Sodium ascorbate
Synonym(s):(+)-Sodium L -ascorbate;L (+)-Ascorbic acid sodium salt;E301; Vitamine C sodium salt;Vitamin C sodium salt
- CAS NO.:134-03-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H7NaO6
- Molecular Weight: 198.11
- MDL number: MFCD00082340
- EINECS: 205-126-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:07
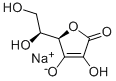
What is Sodium ascorbate?
Chemical properties
Sodium ascorbate occurs as a white or slightly yellow-colored, practically odorless, crystalline powder with a pleasant saline taste.
The Uses of Sodium ascorbate
Sodium Ascorbate is an antioxidant that is the sodium form of ascorbic acid. it is soluble in water and provides a nonacidic taste. a 10% aqueous solution has a ph of 7.3–7.6. in water, it readily reacts with atmospheric oxygen and other oxidizing agents, making it valuable as an antioxidant. one part sodium ascorbate is equivalent to 1.09 parts of sodium erythorbate. see ascorbic acid.
The Uses of Sodium ascorbate
L-Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is a water soluble molecule used in a wide variety of applications, including cell culture, as a reducing agent that helps reduce oxidative stress.
The Uses of Sodium ascorbate
As antimicrobial and antioxidant in foodstuffs.
What are the applications of Application
(+)-Sodium L-ascorbate is L-Ascorbate can be regenerated by biological systems
Definition
ChEBI: Sodium ascorbate is an organic sodium salt resulting from the replacement of the proton from the 3-hydroxy group of ascorbic acid by a sodium ion. It has a role as a food antioxidant, a flour treatment agent, a coenzyme, a plant metabolite, a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite and a reducing agent. It is an organic sodium salt and a vitamin C. It contains a L-ascorbate.
Production Methods
An equivalent amount of sodium bicarbonate is added to a solution of ascorbic acid in water. Following the cessation of effervescence, the addition of propan-2-ol precipitates sodium ascorbate.
brand name
Ascorbin (Marion Merrell Dow).
General Description
Minute crystals or white powder. pH of aqueous solutions 5.6 to 7.0 or even higher (a 10% solution, made from a commercial grade, may have a pH of 7.4 to 7.7).
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are subject to quick air oxidation at pH greater than 6.0.
Reactivity Profile
A weak base. Materials in this group are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Ingestion of 10 grams or more of this type of compound may cause diarrhea.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Sodium ascorbate are not available. Sodium ascorbate is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium ascorbate is used as an antioxidant in pharmaceutical
formulations, and also in food products where it increases the
effectiveness of sodium nitrite against growth of Listeria monocytogenes
in cooked meats. It improves gel cohesiveness and sensory
firmness of fiberized products regardless of vacuum treatment.
It is also used therapeutically as a source of vitamin C in tablets
and parenteral preparations.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ascorbic acid exhibits anti-oxidant properties. It is a primary substrate for detoxifying hydrogen peroxide. Ascorbic acid is a co-factor for the synthesis of adrenal steroids and catecholamines. L-Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is a water soluble molecule used in a wide variety of applications, including cell culture, as a reducing agent that helps reduce oxidative stress. L-Ascorbate can be regenerated by biological systems.
Safety Profile
Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O.
Safety
The parenteral administration of 0.25-1.00 g of sodium ascorbate,
given daily in divided doses, is recommended in the treatment of
vitamin C deficiencies. Various adverse reactions have been
reported following the administration of 1 g or more of sodium
ascorbate, although ascorbic acid and sodium ascorbate are usually
well tolerated; see Ascorbic acid. There have been no reports of
adverse effects associated with the much lower concentrations of
sodium ascorbate and ascorbic acid, which are employed as
antioxidants.
The WHO has set an acceptable daily intake of ascorbic acid,
potassium ascorbate, and sodium ascorbate, as antioxidants in
food, at up to 15 mg/kg body-weight in addition to that naturally
present in food.
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
Sodium ascorbate is relatively stable in air, although it gradually
darkens on exposure to light. Aqueous solutions are unstable and
subject to rapid oxidation in air at pH > 6.0.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed nonmetallic
container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizing agents, heavy metal ions, especially copper and iron, methenamine, sodium nitrite, sodium salicylate, and theobromine salicylate. The aqueous solution is reported to be incompatible with stainless steel filters.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV preparations; oral tablets). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium ascorbate
| Melting point: | 220 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 235 °C |
| alpha | 104 º (c=1, H2O 25 ºC) |
| Density | 1.66 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 105.5 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white to slightly yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| PH | 7.48(1 mM solution);7.71(10 mM solution);7.64(100 mM solution);7.62(1000 mM solution) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +105±2°, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | 620 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,830 |
| BRN | 3767246 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 134-03-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium ascorbate (134-03-2) |
Safety information for Sodium ascorbate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium ascorbate
Sodium ascorbate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sodium Ascorbate 99%View Details
Sodium Ascorbate 99%View Details -
 Sodium ascorbate 98%View Details
Sodium ascorbate 98%View Details -
 Sodium ascorbate 99%View Details
Sodium ascorbate 99%View Details -
 Sodium Ascorbate Ip PowderView Details
Sodium Ascorbate Ip PowderView Details
134-03-2 -
 Sodium Ascorbate PowderView Details
Sodium Ascorbate PowderView Details
134-03-2 -
 Sodium AscorbateView Details
Sodium AscorbateView Details
134-03-2 -
 Sodium L AscorbateView Details
Sodium L AscorbateView Details
134-03-2 -
 Sodium Ascorbate FCCView Details
Sodium Ascorbate FCCView Details
134-03-2
