconvert, all are considered active forms of vitamin B6 in vivo. Although PLP is the major coenzyme form, PMP can also function as a coenzyme primarily in aminotransferases. The major metabolite is 4-pyridoxic acid, which is excreted in the urine.
Biological Activity
pyridoxine (pyridoxol, vitamin b6, gravidox), also known as vitamin b6, is a form of vitamin b6 found commonly in food and used as dietary supplement. pyridoxine exerts antioxidant effects in cell model of alzheimer's disease via the nrf-2/ho-1 pathway.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pyridoxine plays a key role in cell maintenance and amino acid metabolism. Deficiency of vitamin B6 leads to anemia especially in pregnant women and seizures in newborns. It serves as cofactor for heme biosynthesis during δ-amino levulinic acid formation, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transaminase and glutamic acid decarboxylase. Vitamin B6 also helps in reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging and helps plants in overcoming the abiotic and biotic stress.
Pharmacokinetics
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is a water-soluble vitamin used in the prophylaxis and treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and peripheral neuropathy in those receiving isoniazid (isonicotinic acid hydrazide, INH). Vitamin B6 has been found to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a small group of subjects with essential hypertension. Hypertension is another risk factor for atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Another study showed pyridoxine hydrochloride to inhibit ADP- or epinephrine-induced platelet aggregation and to lower total cholesterol levels and increase HDL-cholesterol levels, again in a small group of subjects. Vitamin B6, in the form of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, was found to protect vascular endothelial cells in culture from injury by activated platelets. Endothelial injury and dysfunction are critical initiating events in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Human studies have demonstrated that vitamin B6 deficiency affects cellular and humoral responses of the immune system. Vitamin B6 deficiency results in altered lymphocyte differentiation and maturation, reduced delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses, impaired antibody production, decreased lymphocyte proliferation and decreased interleukin (IL)-2 production, among other immunologic activities.
Pharmacology
The metabolically active form of vitamin B6 is pyridoxal phosphate, which serves as
a coenzyme of numerous enzymes, most of which are involved in the metabolism of
amino acids. Vitamin B6 functions through the following general mechanisms:
decarboxylation, transamination, racemization, elimination, replacement reactions,
and β-group interconversions.
Pyridoxal phosphate is practically involved in all amino acid metabolism reac tions, such as transaminations, transsulfuration, and selenoamino acid metabolism,
in both their biosynthesis and their catabolism. Vitamin B6 also plays an important
role in the tryptophan–niacin conversion, histamine synthesis, neurotransmitter syn thesis, and hemoglobin synthesis.
Vitamin B6 has two roles in gluconeogenesis, transaminations and glycogen uti lization. It is required for the utilization of glycogen to release glucose by serving as
a coenzyme of glycogen phosphorylase.
Clinical Use
Pyridoxine is indicated in the treatment and prevention of known or suspected vitamin B6 deficiency, which is most likely to occur in the setting of alcoholism in developed countries. At least seven genetic disorders that result in a vitamin B6 deficiency syndrome in the presence of an adequate dietary intake have been identified. These result from defects in enzymes that are responsible for the bioactivation or utilization of vitamin B6.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects: ataxia, local anesthetic, paresthesia. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Nox
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Pyridoxine use in veterinary medicine is relatively infrequent. It
may be of benefit in the treatment of isoniazid (INH) or crimidine
(an older rodenticide) toxicity. Pyridoxine deficiency is apparently
extremely rare in dogs or cats able to ingest food. Cats with severe
intestinal disease may have a greater requirement for pyridoxine in
their diet. Experimentally, pyridoxine has been successfully used
in dogs to reduce the cutaneous toxicity associated with doxorubicin
containing pegylated liposomes (Doxil?). Pyridoxine has been
demonstrated to suppress the growth of feline mammary tumors
(cell line FRM) in vitro.
In humans, labeled uses for pyridoxine include pyridoxine deficiency
and intractable neonatal seizures secondary to pyridoxine
dependency syndrome. Unlabeled uses include premenstrual syndrome
(PMS), carpal tunnel syndrome, tardive dyskinesia secondary
to antipsychotic drugs, nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, hyperoxaluria
type 1 and oxalate kidney stones, and for the treatment
of isoniazid (INH), cycloserine, hydrazine or Gyometra mushroom
poisonings.
Metabolism
Pyridoxine is a prodrug primarily metabolized in the liver. The metabolic scheme for pyridoxine is complex, with formation of primary and secondary metabolites along with interconversion back to pyridoxine. Pyridoxine's major metabolite is 4-pyridoxic acid.
Properties of Pyridoxine
| Melting point: | 214-215 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 298.46°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2435 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5100 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| pka | pKa 5.00(H2O
t = 25.0
I = 0.15
(mixed)) (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 65-23-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Methyl-3-hydroxy-4,5-dihydroxymethylpyridine(65-23-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 3,4-Pyridinedimethanol, 5-hydroxy-6-methyl- (65-23-6) |
Safety information for Pyridoxine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Pyridoxine
| InChIKey | LXNHXLLTXMVWPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Pyridoxine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
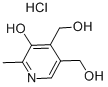
You may like
-
 65-23-6 Pyridoxine 98%View Details
65-23-6 Pyridoxine 98%View Details
65-23-6 -
 65-23-6 99%View Details
65-23-6 99%View Details
65-23-6 -
 Pyridoxine CAS 65-23-6View Details
Pyridoxine CAS 65-23-6View Details
65-23-6 -
 Pyridoxin Hydrochloride, Vitamin B6 Powder, Grade Standard: USP, Greater than 99%View Details
Pyridoxin Hydrochloride, Vitamin B6 Powder, Grade Standard: USP, Greater than 99%View Details
65-23-6 -
 Pyridoxine HCL USP/BP/EP/JP/IP, 99%View Details
Pyridoxine HCL USP/BP/EP/JP/IP, 99%View Details
8064-77-5 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
