VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE
Synonym(s):Vanadium dioxide
- CAS NO.:12036-21-4
- Empirical Formula: O2V
- Molecular Weight: 82.94
- MDL number: MFCD00049702
- EINECS: 234-841-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
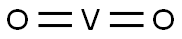
What is VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE?
Description
Vanadium dioxide [vanadium(IV) oxide, (VO2)] is one of four relatively common oxides of vanadium. Others are
In addition, several mixed vanadium oxides exist, many in nature. Examples are V3O7 (VO2 + V2O5) and V4O7 (2VO2 + V2O3). The vast range of vanadium oxides differ widely in terms of color, crystal structure, and chemical properties.
VO2 itself is sometimes expressed as V2O4, V4O8, or other VnO2n?formulas, depending on its crystalline symmetry. At temperatures less than 67 oC, VO2 has a monoclinic crystal structure (shown). When heated to more than 67 oC, it transitions to a tetragonal structure. At the same temperature, crystalline VO2 converts from an electrical insulator to a conductor.
But wait, there’s more: In 2013, a team led by Masaki Nakano at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (Wako) and Tohoku University (both in Japan) built on the insulator–conductor phenomenon to affect light transmission through VO2 glass. It had previously been shown that low-temperature (<30 oC) VO2 glass is transparent to infrared (IR) radiation, but at >60 oC, it reflects IR light. Nakano et al. accomplished the same result by applying an external voltage to a thin film of VO2. This discovery is the basis of new field-effect transistors.
And still more: In 2017, Olivier Delaire at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (TN) and Duke University (Durham, NC); Junqiao Wu at the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; and colleagues worldwide showed that VO2 violates the venerable (1853) Wiedemann–Franz law, which holds that the ratio of the electronic component of the thermal conductivity of a metal to its electrical conductivity is proportional to the metal’s temperature. At and below the insulator–conductor transition temperature, the electronic thermal conductivity is anomalously low, which, the authors state, “is a signature of the absence of quasiparticles in a strongly correlated electron fluid where heat and charge diffuse independently."
What will scientists discover next about VO2?
Chemical properties
Blue-black powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alkalies and acids.
Chemical properties
Vanadium(IV) Oxide (vanadium dioxide, VO2) is a blue-black solid, having a distorted rutile (TiO2) structure. It can be prepared from the reaction of V2O5 at the melting point with sulfur or carbonaceous reductants such as sugar or oxalic acid. The dioxide slowly oxidizes in air. Vanadium dioxide dissolves in acids to give the stable (VO)2+ ions and in hot alkalies to yield vanadate(IV) species, eg, (HV2O5)?.
The Uses of VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE
Vanadium(IV) oxide is used in chemical sensors, energy-conserving coatings, transparent conductors and switching materials. It acts as a stationary optical shutter, optical modulators, cameras and data storage. As infrared modulators, it is used for the missile guidance systems. Thin films made up of vanadium dioxide find applications in electro-optical switches, micro-optical switch, passive smart radiators and sunshields for spacecraft.
What are the applications of Application
Vanadium(IV) oxide is an amphoteric inorganic compound
Definition
ChEBI: Vanadium dioxide is a vanadium oxide.
Hazard
Toxic and irritating.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Properties of VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE
| Melting point: | 1967°C |
| Density | 4.339 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in acid solutions, alkaline solutions |
| form | Powder |
| appearance | dark blue, black, or gray crystals or powder |
| color | black |
| Specific Gravity | 4.339 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: Ceiling 0.05 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12036-21-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Vanadium oxide (VO2) (12036-21-4) |
Safety information for VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for VANADIUM(IV) OXIDE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
12036-21-4 -
 Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
12036-21-4 -
 Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
Vanadium(IV) oxide CAS 12036-21-4View Details
12036-21-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8