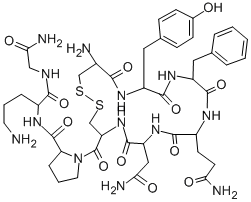
Vasopressin
Synonym(s):[Arg8]-Vasopressin;Argipressin
- CAS NO.:9034-50-8
- Empirical Formula: C43H67N15O12S2
- Molecular Weight: 1050.22
- MDL number: MFCD03839092
- Update Date: 2025-07-29 17:05:30
What is Vasopressin?
Description
Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (A D H) or arginine vasopressin (AVP), is another hormone key to water homeostasis and blood pressure regulation. A rginine vasopressin is produced in the neurones of the hypothalamus and stored in vesicles within the posterior pituitary. Vasopressin is released in response to increased blood osmolality detected by hypothalamic osmoreceptors; systemic hypotension or hypovolaemia detected by cardiopulmonary baroreceptors of the great veins and atria; or angiotensin I I acting on the hypothalamus.
The Uses of Vasopressin
Hormone (antidiuretic).
The Uses of Vasopressin
Vasopressin is a peptide hormone secreted by the hypothalamus via the posterior pituitary. Its primary role is the regulation of body fluid balance. It is secreted in response to hypotension and promotes retention of water by action on specific cAMP-coupled V2 receptors. It causes vasoconstriction by stimulating V1 receptors in VSM and is particularly potent in hypotensive patients. It is increasingly used in the treatment of refractory vasodilatory shock which is resistant to catecholamines. The vasopressin analogue desmopressin is used to treat diabetes insipidus and in the management of von Willebrand's disease. Terlipressin (another analogue) is used to limit bleeding from oesophageal varices in patients with portal hypertension. When used for the management of low SVR states, vasopressin is administered as an i.v. infusion at a rate of 0.01–0.1 units min–1.
brand name
Pitressin (Parke-Davis).
Biological Functions
Human vasopressin, or Arg-vasopressin, is chemically very similar to oxytocin and therefore sometimes is referred to as [Phe3, Arg8]oxytocin. The physiological role of vasopressin is the regulation of water reabsorption in the renal tubules (an antidiuretic action, thus often referred to as the antidiuretic hormone). In high doses, vasopressin promotes the contraction of arterioles and capillaries, resulting in an increase in blood pressure, thus the name vasopressin. An inadequate output of pituitary antidiuretic hormone can cause diabetes insipidus, which is characterized by the chronic excretion of large amounts of pale urine and results in dehydration and extreme thirst.
Clinical Use
lly as a long-lasting and selective V2aR agonist for the treatment of central diabetes insipidus. For X-CNDI, the use of nonpeptide antagonists (pharmacological chaperones) and nonpeptide agonists (vaptans) has been tested. These cell-permeable reagents stabilize ERretained misfolded V2aR mutants, allowing the receptors to reach the plasma membrane or to initiate a cAMP response, leading to AQP2 translocation. Strategies bypassing nonfunctional or mislocalized V2aR to induce AQP2 translocation and phosphorylation have also been tested. OPC41061 (V2aR antagonist, tolvaptan) has been approved in the United States and Europe for the treatment of hyponatraemia in SIADH. Recently, the VP system (V1aR) was proposed as a novel therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer. The results of clinical trials to improve autism spectrum disorder by targeting the AVP/V1aR pathway have been reported.
Clinical Use
The nonapeptide vasopressin is well known for its role on fluid metabolism, but it also is a key regulator of the HPA axis. Stress stimulates the release of vasopressin in the pituitary gland, where it strongly potentiates the effects of CRF on adrenocorticotropic hormone release. These findings suggest that HPA axis dysregulation in depression might be associated with the development of centrally acting vasopressin receptor antagonists for the treatment of depression.
Properties of Vasopressin
| CAS DataBase Reference | 9034-50-8 |
Safety information for Vasopressin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Vasopressin
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
