Nickel(II) oxide
Synonym(s):Nickel oxide;Nickel Monoxide;Nickelous oxide;Nickel Oxide Sinter 75;Nickel(2+) oxide
- CAS NO.:1313-99-1
- Empirical Formula: NiO
- Molecular Weight: 74.69
- MDL number: MFCD00011145
- EINECS: 215-215-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-24 13:31:58
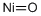
What is Nickel(II) oxide?
Chemical properties
Nickel(II) oxide is Brownish black or black powder.
The Uses of Nickel(II) oxide
Nickel(II) oxide is used in the preparation of nickel alloys including nickel steel alloys, manufacture of glass and porcelain paints. Further nickel oxide is the main component in nickel-iron battery (Edison battery), nickel-cadmium rechargeable battery, and also used in ceramic industry for making frits and porcelain glazes. It also acts as a hydrogenation catalyst. NiO/CNTs (nickel oxide/carbon nanotubes) could be a potential cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in microbial fuel cells (MFCs). It is blended with other high purity oxides and used in a variety of semiconductor applications such as thermistors and varistors.
The Uses of Nickel(II) oxide
Nickel salts, porcelain painting, fuel cell electrodes.
The Uses of Nickel(II) oxide
Nickel oxide nanowires have been studied for use in magnetic memory devices; as well as in luminescent materials.
Preparation
Nickel oxide is prepared by heating pure nickel powder with oxygen at a temperature above 400°C. In some commercial processes, green nickel oxide is made by heating a mixture of nickel powder and water in air at 1,000°C. Adding some nickel oxide to the above mixture enhances the rate of reaction. An alternative method of preparation of the green oxide involves thermal decomposition of an oxo acid salt of nickel at elevated temperatures. Thus, nickel nitrate, nickel sulfate or, more conveniently, nickel carbonate when heated at 1,000°C, yields the green oxide. The black oxide, on the other hand, is produced at a lower temperature from incomplete calcination of the carbonate or nitrate salt at 600°C. The oxygen content of the black form is slight-ly greater than its green counterpart.
Reactions
Nickel(II) oxide is insoluble in water but soluble in acids as long as it has not been ignited at a high temperature (under these latter conditions it is converted into grey-black octahedra having a metallic lustre). It reacts reversibly with hydrogen, the reaction NiO+H2 ? Ni+H20 proceeding from left to right at relatively low temperatures in a stream of hydrogen.
General Description
Nickel(II) oxide (NiO) is a metal oxide based nanomaterial with a good semiconducting property. Nanosized nickel oxide can be found in a variety of morphologies which include nanoflowers, spheres, wires, and tubes. It exhibits high performance in applications which require charge transfer and charge transport based processes. It can be prepared by a variety of physical and thermal methods such as sol-gel, hydrothermal and solvothermal techniques.
Hazard
Confirmed carcinogen.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Poison by intratracheal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Mutation data reported. Can react violently with fluorine, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen sulfide, iodine, barium oxide + air. See also NICKEL COMPOUNDS.
Properties of Nickel(II) oxide
| Melting point: | 1960 °C |
| Density | 6.67 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in acid solutions |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | green |
| Specific Gravity | 6.67 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,6512 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 10 mg/m3; TWA 0.015 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/Ni.O |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1313-99-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nickel(II) oxide (1313-99-1) |
Safety information for Nickel(II) oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Nickel(II) oxide
| InChIKey | GNRSAWUEBMWBQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=[Ni] |
Nickel(II) oxide manufacturer
Monopoly Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel(II) oxide, Puratronic™ CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel(II) oxide, Puratronic™ CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel(II) oxide CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel (II) Oxide pure CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel (II) Oxide pure CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel (II) Oxide Black pure CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel (II) Oxide Black pure CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1 -
 Nickel oxide green 75% CAS 1313-99-1View Details
Nickel oxide green 75% CAS 1313-99-1View Details
1313-99-1